IVF Process Timeline: What Happens During IVF Treatment?
Fertility Treatment
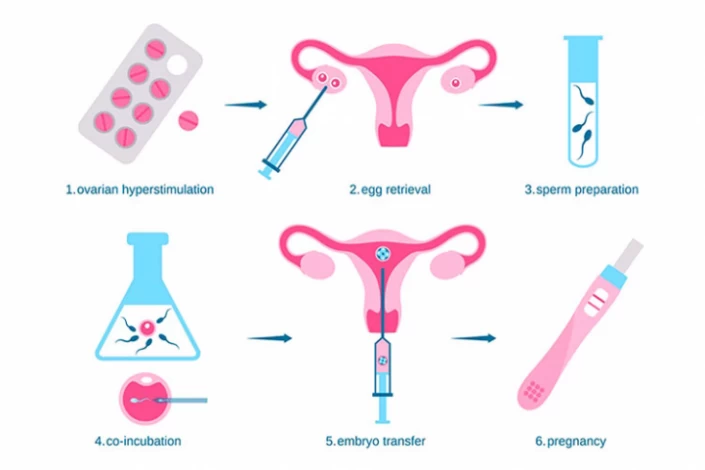
n vitro fertilization (IVF) is the most commonly known assisted reproductive technology for fertility treatment. The IVF process timeline involves seven steps, starting from taking hormonal medications to the embryo transfer procedure.
IVF treatment is considered one of the best assisted reproductive methods. It increases the chance of fertilization between sperm and egg by contributing to the proper function of male and female sex cells when they join each other in the laboratory. Most patients believe that realizing how IVF works helps them prepare better and have a more realistic outlook toward it.
Having taken advantage of prominent physicians, infertility clinics, and centers offering advanced fertility treatments, Iran is considered a leading country in the Middle East to provide effective treatments and a top country worldwide.

What Is IVF and How Does It Work?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a complex medical procedure designed to assist individuals and couples facing infertility challenges in achieving pregnancy.
The IVF process typically involves several steps. First, the woman undergoing treatment takes medications to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. This process is monitored closely through ultrasound and blood tests to ensure proper egg development. Once the follicles (structures containing the eggs) are mature, eggs are retrieved from the woman's ovaries through a minor surgical procedure (egg retrieval). Simultaneously, the male partner provides a sperm sample, which is then prepared to increase the likelihood of fertilization.
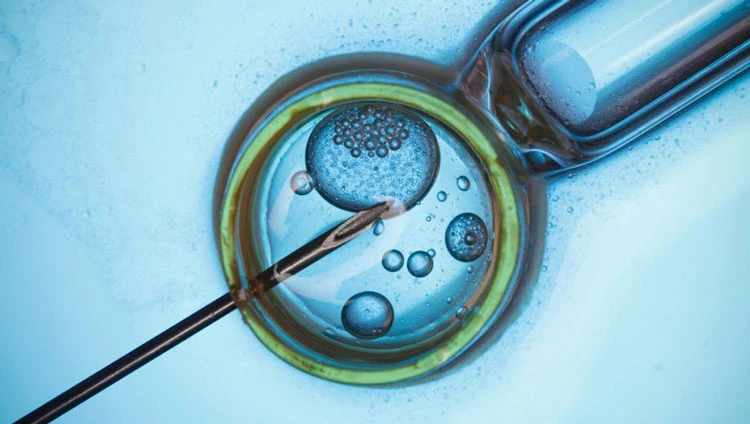
The retrieved eggs and prepared sperm are combined in a laboratory dish, allowing fertilization. In some cases, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is used to inject a single sperm directly into an egg, which is particularly beneficial for men with low sperm counts or motility issues. Once fertilization occurs, the resulting embryo is monitored for its development in the lab. Once the embryo has reached a suitable stage of development, it is carefully transferred into the woman's uterus.
The success rate of the IVF process varies depending on several factors, including the age of the woman, the underlying causes of infertility, and the skill of the clinic performing the procedure. After the embryo transfer, the woman will typically take hormones to support the pregnancy. Pregnancy tests are then used to confirm if the procedure was successful.
Depending on the situation of the infertile couple, the IVF process can be performed in the following ways:
- Use of the woman's eggs and her partner's sperm;
- Use of a donated egg and the male partner's sperm;
- Use of a donated embryo.
However, the doctor may use surrogacy or uterus transplants in women with uterine insufficiency.
Pre-IVF preparations
Before undergoing the IVF process, there are several essential steps to follow:
- Ovarian Function Assessment: Conduct tests to measure follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels, providing insights into egg size and quality;
- Semen Analysis: Collect a semen sample from the male partner to evaluate sperm count, morphology (shape), and motility (movement), especially if using the ICSI method;
- Ovarian Reserve Testing: Assess the quantity and quality of eggs through hormone level measurements, including estrogen, FSH, and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH test);
- Infectious Disease Screening: Conduct blood tests to screen for infectious diseases, including HIV/AIDS, to ensure a safe IVF process;
- Uterine Evaluation: Undergo ultrasounds and tests to assess uterine condition, often using sonohysterography.
- Embryo Transfer Planning: Discuss with your doctor the number of embryos to be transferred and the fate of any remaining embryos.
Additional Monitoring: On the fifth day of the menstrual cycle, a secondary ultrasound is required to monitor follicle growth and endometrial thickness, along with two blood tests to evaluate estrogen levels.
IVF Process Step-by-Step
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a highly effective form of assisted reproductive technology designed to help couples conceive. The process involves retrieving a mature egg from a woman's ovary, fertilizing it with sperm in a laboratory setting, and transferring the resulting embryo into the uterus.
Typically, the entire IVF process takes approximately three weeks. However, in certain situations, the cycle may be divided into multiple stages, extending the timeline.
Below, we will outline the complete IVF timeline, detailing each phase from start to finish:
- Initial Consultation & Assessment
- Stimulation of the ovaries
- Oocyte maturation (Trigger Injection)
- Egg retrieval
- Egg fertilization
- Embryo transfer
Step1: Initial Consultation & Assessment
Before starting the IVF program, your doctor may recommend taking birth control pills. These pills help minimize the risk of ovarian cysts and can prevent ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. However, it's important to note that there is some debate among medical professionals regarding the necessity of this approach.
If you have an irregular menstrual cycle, your doctor may prescribe progesterone to help regulate it. After six days of progesterone treatment, some doctors may also suggest injectable antagonists or agonists to further influence ovulation.
An IVF treatment cycle starts on the first day of your menstrual period. On the second day, you will undergo blood tests and a vaginal ultrasound. The blood tests measure your estrogen and estradiol levels, while the ultrasound assesses the size of your follicles.
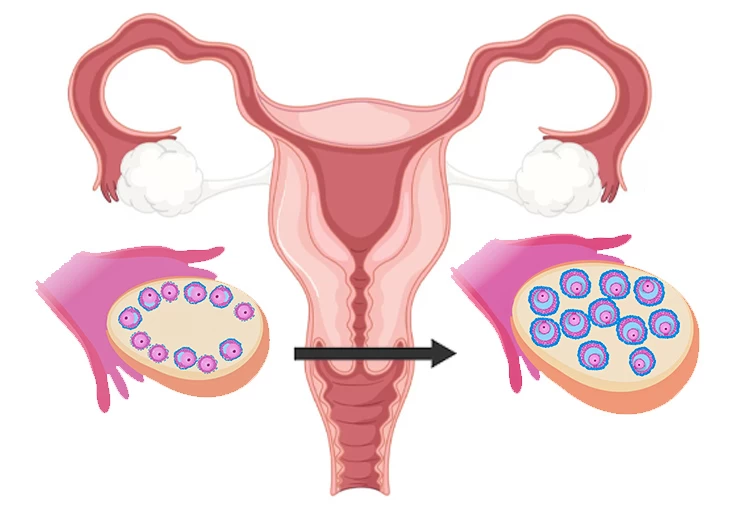
Step 2: Stimulation of the ovaries
During the Ovarian Stimulation stage, the patient is administered injectable fertility medications designed to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple viable eggs. Typically, these injections are given once or four times a day for 7 to 10 days. The purpose of these IVF injections is to carefully regulate the growth of the ovaries and promote the development of oocytes, which are immature egg cells.
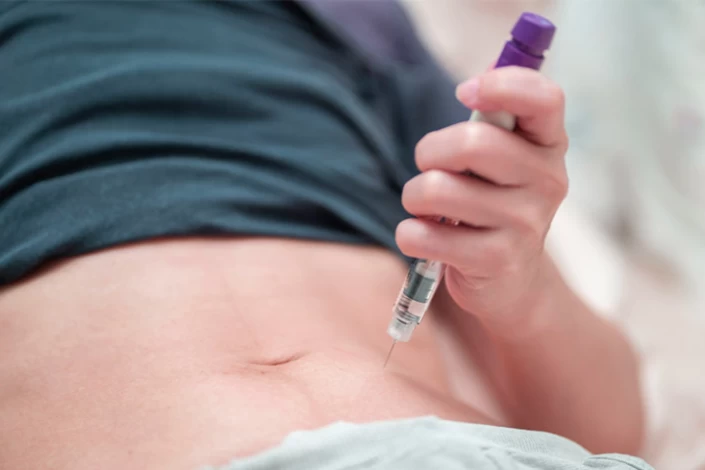
Step 3: Oocyte maturation (Trigger Injection)
After the administration of fertility medications, the patient's response is closely monitored through blood tests and transvaginal ultrasounds. These tests help assess hormone levels and track the growth and development of ovarian follicles, which contain the oocytes.
A trigger shot is administered once the follicles reach an appropriate size and enough mature oocytes. This injection typically contains human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) or a GnRH agonist, which helps to induce the final maturation of the oocytes and prepares them for retrieval.
Timing is crucial when administering HCG injections. If the injection is given too early, the eggs may not mature sufficiently; conversely, if administered too late, the eggs may become overripe. Typically, HCG injection is administered when at least four follicles have reached a size of 18 to 20 mm, and the estrogen level has risen to approximately 2000 pg/ml.
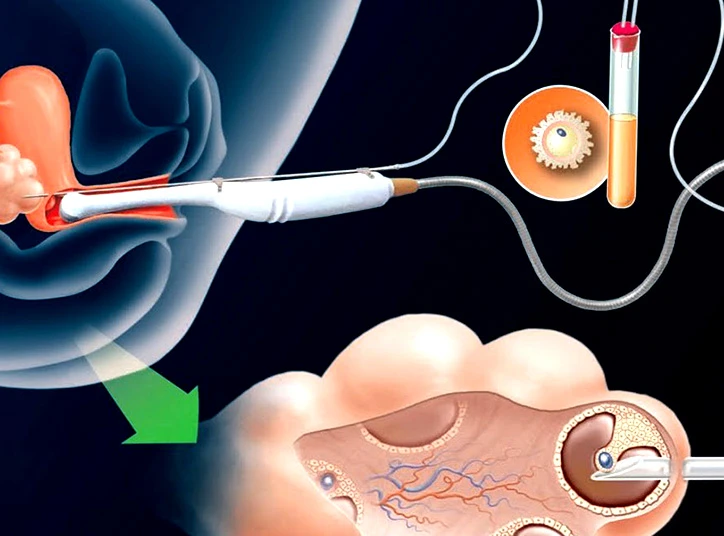
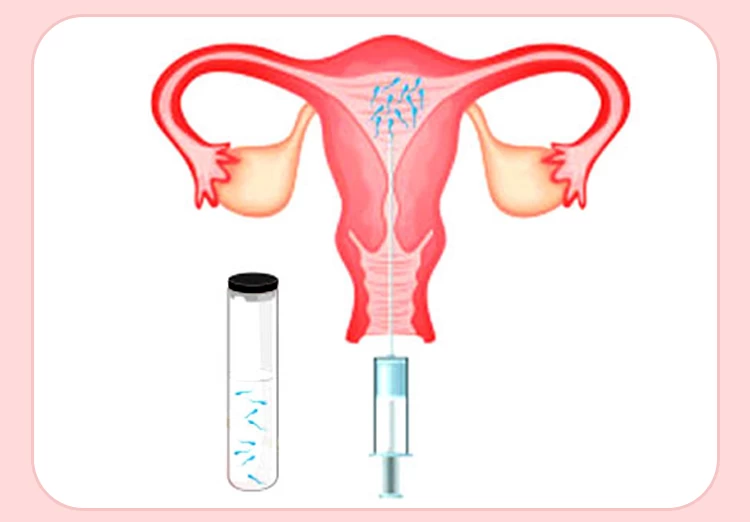
Step 4: Egg retrieval
Egg retrieval is typically performed 34 to 36 hours after the HCG trigger shot. During this outpatient procedure, a doctor uses local anesthesia to collect mature eggs (oocytes). The number of eggs retrieved usually ranges from 8 to 15. A transvaginal ultrasound probe is used to locate the follicles containing the eggs. Sometimes, an abdominal ultrasound is used for better visualization and guidance of the needle used to aspirate the eggs.
Following retrieval, the eggs are placed in a nutrient-rich solution and prepared for fertilization with the sperm in the laboratory. It's important to note that not all eggs will fertilize successfully due to quality variations. Post-retrieval, mild spotting, cramping, or lower abdominal pressure are common, and they typically resolve within a few days.
Step 5: Egg fertilization
Egg fertilization in IVF involves combining the retrieved eggs with the sperm in a laboratory setting. The process can involve either insemination (placing the sperm in the egg) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), where a single sperm is directly injected into the egg.
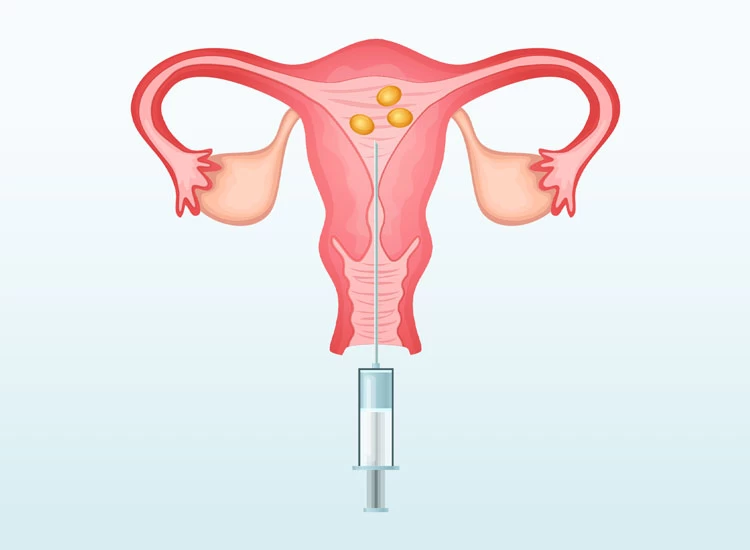
Step 6: Embryo transfer
The embryo transfer typically occurs 2 to 5 days after fertilization, depending on the developmental stage of the embryos. At this stage, embryos may be at the cleavage stage (Day 3) or the blastocyst stage (Day 5). Blastocyst transfers are often preferred because they are more advanced and have a higher implantation potential.
Before the transfer, the patient may undergo a final assessment, including an ultrasound to evaluate the uterine lining (endometrium) to ensure it is receptive to implantation.
The procedure is straightforward and can be performed in a clinic without anesthesia. A thin catheter gently places the selected embryo(s) into the uterine cavity. The process is generally quick, almost 15 minutes.
Embryologists assess the quality of the embryos based on their appearance and developmental stage. Typically, one or two of the best-quality embryos are selected for transfer, balancing the chances of success with the risk of multiple pregnancies.
Luteal Phase Support (LPS)
After egg retrieval and embryo transfer, the body may not produce sufficient progesterone, a hormone essential for maintaining the uterine lining. LPS typically involves the administration of progesterone supplements, either through injections, vaginal suppositories, or pills.
The main goal of luteal phase support is to ensure the hormone levels are right to support a pregnancy until the placenta can take over hormone production, which happens around 10 to 12 weeks into the pregnancy. By providing this support, doctors aim to lower the risk of miscarriage and improve the chances of a successful pregnancy for patients undergoing IVF.
What Medications Are Used in IVF?
In the IVF process, the doctor prescribes different hormonal medications for the mother, which are used either orally or as an injection. In some cases also, she should take her drugs transdermal or as vaginal suppositories to avoid digestive problems. The main medications used in IVF include,
- FSH: A follicle-stimulating hormone helps the ovaries produce more eggs. Usually, the intended mother has to take FSH injections for 14 days.
- hCG: Human chorionic gonadotropin injections improve the quality of eggs, mature them, and boost ovulation.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH): these medications, like leuprolide acetate, prevent premature ovulation.
- Progesterone supplements are used to thicken the endometrium and prepare it for implantation.
- Letrozole: it increases the number of eggs in ovaries and soars the chance of successful ovulation.
PGD (Gender Selection) with IVF
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) is a highly accurate method for gender selection, boasting a success rate of 95%. This advanced technique involves retrieving one or more cells from an embryo using focused laser beams or a biopsy method to analyze its chromosomal composition. If the embryo has two X chromosomes (XX), it is identified as female; if it has one X and one Y chromosome (XY), it is identified as male.
PGD is utilized not only for couples wishing to conceive a child of a specific gender but also as a preventive measure against transferring gender-linked genetic disorders, such as Turner syndrome, to their offspring. This innovative approach gives families greater control over their reproductive choices while ensuring healthier outcomes for their children.

IVF Timeline
IVF Stage | IVF without PGT | IVF Timeline with PGT | Detail |
Initial Consultation & Assessment | Before Cycle Start (The IVF process starts from day 1 of the menstrual period) | Before Cycle Start (The IVF process starts from day 1 of the menstrual period) | Discuss medical history, tests, and IVF/PGT process |
Ovarian Stimulation (hormone therapy) | Day 2 or 3 of Cycle | Day 2 or 3 of Cycle | Hormonal injections to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. |
Trigger Shot | Day ~ 14 of Cycle | Day ~ 14 of Cycle | Administer hCG or similar to trigger ovulation |
Egg Retrieval | 36 hours after the trigger shot (Day 16 of the Cycle) | 36 hours after the trigger shot (Day 16 of the Cycle) | Minor surgical procedure to collect eggs from the ovaries, typically under sedation. |
Sperm Collection | Day of Egg Retrieval | Day of Egg Retrieval | Fresh sperm samples were collected, or frozen sperm was used. |
Fertilization | Day 1 post-retrieval | Day 1 post-retrieval | Eggs are fertilized with sperm in the lab (conventional or ICSI). |
Embryo Culture | Day 3-5 post-retrieval | Day 3-5 post-retrieval | Embryos are cultured to assess development; PGT requires a longer culture for biopsy. |
PGT Biopsy | Not applicable | Day 5-6 of embryo development | Biopsy of embryos for genetic testing is performed on Day 5 of culture. |
Genetic Testing Results | Not applicable | 5-10 days post-biopsy | The results of genetic testing determine which embryos are viable for transfer. |
Embryo Transfer | Day 5-6 after fertilization | Day 5 (after PGT results) | Selected embryos are transferred into the uterus; timing may vary based on embryo development |
Luteal Phase Support | 10-14 days post-transfer | 10-14 days post-transfer | Hormonal medications, such as progesterone, may be prescribed to support the uterine lining and enhance the chances of implantation. |
Pregnancy Test | Day 14+ post embryo transfer | Day 14+ post embryo transfer | Blood test to check for pregnancy; |

How long Does the IVF Process Take From Start To Finish?
In general, the IVF treatment process takes about 4 to 6 weeks. It takes a few weeks for the eggs to mature, and it will take almost half a day for ovulation, a semen sample of man, and fertilization in the laboratory. If the uterus condition is favorable, the resulting embryos are transferred into the uterus about 2 or 5 days later.
Most patients will not need to be hospitalized during the IVF process. However, in rare instances where many eggs are retrieved from the ovaries, the doctor may recommend an overnight hospital stay following the egg retrieval procedure. It’s important to note that the success rate of IVF and the likelihood of a healthy delivery are influenced by various factors, including the couple's age and the overall health of their reproductive systems.
What to do after the embryo transfer?
After embryo transfer, it is common for women to experience spotting or light bleeding. This spotting may be a result of the embryo implanting in the uterine lining, but it can also occur due to the use of vaginal suppositories. If you experience severe bleeding, it is crucial to contact your doctor immediately.
In general, after the embryo transfer, you should consider the following:
- Take partial rest for three days;
- Avoid strenuous activities;
- Abstain from sexual intercourse for 17 days;
- Avoid heavy lifting or moving bulky objects;
- Maintain a healthy diet containing fresh vegetables and fruits as well as laxatives to prevent constipation;
- Do not use vaginal douches and tampons;
- Refrain from using bathtubs or swimming for at least 48 hours.
Sleeping or resting is allowed in any situation. It is recommended that you see a doctor in case of severe bleeding, shortness of breath, nausea, or severe pain.
To know more about what to eat after embryo transfer, check the best foods after embryo transfer article.

When Is IVF Recommended?
The IVF method is often recommended in the case of the following conditions:
- Advanced Maternal Age (Women over 35 years old);
- Blockage or damage of the fallopian tubes;
- Poor ovarian function;
- Endometriosis;
- Uterine fibroids;
- Male Factor Infertility: Low sperm count, poor sperm motility, sperm deformity, or other issues with the sperm;
- Specific genetic disorders;
- Unexplained infertility;
- Secondary infertility;
- Recurrent miscarriages;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Previous unsuccessful fertility treatments (If other methods like ovulation induction or intrauterine insemination (IUI) have not resulted in a pregnancy).

IVF Success Rate
The success rate of in vitro fertilization (IVF) varies based on several factors, including the mother's age, weight, and lifestyle. On average, the overall success rate of IVF is less than 50%. However, it fluctuates significantly according to the mother's age:
- Over 40 years old: 13-18%
- Ages 38 to 40: 23-27%
- Ages 35 to 37: 33-36%
- Under 35 years old: 41-43%
As illustrated above, the IVF success rate declines notably for women over the age of 40. Specifically, women's fertility decreases by approximately 9% each year starting at age 35. Additionally, genetic abnormalities are prevalent in most eggs after age 45.
However, through preimplantation genetic diagnosis and screening (PGD/PGS), it is possible to select embryos free from chromosomal defects for transfer. This approach not only reduces the risk of miscarriage in older mothers but also enhances the likelihood of a successful IVF outcome by an estimated 10%.

What factors determine IVF success rates?
Several factors influence the success rates of IVF:
- Mother's Age: Younger women typically have higher success rates, with fertility declining significantly after age 35 and more steeply after 40.
- Cause of Infertility: Conditions like PCOS, endometriosis, or male factor infertility can impact IVF success;
- Previous Pregnancy History: Women with prior successful pregnancies may have better chances with IVF;
- Quality of Eggs and Sperm: The quality of the retrieved eggs and sperm is crucial for embryo development and implantation;
- Number of Embryos Transferred: Transferring multiple embryos can increase pregnancy chances but also the risk of multiples;
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, alcohol use, body weight, and stress levels can affect fertility and IVF outcomes;
- Genetic Testing: Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) can help select the healthiest embryos, potentially improving success rates.
What to Expect After Embryo Transfer?
In most cases, women experience spotting, light bleeding, breast tenderness, and constipation after embryo transfer. Spotting can be a normal sign of embryo implantation, but it may also result from the use of vaginal suppositories. It’s important to consult a doctor if you experience severe bleeding, shortness of breath, nausea, or intense pain. To know more about what to eat after embryo transfer, check the best foods after embryo transfer article.
IVF Aftercare
After IVF embryo transfer, specialists recommend following certain tips to enhance the chances of success:
- Rest adequately, especially if you have a history of miscarriages or complications;
- Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities;
- Avoid doing sports like swimming, horse riding, Pilates, and aerobics;
- Refrain from sexual intercourse and orgasms for two months post-transfer;
- Do not smoke or consume alcohol;
- Engage in gentle exercises like walking and yoga to alleviate stress and improve circulation;
- Avoid hot baths, sunbathing, saunas, or hot tubs until cleared by your doctor;
- Consider taking omega-3 and folic acid supplements for fetal health;
- Aim for 8 to 9 hours of sleep in a dark environment to promote healthy follicle production;
- Maintain a balanced BMI with a nutritious diet rich in iron, magnesium, potassium, calcium, and protein.

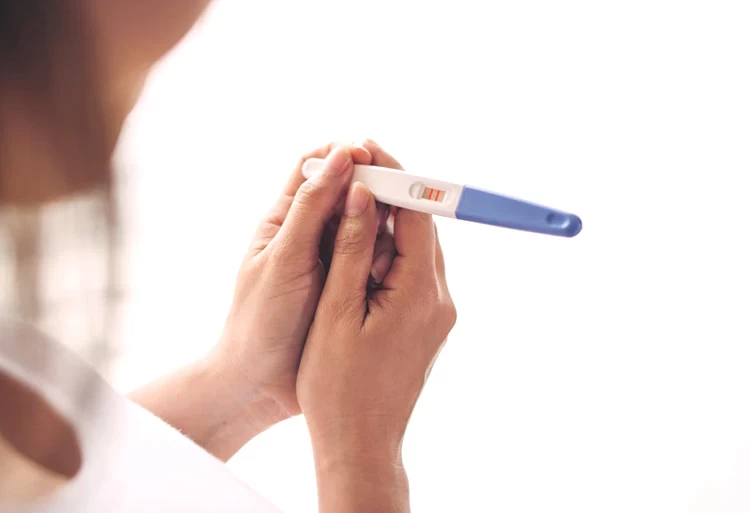
Pregnancy Test After IVF
Approximately 10 to 14 days after the embryo transfer, a blood test known as the beta-hCG test is conducted to determine whether implantation has occurred and whether pregnancy has been achieved.
Causes of IVF Failure
IVF failure can occur for several reasons:
- Failure in Implantation: Over 95% of IVF failures are due to the mother's body rejecting the embryo, recognizing it as foreign, which hinders its growth and implantation;
- Poor Embryo Quality: Even high-quality embryos in the lab may not possess the necessary qualities for successful implantation in the uterus;
- Hormonal Issues: Ovulation induction drugs may fail to stimulate ovulation effectively, particularly in women over 37, leading to IVF failure;
- Chromosomal Abnormalities: These are more common in women over 40, as aging affects cell division. Sperm chromosomal disorders are less frequent than those in eggs.
Additional factors contributing to IVF failure include:
- Fibroma;
- Endometrial polyps;
- Thin uterine lining;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (POS); and
- Hydrosalpinx.
If you want more information about IVF failure reasons, don't miss the (Main reasons for IVF implantation failure) article.

Frozen Embryo Transfer in IVF
If a woman has a low ovarian reserve, cancer, or other health issues, the IVF specialist suggests the couple use frozen embryos for IVF. Using a frozen embryo allows the couple to perform IVF anytime, significantly reducing the mother's health issues.
During frozen embryo transfer (FET), the embryo is first defrosted and injected into the mother's uterus using a narrow plastic tube. Before FET, the doctor asks the mother to take several blood tests and perform physical examinations to ensure that her body and uterus are ready for implantation. IVF with frozen embryos has a higher success rate in many cases because it lets the uterus return to its normal state after IVF medication.
What are the Risks and Side Effects of IVF?
IVF can be a stressful experience for infertile couples due to its time-consuming nature, high costs, and uncertain outcomes. Complications may arise from ovarian stimulation drugs and procedures like egg retrieval or embryo transfer. It's important to consult a doctor if any abnormal symptoms occur during IVF.
While most complications are rare, being aware of potential risks associated with the IVF process is essential.
- Fetal weight loss and preterm birth due to multiple pregnancies from the placement of multiple sperm;
- Pregnancy loss or abortion;
- Ectopic pregnancy occurs in 2-5% of cases, which leads to the impossibility of continuing the pregnancy;
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, causing fluid accumulation in the chest and abdomen after HCG injections;
- Risks of infection, bleeding, and rare damage to the bladder or intestines;
- Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, flatulence, severe stomach pain, dizziness, and significant weight gain within a few days;
- Inflammation and potential damage to internal organs and blood vessels from egg retrieval;
- Psychological stress.
It's important to note that while some researchers have raised concerns about potential issues related to IVF, such as congenital disabilities and ovarian cancer, there is currently no credible evidence to support these claims.
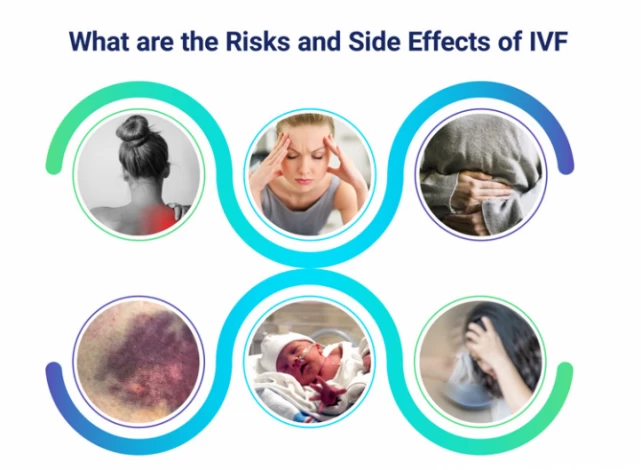
Side Effects of IVF Stimulation Drugs
- Mood swings;
- Hot flashes and bloating;
- Constipation and breast pain;
- Rapid weight gain within 3 to 5 days;
- Oliguria;
- Shortness of breath;
- Ovarian cancer.
- Severe uterine bleeding;
- Pelvic pain;
- The presence of blood in the urine;
- A fever over 38° C;
- Infection;
- Damage to the intestines, bladder, or blood vessels;
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).

How Long Should I wait between two IVF cycles?
To Reach a regular menstrual cycle, doctors recommend spacing between two IVF cycles for two or three months after two menstrual cycles have passed. Of course, to restart the IVF process, it is unnecessary to see a doctor precisely two months after the first treatment period; instead, you can repeat the second IVF cycle whenever you are ready.
We should note that some tests have a validity date of 6 months and may need to be repeated if restarting treatment takes longer. However, couples with frozen embryos must not repeat the IVF procedure. Doctors will only repeat the embryo transfer stage.
The following steps are taken to repeat the IVF Process:
- Use birth control pills on the third day of menstruation;
- Performing ultrasound scanning and prescribing diphtheria ampoules on the 17th day of menstruation;
- Re-examination and performing another ultrasound along with prescribing estradiol tablets on the second or third day of the next menstrual period;
- It evaluates the effect of estradiol within 6-7 days after its consumption and adjusts the intake amount to help the endometrial thickness reach 7-8 mm.
Cost of IVF in Iran: What to Expect
Iran has emerged as a leading hub for fertility treatments in the region, thanks to its well-equipped medical centers and highly experienced doctors. This reputation has made it a preferred destination for many couples facing infertility from around the world. One of the primary reasons international patients choose Iran for fertility services is the significantly lower treatment costs, allowing them to save up to 50% compared to other countries.
The cost of IVF in Iran typically ranges from $1,200 to $2,500, depending on factors such as the doctor's fees, the facilities and location of the fertility clinic, the cost of fertility medications, laboratory tests, the number of ultrasounds required, consultation fees, and whether eggs are utilized.

Frequently Asked Questions About IVF Treatment
How long is the entire IVF process?
The entire process, from initial consultation to potential pregnancy confirmation, typically takes 2-3 months. However, this can vary depending on individual circumstances and the specific clinic's protocols.
What if ovulation occurs before the egg is removed?
The occurrence of ovulation before the egg removes the possibility of egg retrieval and prevents further treatment. For this reason, careful and regular check-ups by the medical team are essential to know the level of blood hormones and to determine the time of ovulation.
Is it normal to spot after egg retrieval?
Spotting after egg retrieval is common, usually due to needle puncture. Light spotting within 2-3 days is expected. Heavy bleeding requires immediate medical attention. Spotting can sometimes, but not always, indicate implantation or embryo rejection. Contact your doctor with any concerns.
How many times is it possible to repeat the IVF cycle?
The recurrence of the IVF procedure is not restricted; it is up to the couple and the doctor.
Is it wrong to have intercourse between the onset of IVF and ovulation?
The man is recommended to refrain from ejaculating for 84 hours before taking a semen sample. Of course, it is better to ejaculate 5 to 6 days before semen sampling, resulting in the highest number of healthy and motile sperm on the sampling day.
When is a woman's pregnancy or non-pregnancy determined?
If the IVF treatment is successful, the person will have symptoms like a normal pregnancy. The most accurate way is to perform a pregnancy test two weeks after the embryo transfer.
How many embryos are transferred to the uterus?
As mentioned above, in most cases, more than one embryo is transferred to the uterus to increase the chance of pregnancy. This depends on several factors, such as the results of medical examinations, the couple's readiness to have multiple children, the percentage of multiple pregnancies in the medical center, the mother's age, and embryo grading.
In most cases, a maximum of three embryos are transferred to the uterus; however, if the mother is older – for example, over 53 years – sometimes, transferring more than three embryos is permitted.
When can you start your daily activities after the embryo transfer?
It is usually best to take a complete 42-hour break after embryo transfer. About two weeks after the transfer, until pregnancy is confirmed, strenuous exercise, such as swimming, horseback riding, running, etc., should be avoided. However, daily light activities are not prohibited.
Is there a possibility of multiple births in IVF?
Yes. Usually, some embryos are transferred to the uterus to increase the chance of implantation, and the chance of having multiple children also increases.
We should note that the probability of having twins in a natural pregnancy is about one in eighty, while in IVF pregnancies, this rate reaches about 52%. However, the probability of having triplets in IVF treatment is also about 2 to 3%.
When to have sexual intercourse after the embryo transfer?
It is impossible to pinpoint an exact time for sexual intercourse after IVF, but doctors recommend delaying sexual intercourse for at least two or three weeks. Vaginal muscle contractions during orgasm may adversely affect the fetal implantation process.
However, it should be noted that, according to doctors, having sex the night before the embryo transfer will increase pregnancy chances.
What happens to the remaining embryos in IVF?
More than one egg is usually extracted during each egg retrieval process, so more than one embryo can be produced in the laboratory. If the first one is unsuccessful, several resulting embryos are transferred to the uterus while the rest are frozen to be used in further IVF cycles.
Furthermore, these frozen embryos can be used if the couple wishes to have children again in the coming years. Although the chances of a successful pregnancy with frozen embryos are slightly lower, their lower cost and the reduced risks and complications of re-egg retrieval make this method a perfect option.
How Long Should I wait between two IVF cycles?
To achieve a regular menstrual cycle, doctors recommend a 2-3 month gap between IVF cycles after two menstrual periods. Couples can start the next IVF cycle whenever they feel ready, but some tests may need to be repeated if the wait exceeds six months. For those with frozen embryos, only the embryo transfer stage is repeated, not the entire IVF process. The steps to repeat IVF include taking birth control pills on the third day of menstruation, conducting ultrasound scans, and prescribing medications to prepare the endometrium. Estradiol tablets are given, and their effects are evaluated after 6-7 days to ensure proper endometrial thickness.
Is IVF painful?
IVF can involve complications and may cause mild to moderate pain. Initially, women may experience discomfort from hormonal injections, which is generally manageable. As the ovaries enlarge due to ovulation induction drugs, bloating and mild abdominal pain may occur. The egg retrieval and embryo transfer processes are invasive but performed under local anesthesia, minimizing severe pain. Any post-procedure discomfort is often due to using a speculum during the process.






 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
 Telegram
Telegram
 Facebook
Facebook
 Email
Email

















User
-Hi. How do IVF injections work?
Habib Ebrahimi
-Hi,
You’ll take injectable hormone medications during your IVF cycle to encourage the entire group of that cycle’s eggs to mature simultaneously and fully. Your healthcare provider will determine the type of drug, frequency and dosages you need for your treatment. This is based on your age, medical history, hormone levels, and response to previous IVF cycles, if applicable. You can expect to inject fertility medicine for around eight to 14 days.
Habib Ebrahimi
-Hi,
You’ll take injectable hormone medications during your IVF cycle to encourage the entire group of that cycle’s eggs to mature simultaneously and fully. Your healthcare provider will determine the type of drug, frequency and dosages you need for your treatment. This is based on your age, medical history, hormone levels, and response to previous IVF cycles, if applicable. You can expect to inject fertility medicine for around eight to 14 days.
User
-What is the difference between IVF and IUI?
User
-How many injections do I need during ivf treatment?
User
-How Many Embryos Can Be Transferred in IVF?
Habib Ebrahimi
-In IVF treatment, there are two types of embryos that can be transferred to the uterus; fresh and frozen. Based on the mother’s age and health condition as well as the quality of embryos, two or three embryos are usually transferred in each cycle. In fact, most fertility doctors transfer more than one embryo -whether fresh or frozen- in each cycle to increase the chance of pregnancy
User
-Good articles. Thanks for sharing
User
-1