What to Eat After IUI to Help Implantation?
Fertility Treatment
nfertility cases are soaring due to many factors, including congenital reproductive tract disorders, certain medications, unhealthy lifestyles, etc. Luckily, assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as IVF and IUI have been developed to help almost 50 million infertile couples extend their families. IUI is the second most popular method of assisted conception, which increases the likelihood of fertilization to a great extent. This article explores different foods to help implantation after IUI and provides useful tips about what to eat after IUI for success and the foods to avoid.

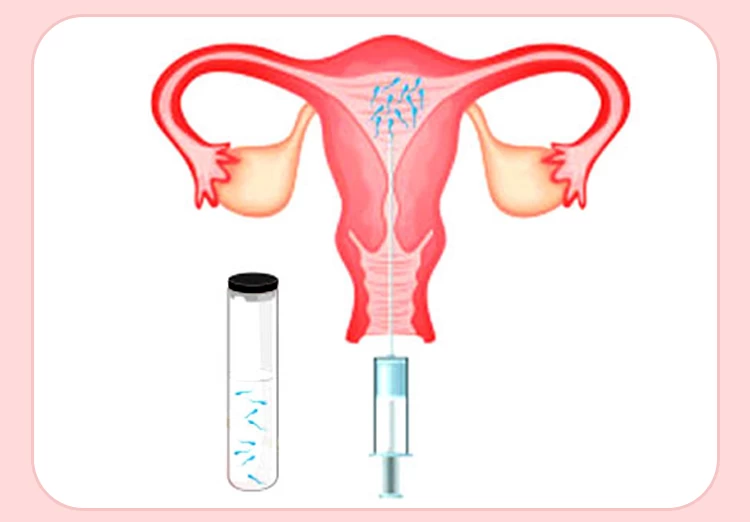
What Is IUI?
Intrauterine insemination, or IUI, is a minimally invasive fertility treatment in which a healthy and motile sperm is directly injected into a woman’s uterus. This method is mainly used for couples struggling with endometriosis, ovulation disorders, low sperm count, poor sperm morphology, cervix disorders, and semen allergy.
The success rate of IUI depends on the maternal age, the quality of eggs and sperm, and the parent’s lifestyle. Generally, women under 35 have a 13 to 15% chance of IUI conception, while this number falls to 3 to 9% in women over 40. Therefore, IUI requires extensive care, and the couple (especially the mother) should follow a healthy nutritional regimen during treatment.
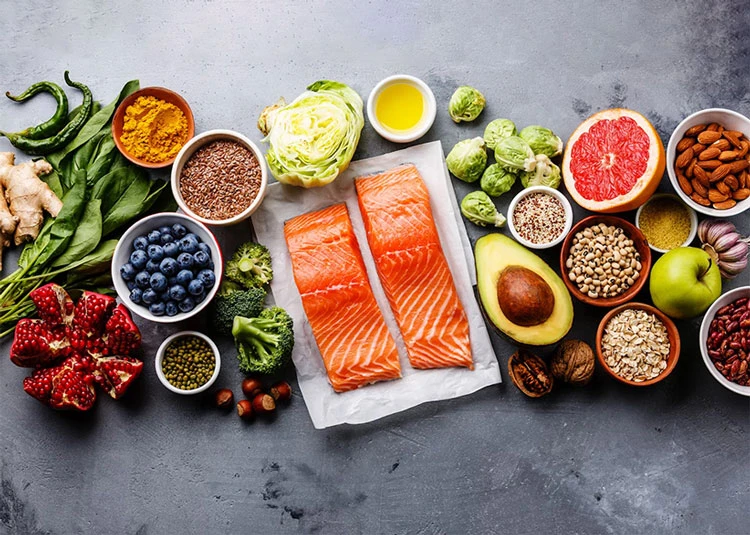
Foods to Help Implantation After IUI
A proper diet after the IUI procedure can increase the chance of implantation and successful pregnancy. If you wonder what the IUI implantation foods are, read the following:
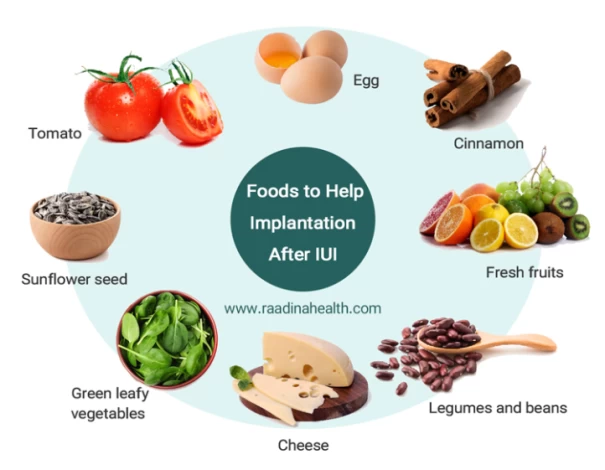
Green leafy vegetables
Leafy green vegetables are important parts of a healthy diet after IUI procedure as they are rich in vitamins, fiber, and minerals but have a low percentage of calories. Leafy vegetables such as spinach, lettuce, kale, and cabbage contain iron, magnesium, phosphorus, folic acid, calcium, and vitamin B12, so they should be included in your diet after IUI. Also, they balance the mother’s blood pressure and help the development of the fetus’s brain and spine during pregnancy.
Legumes and beans
Legumes and beans such as kidney beans, green peas, lentils, chickpeas, and fava beans are plant-based sources of fiber, protein, folate, and vitamin B9, so you have to get 60 grams of them per day to support the IUI implantation. In women with gestational diabetes, legumes can lower blood sugar and regulate their blood pressure. However, you should go easy on legumes if you have serious digestive problems such as hyperemesis gravidarum, gastroesophageal reflux, or severe diarrhea or constipation.
Sunflower seed
Sunflower seeds and oil are rich in folic acid, vitamin E, magnesium, potassium, and fiber. They lower blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar in expectant mothers. Whether being used as fresh, dried, or roasted, sunflower seeds boost the embryo’s immune system and help the implantation process to a great extent.
Fresh or dried fruits
Fruits, especially citruses such as orange and lemon, are excellent sources of vitamin C and folate and can help the fetus grow in the womb. Bananas, berries, apples, and mangoes can relieve pregnancy symptoms such as constipation and nausea. Moreover, dried fruits contain vital vitamins such as B9 and B2, amino acids, and minerals and can balance the hormones and increase the chance of successful IUI. Incorporating fruits to eat after IUI, such as these mentioned, can provide essential nutrients to support reproductive health and improve the chances of conception.
Cheese
Pasteurized and hard cheeses such as cheddar, parmesan, and stilton are rich sources of polyamine putrescine and calcium, highly beneficial for female fertility. On the other hand, unpasteurized and soft cheeses can cause miscarriage or stillbirth as they may contain an infectious bacteria called Listeria.
Pasteurized dairies
Full-fat and pasteurized dairy such as whole milk, cheese, and yogurt are good sources of vitamins D, K, A, E, and K2. Therefore, you must consume dairy products twice daily to help the IUI implantation and embryo development. Remember that if you’re lactose intolerant, you should refrain from having dairy products as they may cause digestive problems.
Tomato
Tomato contains a high level of antioxidants, a natural substance that prevents miscarriage, damage to embryo cells, and fetal growth restriction. Daily, having one or two raw, roasted, or cooked tomatoes can improve fertility and support IUI implantation.
Fatty acids
Two types of fatty acids that should be included in your post-IUI diet are omega-3 and omega-6. These fatty acids play an important role in the embryo’s attachment to the endometrium, developing the fetus’s brain and retina and preventing preterm delivery. In addition to dietary supplements, fatty acids can be found in walnuts, chia seeds, soybean oil, fish, egg, and olive oil.
Egg
Eggs, especially their yolks, are rich in iron, calcium, zinc, vitamin B6, folate, omega-3, and vitamin B12. Eggs are also regarded as good sources of protein and healthy fats, so they should be consumed at least three times a week as poached, fried, or scrambled.
Cinnamon
Normal doses of cinnamon can lower the risk of infection, decrease blood pressure, and help women with polycystic ovary syndrome to have an easier pregnancy. You can add a pinch of cinnamon to your tea or on your homemade cookie to improve your chance of successful IUI.
Supplements
Discussing what to eat after IUI for success, supplements should be taken after IUI to promote the IUI success chance and help the uterus to hold the baby. The supplements should contain vital vitamins and minerals such as E, A, C, omega-3, folate, and calcium. Some fertility specialists also recommend using progesterone supplements to thicken the uterine wall.
to Eat | Foods to Avoid |
Green leafy vegetables | Processed meat |
Legumes and beans | Refined carbohydrates |
Fresh or dried fruits | Artificial sweeteners |
Pasteurized dairies | Junk foods |
Fatty acids | Fast foods |
Foods to Avoid After IUI
Besides the foods you must add to your diet to help implantation after IUI, you should avoid certain foods to achieve successful conception. It's essential to be mindful of after IUI food to avoid to support the reproductive process effectively.

Processed meat
Red and processed meats (such as ham, sausage, roast beef, turkey, etc.) are rich in trans and saturated fats, so you should avoid having them while trying to conceive through IUI.
Refined carbohydrates
Refined carbs such as white rice, pasta, bread, and tortillas, foods made with white flour, etc., can impact your fertility and decrease your chance of IUI implantation. Therefore, reducing the refined carbs in your diet is suggested and replacing them with healthy carbs such as oats, barley, quinoa, etc.
Artificial sweeteners
Foods and drinks containing artificial sweeteners, such as sodas, candies, chocolate syrup, and frozen desserts, can negatively affect the quality and health of the sex cells and embryo. Therefore, you can replace them with natural sweeteners such as honey, dates, coconut sugar, and maple syrup.
Junk foods
You must avoid having junk foods before and after IUI as they can cause high blood pressure and gestational diabetes in the mother and asthmatic tendencies in the baby. You can replace junk foods with nuts, dried fruits, sugar-free beverages, and homemade smoothies.
Fast foods
Although having one or two slices of pizza wouldn’t harm the baby, most fertility specialists recommend avoiding fast foods after IUI as they contain trans fats and a large amount of sodium.
The Best Diet After IUI
Many women think they need a different and more diverse nutrient regimen than they’ve had so far. But you should know you can resume your diet and add more nutrients. In the following, a sample of the post-IUI diet is provided:
Early in the morning, drink a smoothie made of strawberry, apple, banana, and flaxseed on an empty stomach. If you have an upset stomach, drink warm water with honey or a date.
Breakfast: Have one bowl of sugar-free cereal or oatmeal with whole-fat milk. Add almonds, walnuts, and dark chocolate chips to your breakfast.

Morning snack: Have 100-150 grams of fresh fruit or juice.
Lunch: Have brown rice with whatever stew you like, a bowl of salad containing tomato, spinach, or kale, and a cup of pasteurized yogurt.
Evening snack: a cup of milk or tea with cinnamon or one or two medium-sized sweet potatoes.
Dinner: a bowl of cooked or raw vegetables with a roasted chicken breast and a glass of juice.
How to Make IUI Successful?
After IUI, you should consider the following points to increase your odds of pregnancy:
- Have a balanced and healthy diet;
- Stay hydrated;
- Cut out junk and fatty foods, artificial sweeteners, and processed foods;
- Have an exercise routine to regulate your blood flow;
- Avoid stress and maintain a positive attitude;
- Take your prescribed medications and supplements as you have been instructed;
- Avoid strenuous activities such as lifting, pushing, and bending;
- Maintain a healthy sleep pattern;
- Refrain from doing heavy sports such as weight lifting, swimming, karate, etc., until your doctor allows you;
- Do not miss your appointments, as you should be constantly monitored;
- Have a healthy lifestyle and avoid smoking and drinking alcohol;
- Take progesterone (in the form of pill, suppository, and injection) to thicken your uterine wall and increase your uterus’s receptivity;
- Get enough sleep, but avoid bed rest.
If you are considering more information about what to do after IUI to increase the chances of implantation, read this article.
IUI in Iran
Infertility treatment in Iran has witnessed notable advancements in recent years. The country demonstrates a comprehensive approach to addressing the issue of infertility through its healthcare system, making various treatment options accessible to couples struggling to conceive. Clinics and specialized fertility centers provide a range of services, including diagnostic tests, assisted reproductive technologies, and surgical interventions.
Iranian medical professionals utilize cutting-edge techniques such as in-vitro fertilization (IVF), intrauterine insemination (IUI), and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) to increase the chances of successful conception. Moreover, Iran's well-established healthcare infrastructure, state-of-the-art facilities, and medically trained staff contribute to the country's reputation as an increasingly popular destination for couples seeking reliable and affordable infertility treatments.
FAQs about Surrogacy in Iran
1.What is the best sleeping position after IUI treatment?
After an IUI treatment, you should rest. The best sleeping positions are on the side or flat on the back. Avoid sleeping on the stomach during your IUI treatment.
2.What vegetables to avoid after IUI?
Most vegetables are healthy. However, some may cause discomfort after IUI. Avoid cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage, as they can cause bloating or gas. Raw vegetables that are hard to digest may also be tough on your stomach. Cooked vegetables are easier to digest. Therefore, it is better to focus on non-cruciferous vegetables like leafy greens, carrots, and zucchini.
3.Can you eat eggs after IUI treatment?
Eggs are a great source of protein and contain essential nutrients that can support reproductive health, making them a healthy choice after IUI. They contain choline for brain development and healthy fats for hormone production. Many doctors recommend including eggs in your IUI diet.
4.What to eat before IUI procedure?
Before your IUI treatment, eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients. Focus on leafy greens, colorful fruits, whole grains, nuts, and lean proteins. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. It's better to avoid processed foods, excess sugar, and caffeine in the days leading up to your IUI procedure to make a healthy environment for conception.
5.Can I eat chicken after IUI?
Chicken is a great option after IUI as it's a good source of protein that helps with energy and tissue repair. Choose skinless, grilled, or baked chicken. Chicken also provides important nutrients like B vitamins and zinc, which are good for reproductive health. Make sure it's cooked completely to avoid foodborne illnesses.
6.Can I eat pizza after IUI?
Eating pizza after IUI is generally permissible. However, as fast foods are typically high in trans fats and a significant amount of sodium, most fertility doctors recommend avoiding them after IUI.
7.What nutrients that can help implantation?
Nutrients such as folic acid, vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants can help create a healthy environment for implantation after IUI.
 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
 Telegram
Telegram
 Facebook
Facebook
 Email
Email




User
-This article helped me a lot! Thank you so much! God bless you. ❤️ I tried finding info everywhere, but you have kept the conversation concise, and to the point and even shared a sample diet chart! 🙏🙌 Utterly grateful! ❤️🥲
کارشناس رادینا سلامت
-.It's a pleasure. We are glad you found our article helpful