How to Get Pregnant with Low Ovarian Reserve?
Fertility Treatment
xamining ovarian reserve is one of the first steps to finding the causes of female infertility. Many women with low ovarian reserve wonder if this problem will affect their pregnancy or IVF treatment. This article mentions low ovarian reserve symptoms, causes, treatments, etc., of a diminished ovarian reserve and discusses its impact on fertility. Additionally, it provides information on low ovarian reserve treatment options, which may include fertility medications, lifestyle changes, or assisted reproductive technologies such as IVF.
What Is Ovarian Reserve?
Ovarian reserve meaning the number of oocytes in a woman's ovaries, is crucial for fertility. A 20th-week female fetus has seven million eggs when she is in her mother's womb. Over time, this number decreases, and she has almost 200,000 eggs when she is born. Of course, every baby girl is born with a certain number of follicles in her ovaries.
As the girl reaches puberty and her ovulation begins, one of these follicles is released in the form of an egg every month until she reaches the age of menopause. Therefore, her ovarian reserve decreases gradually as she gets older.
Normal Ovarian Reserve for Pregnancy
Ovarian reserve is directly related to females' fertility. The normal range for ovarian reserve is between 5 and 5.6. An ovarian reserve of less than one greatly reduces the chance of pregnancy, in which case ovarian induction drugs should be used to boost egg production. Usually, fertility specialists prescribe these drugs for women with irregular periods and IVF candidates.
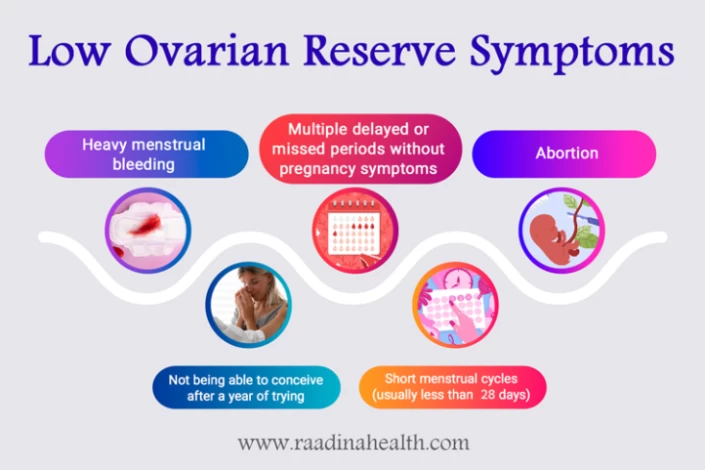
Low Ovarian Reserve Symptoms
In the majority of cases, diminished ovarian reserve has no distinct symptoms. However, medical tests and physical checkups can be used as a way of a diminished ovarian reserve diagnosis. The symptoms listed below are present in the majority of low ovarian reserve females:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding;
- Multiple delayed or missed periods without pregnancy symptoms;
- Abortion;
- Not being able to conceive after a year of trying and
- Short menstrual cycles (usually less than 28 days).
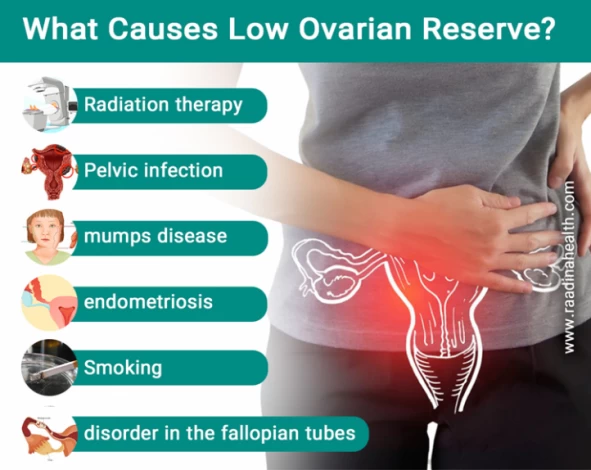
What Causes Low Ovarian Reserve?
One of the main reasons for low egg count is aging. However, some factors lead to diminished ovarian reserve at a young age. The most common causes of decreased ovarian reserve include:
- Having endometriosis;
- History of mumps disease;
- Having a disorder in the fallopian tubes;
- Genetic and congenital abnormalities such as fragile X syndrome (FXS);
- Pelvic infection;
- Radiation therapy and chemotherapy;
- Some autoimmune disorders and
- Smoking.
These factors are only part of the known causes of low ovarian reserve. At the same time, the reason for this problem is sometimes entirely unknown. It should also be noted that follicular puncture -one of the steps in assisted reproductive techniques such as IVF- does not cause low ovarian reserve because only a few eggs are retrieved during this process.
How Does Ovarian Reserve Impact Fertility?
As mentioned earlier, women are born with a certain number of eggs in their ovaries. With each period, they lose one mature and more than 1,000 immature eggs. So, having a lower chance of fertility at the age of 35 is not a surprise. A diminished ovarian reserve is one of the primary causes of infertility in women of higher ages. It takes more time for women with DOR to get pregnant. Also, they have higher rates of miscarriage and chromosomal abnormalities in their embryos. Note that DOR is not the only element affecting fertility. Other factors such as overall health, reproductive anatomy, hormonal balance, and sperm quality also play significant roles in determining fertility outcomes.
Pregnancy with Diminished Ovarian Reserve
If you have severe DOR, you have no other choice but to use In-vitro fertilization. Usually, the IVF is successful if the DOR test shows a number between 1 ng/ml and 3 ng/ml, IVF will be successful; however, if the number of follicles is less than 1 ng/ml, the chance of IVF success is low, and the couple should use a donor egg.

IVF with Low Ovarian Reserve
Ovarian reserve is strongly correlated with the success of IVF. The lower the ovarian reserve, the lower the chance of IVF pregnancy. Of course, the success rate of IVF does not depend only on the ovarian reserve and the number of eggs. Other factors, such as the quality of eggs and sperm, will also affect the result of this method. The quality of the egg is more important than its quantity; so, if someone has a low ovarian reserve but high-quality eggs, her chance of successful IVF is high.Other things jeopardizing IVF are:
●Uterine problems
●Fallopian tubes abnormalities
●A problem with the sperms’ shapes and quantity
IVF with Donor Egg
Sometimes, in cases where the woman has a low ovarian reserve and the remaining eggs lack enough quality, the doctor suggests using a donor egg. Other things jeopardizing IVF are:
●Uterine problems
●Fallopian tubes abnormalities
●A problem with the sperms’ shapes and quantity
Evaluation of Ovarian Reserve
In the following, some ways of measuring the ovarian reserve are mentioned:
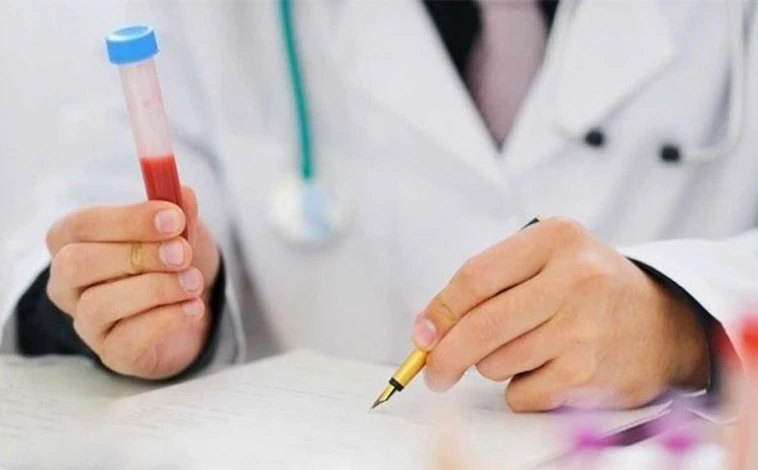
Taking estradiol test
Estradiol is one of the female sex hormones. The estradiol test also called the E2 test, is performed on the third day of the period cycle to measure the hormone estradiol in the blood. In premenopausal women, the average estradiol level is 30 to 400 pg/ml; in postmenopausal women, it is 0 to 30 pg/ml. A low estradiol level in the blood signifies diminished ovarian reserve.
Performing ultrasound to count antral follicles
The number of follicles with a diameter of 2 to 10 mm can be identified by performing an ultrasound on the second to fourth days of the menstrual cycle. These follicles, which are known as antral follicles and resting follicles, contain immature eggs and indicate how much the body has responded to gonadotropin medications. If the number of eggs is less than 10, the patient has a low ovarian reserve. Although this method is very practical, its results highly depend on the doctor's accuracy and skill and the ultrasound machine's quality. Also, this test can only measure the number of eggs, not their quality.
Taking FSH test
In the FSH test, which is a part of the infertility treatment process, the quantity of eggs is measured. This test is performed on the second or third day of the menstrual period, and if the level of FSH is low, the patient has diminished ovarian reserves. In fact, during this test, hormonal drugs containing FSH or a combination of FSH and LH are injected to stimulate the ovaries. If the maternal age is over 35, higher doses of hormones should be injected. Unfortunately, taking too many of these drugs reduces the chance of IVF success.
Taking clomiphene citrate challenge test (CCCT)
The CCCT test consists of two phases. In the first phase, the patient takes a blood test to measure the amount of FSH and estradiol in her blood. In the second phase, the patient should take ovulation induction drugs and take a blood test to measure the FSH and estradiol levels. Usually, high levels of these hormones before and after taking the drugs indicate low ovarian reserve and a lower chance of pregnancy.
Taking tests to measure AMH level
Females are not born with the Anti-Müllerian hormone. When a girl reaches puberty, this hormone is secreted by the granulosa cells that exist in the follicles in her ovaries. When she reaches menopause age, her body's amount of AMH hormone becomes almost zero. The AMH test results show that the patient has a low ovarian reserve. Since the amount of this hormone does not fluctuate much during menstruation, this test can be done on the first day of the period. Causes of low AMH, such as advanced age, genetic factors, autoimmune disorders, or previous ovarian surgery, can manifest in symptoms of low AMH, including irregular menstrual cycles, difficulty conceiving, and shorter menstrual cycles.

Determining Egg Quality for IVF
The quality of a female’s egg highly depends on her age. Usually, in women over the age of 40, the quality of the eggs decreases to such an extent that the chance of IVF success becomes zero, even if they have a high ovarian reserve. Although pre-pregnancy tests and ultrasounds evaluate the ovarian reserve, they do not check the quality of the eggs. Therefore, checking the mother's age is the only factor determining their quality.
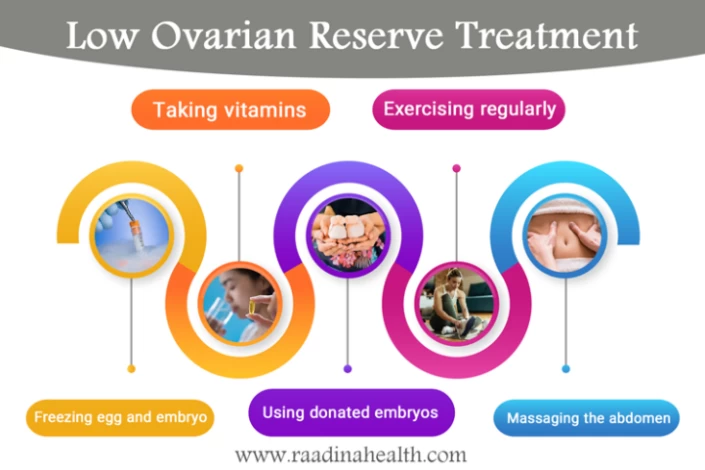
Low Ovarian Reserve Treatment
Unfortunately, there is no specific method to treat low ovarian reserve or prevent its progression; however, some medical procedures and home remedies can increase the chances of pregnancy in women with poor ovarian reserve.
The most common ways to treat infertility caused by diminished ovarian reserves are taking ovulation induction drugs and using assisted reproductive techniques such as IVF. Other methods of treating low ovarian reserve include:
- Freezing egg and embryo: couples who want future children can freeze their eggs or embryos at a young age.
- Hormone therapy: women with a low ovarian reserve can use hormone therapy to balance their hormones and increase their chance of pregnancy. Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and coenzyme Q10 are useful medications that improve the quality and quantity of eggs.
- Using donated embryos: in some couples, not only the female's ovarian reserve is low, but also the sperms lack necessary parameters such as motility, normal morphology, etc.; therefore, the doctor suggests using a donated embryo. In this method, the baby does not share genetic features with their parents, but she will grow in the recipient's womb.

- Exercising regularly: exercising at a gym, swimming, walking, and cycling twice or three times a week can maintain the ovarian reserve and improve sperm parameters.
- Taking vitamins: Consumption of supplements for diminished ovarian reserve, such as vitamin C and antioxidants, increases the number of eggs as well as sperms’ motility. Moreover, a suitable level of vitamin A in the body increases fertility because it increases the production of sex hormones in both men and women.
- Massaging the abdomen: Massaging the uterus and ovaries can increase blood flow in the reproductive system and increase the chance of pregnancy. You can either receive a fertility massage from a professional therapist or do it yourself at home. It is better to start the fertility massage after the end of your period.
Conclusion
Overall, the quality and quantity of eggs are the most important factors in increasing the chance of low-risk pregnancy. Other factors affecting successful pregnancy include hormonal balance, proper blood flow in the female reproductive system, and having a healthy lifestyle.
Iran is a central hub in fertility treatment, especially IVF, where you can benefit from high-quality healthcare services at a reasonable price. Contact us for more information on IVF in Iran.
Low Ovarian Reserve FAQs
Does Low Ovarian Reserve Mean Early Menopause?
Diminished ovarian reserve (DOR) does not necessarily mean early menopause. Still, it can be an indicator of reduced fertility potential and a higher risk of experiencing menopause at an earlier age. While DOR can be associated with early menopause, it is not always the case, and women with DOR may still have regular menstrual cycles and experience menopause at a typical age.
Can A Diminished Ovarian Reserve Show Up At 30?
The answer is that diminished ovarian reserve could reveal itself around age 30. While it is usually associated with elderly women, it can happen to anyone at any age. Genetics, medical issues, previous surgeries, and lifestyle choices can all lead to a diminished ovarian reserve.
Are There Any Lifestyle Changes That Can Help Improve Ovarian Reserve?
While lifestyle changes cannot reverse DOR completely, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can support overall reproductive health. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, managing stress levels, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Can Low Ovarian Reserve Be Prevented?
Unfortunately, DOR cannot be entirely prevented as factors like age and genetics primarily influence it. However, certain lifestyle choices, such as avoiding smoking and maintaining a healthy weight, may help preserve overall reproductive health.



 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
 Telegram
Telegram
 Facebook
Facebook
 Email
Email





No reviews
Your comment