Medical Packages
تست

Filters
Cities
- IRAN 18
- Yazd 1
Type
- Treatment 19
Age group
- All 19
We are always ready to help you with all you need to know about cosmetic and medical treatments in Iran

Nose Job in Iran
Treatment
Country
:
IRAN
The price starts at
:
2,800 U.S. dollar

IUI in Iran
Treatment
Country
:
Yazd
The price starts at
:
600 U.S. dollar

Hair Transplant in Iran
Treatment
Country
:
IRAN
The price starts at
:
1,300 U.S. dollar

Breast Reduction in Iran
Treatment
Country
:
IRAN
The price starts at
:
1,600 U.S. dollar

Liposuction in Iran
Treatment
Country
:
IRAN
The price starts at
:
2,500 U.S. dollar
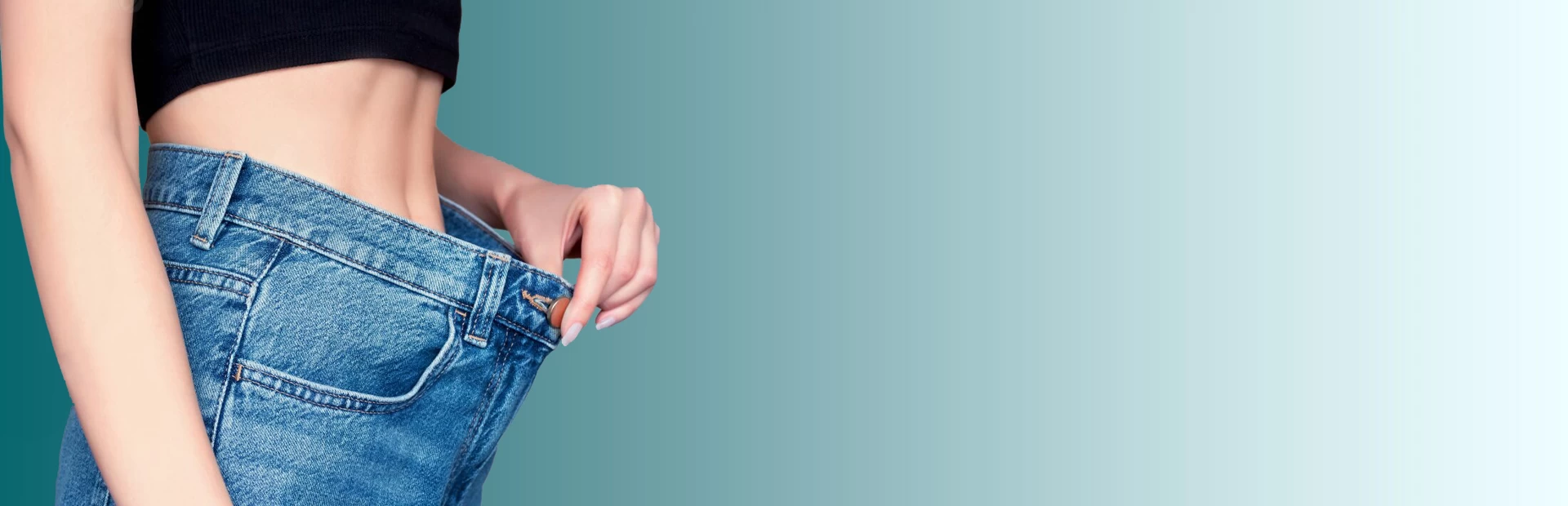

Gastric Sleeve
Treatment
Country
:
IRAN
The price starts at
:
2,000 U.S. dollar
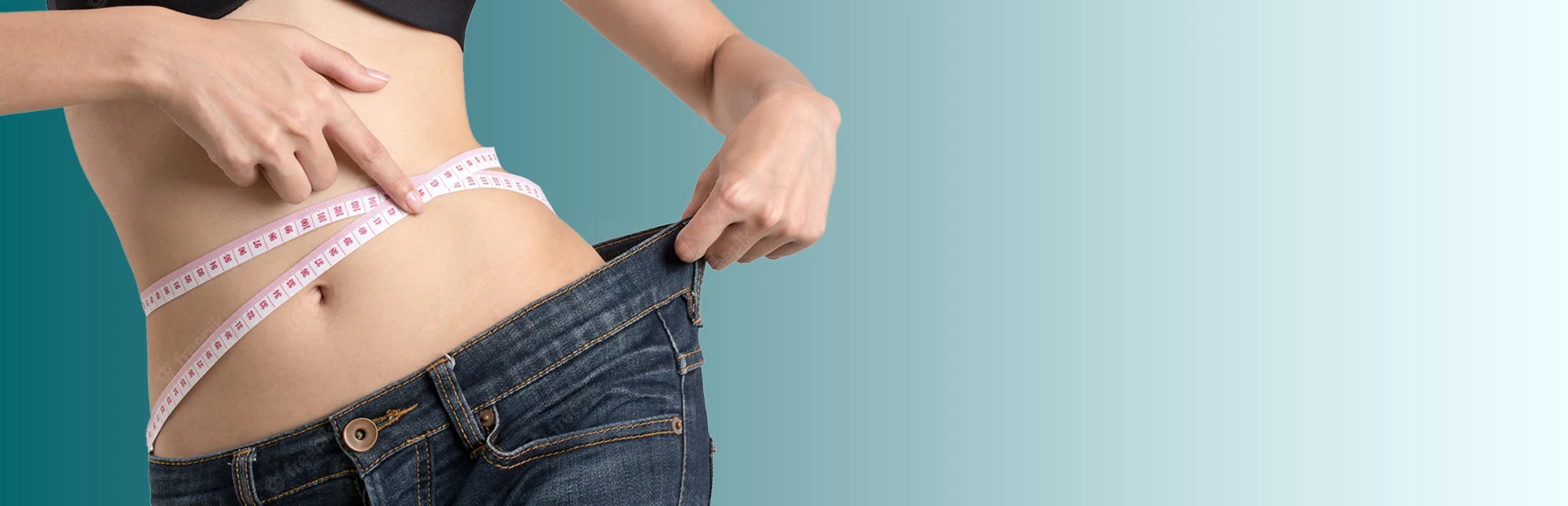

Gastric Bypass
Treatment
Country
:
IRAN
The price starts at
:
2,300 U.S. dollar
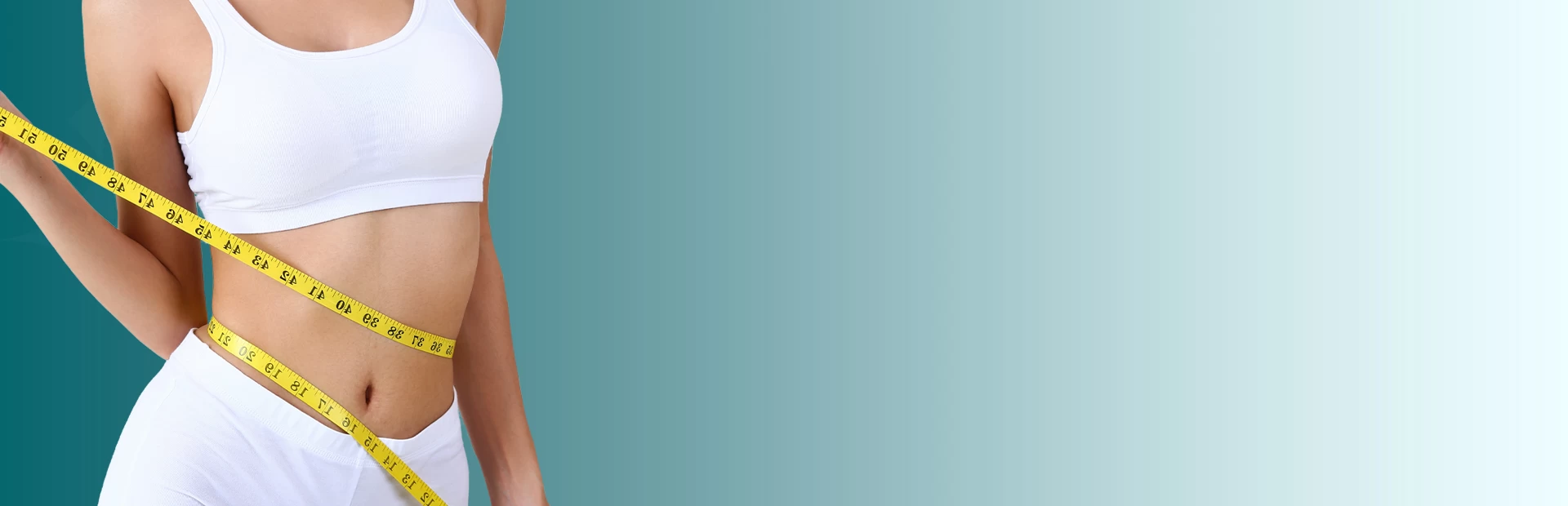

Tummy Tuck in Iran
Treatment
Country
:
IRAN
The price starts at
:
1,600 U.S. dollar
Kidney Transplant in Iran
Treatment
Country
:
IRAN
The price starts at
:
11,000 U.S. dollar

Varicocele Surgery
Treatment
Country
:
IRAN
The price starts at
:
700 U.S. dollar

Dental Implant Surgery in Iran
Treatment
Country
:
IRAN
The price starts at
:
700 U.S. dollar

