How to Prevent Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome After Egg Retrieval?
Fertility Treatment
varian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) is a possible complication of fertility treatments that occurs in some women.
In simple terms, OHSS is mainly an excessive response of the ovary to excess hormones caused by some fertility treatment methods such as IVF (in vitro fertilization), IUI treatment (intrauterine insemination), or ovulation induction injections. Severe symptoms of OHSS after egg retrieval include abdominal pain, dyspnea (shortness of breath), and vomiting.
OHSS, also known as Hyperovulation, is a concern for women who undergo IVF for fertility treatment. Therefore, it is essential to diagnose OHSS in its early stages and learn how to treat it.
What Is Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)?
Ovaries are two small 3-cm-long almond-shaped organs. Every month, during ovulation, one of the ovaries naturally releases a mature egg. When the mature egg enters the fallopian tube, the uterine tube, and advances toward the sperm, fertilization takes place.
The fertilized egg eventually enters the uterus and makes contact with the uterine wall during the implantation stage. In the absence of pregnancy, the uterine wall thickens in preparation for the fertilized egg's implantation, and the menstrual cycle starts.
However, a patient is advised to undergo a fertility treatment like IVF or IUI if the ovulation process cannot happen naturally. One of the negative consequences of these assisted reproductive technologies is OHSS.
What Are the Symptoms of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome?
OHSS usually ranges from mild to moderate, and its severe cases are rare. The mild to moderate symptoms of the condition are temporary and will improve within a week; however, OHSS symptoms worsen if the pregnancy occurs and may last for several weeks.
Symptoms of mild to moderate OHSS after egg retrieval include:
- Rapid weight gain to more than 3 kg;
- Increased waist size;
- Bloating;
- Abdominal pain;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Diarrhea;
- Uterine prolapse.

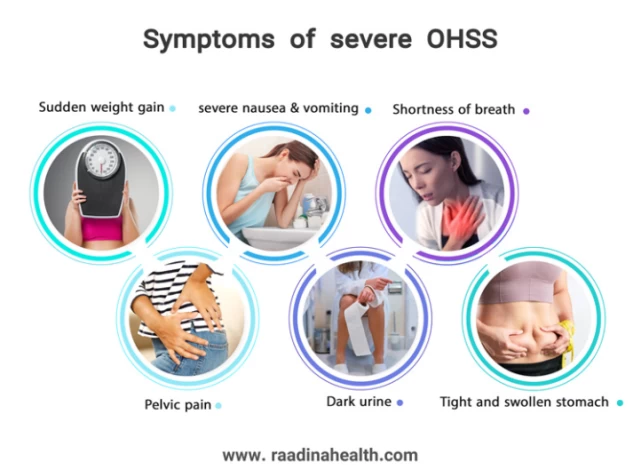
Symptoms of severe OHSS include:
- Extreme rapid weight gain to about 15-20 kg in 10 days;
- Tight or enlarged abdomen;
- Ascites (abdominal fluid);
- Severe abdominal pain;
- Pelvic pain;
- Severe and persistent nausea and vomiting;
- Shortness of breath, cough, and chest pain;
- High blood concentration;
- Decreased urination;
- blood clots in legs,
- Swelling above the ankle,
- Dry skin and hair.
What Causes the Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome?
After egg retrieval, OHSS may result from the use of HCG hormone-induced controlled ovulation hyperstimulation (COH). During pregnancy, women's bodies generate enough HCG hormone. The ovarian blood vessels react when extra HCG is used to induce ovulation, causing fluid to leak out. The ovaries grow and swell as a result of the fluid leak. Following the retrieval of the egg, these fluids may also enter the abdomen and result in abdominal swelling.
What Are the Risk Factors for Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome?
Some physical factors increase the risk of OHSS. However, OHSS may sometimes occur with no risk factors.
Risk factors of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome include:
- Low body weight;
- Age under 30;
- A large number of follicles;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome;
- An increased level of estradiol before ovulation stimulation with HCG injection;
·A history of migraines, OHSS, or multiple pregnancies in the past.
What Are the Complications of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome?
Severe OHSS affects 1% to 2% of women who undergo ovulation stimulation procedures. Numerous complications are linked to this condition, such as:
•imbalances in electrolytes (sodium, potassium, etc.);
•breathing issues;
•blood clots in the large vessels, usually in the legs;
•ascites, or fluid accumulation in the abdomen and occasionally in the chest;
•kidney failure;
•ovarian torsion;
•ruptured ovarian cyst;
•unwanted abortion.
How to Prevent OHSS?
To reduce the odds of OHSS development, patients should take their medications regularly, do frequent ultrasounds to check follicles, and perform blood tests to measure the level of hormones.
Strategies to prevent the incidence of OHSS are as follows:
- Coasting (withdrawing exogenous gonadotrophins): If the estrogen level is high and there are many developed follicles in the body, the doctor will temporarily stop injectable medications and HCG hormone from lowering the hormone levels and reducing ovarian sensitivity. When the levels decline as desired, the injection program continues.
- Avoiding the use of HCG hormone: Since HCG may increase the chance of OHSS development in the body, alternatives to HCG can be used to prevent OHSS. These alternatives include Gn-RH agonists, such as leuprolide (Leuprorelin).
- Using certain medications: The doctor usually prescribes the lowest dose of gonadotropins to induce ovulation. Some specific medications can reduce the risk of OHSS without hurting pregnancy. These include metformin (for women with polycystic ovary syndrome), aspirin, cabergoline, and intravenous calcium infusion.
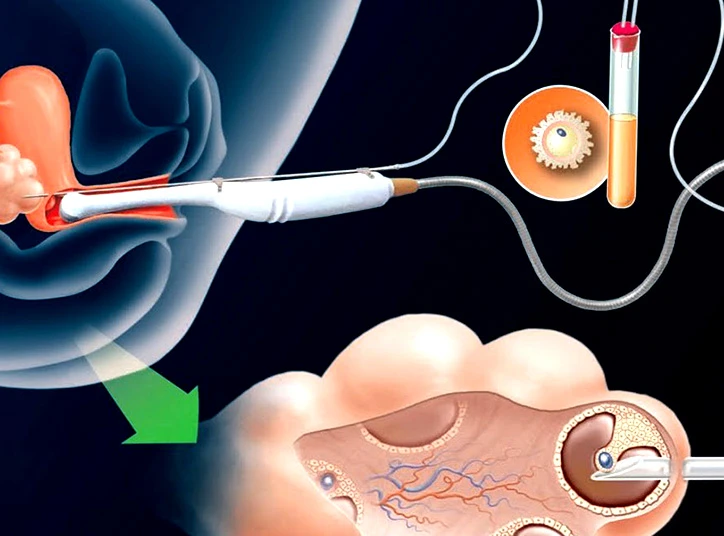
- Embryo freezing: In the case of observing OHSS symptoms while undergoing IVF, the doctor should remove all mature and immature eggs. Therefore, the ovaries can rest for a while. The matured eggs are frozen; the IVF process will continue when the body is ready.
Who Is at Risk of OHSS?
OHSS sometimes occurs in women who take or inject hormonal medications such as HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). These ovulation stimulation medications may increase ovarian activity and cause the ovaries to swell and become painful.
Furthermore, women who undergo ovarian stimulation or fertility treatment with the help of medications such as Clomiphene Citrate are at risk of OHSS. Also, in women with natural twins or multiple pregnancies, the high level of HCG hormone can cause ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
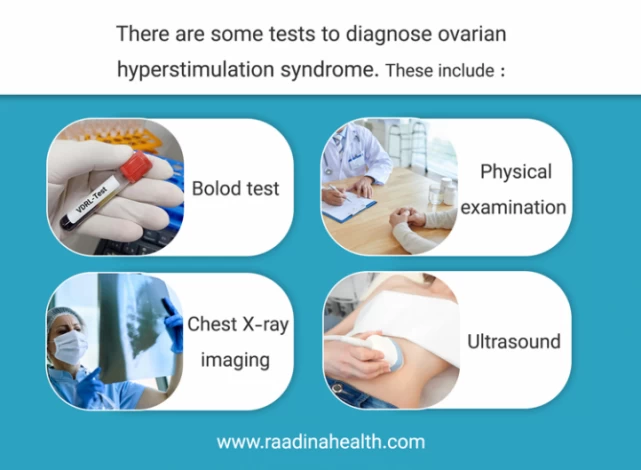
How Is Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) Diagnosed?
There are some tests to diagnose ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. These include:
- Blood test: to measure kidney disorders and examine abnormality in the blood;
- Chest X-ray imaging: to check the possible fluid accumulation;
- Ultrasound: to measure the condition and size of the ovaries (if they are filled with fluid);
- Physical examination: to evaluate any abdominal pain, weight gain, or increased waist size.
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) Treatment
OHSS treatment depends on the disease severity. In mild cases, the condition will improve within 1 to 2 weeks. However, severe cases may need additional treatment at the physician's discretion, and the recovery will take much longer.
Mild to Moderate OHSS Treatment
Mild to Moderate cases of the OHSS condition will improve by drinking more fluid, daily sizing the waist circumference, and measuring urine 24-hour volume. Frequent physical examinations, ultrasounds, electrolyte tests, and draining fluid from the abdomen (paracentesis) will also significantly improve mild OHSS.
Severe OHSS Treatment
In severe cases of OHSS, the doctor uses injectable medications to control and treat the condition, e.g., injectable cabergoline. This medication lowers prolactin hormone levels in the body and relieves the symptoms of severe ovarian effusion.
Anticoagulants also play an effective role in reducing or preventing blood clots in the body. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) antagonists such as letrozole can be used to control high ovarian activity. It reduces the symptoms of OHSS after egg retrieval in patients and speeds up recovery.
Furthermore, appropriate treatment methods for ruptured ovarian cysts and specialized care to prevent liver, kidney, or lung complications are among the effective methods in treating severe OHSS.

Home Remedies for Managing Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
According to sources, using over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen to relieve abdominal pain in OHSS is safe. Avoiding other pain-relieving medications like naproxen and ibuprofen to prevent implantation failure is better.
Additionally, several home remedies help improve OHSS apart from the doctor's treatment methods. One of these home remedies is to have a healthy diet, including 2-3 egg whites daily or salty foods. Consuming plenty of liquids, fruits, and vegetables also helps relieve constipation.
Another home remedy for ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is to make lifestyle changes. Maintaining a normal weight, daily measuring abdomen circumference, avoiding heavy physical activities, and not having sexual intercourse helps prevent an ovarian cyst from rupturing.
How long does it take for OHSS to get better?
The symptoms of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) can vary in severity and duration. Mild cases of OHSS usually improve independently within a few days to a week, while more severe cases may take several weeks to resolve fully. In some cases, hospitalization may be required for monitoring and treatment.
When Is the Best Time to See a Doctor?
Patients should inform their doctor if they observe any OHSS symptoms (even very mild ones) during a treatment cycle. It is better to write down the symptoms of ohss after egg retrieval and list any medications and vitamin supplements they take.
Furthermore, it is necessary to listen to the doctor carefully, ask important questions, and write down important information to avoid more complications and prevent the development of OHSS.
Patients should go to the hospital immediately if they experience any of the following symptoms:
- Severe abdominal pain or bloating that does not improve with rest or pain relievers;
- Rapid weight gain (more than 2 pounds per day) or swelling of the legs or abdomen;
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing;
- Nausea or vomiting that persists for more than 24 hours;
- Decreased or dark-colored urine;
- Dizziness, fainting, or confusion.
The above symptoms may indicate severe OHSS that can lead to complications such as fluid accumulation in the lungs, kidney failure, or blood clots. Therefore, it is recommended that patients seek medical attention right away if they experience any of these symptoms after egg retrieval.
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome FAQs
How long does it take for OHSS to get better?
Most OHSS symptoms should improve in 7-10 days. If the fertility treatment does not lead to a pregnancy, OHSS usually gets better by the time the next period begins. If pregnancy does not occur, OHSS symptoms can worsen for up to a few weeks or more.
How severe can OHSS get?
Severe OHSS is not common but can be life-threatening. The risks may include ascites, i.e., fluid collection in the abdomen or sometimes in the chest.
How to reduce OHSS bloating?
To reduce OHSS bloating, patients can drink lots of electrolytes, eat foods high in protein, sodium, and fiber, and use a heating pad.
















User
-Sure! Here’s a natural-sounding comment you can leave on the blog: This article provides valuable insights into OHSS symptoms after egg retrieval. It's crucial for patients undergoing IVF to be aware of potential complications and seek timely medical attention. As someone interested in reproductive health, I appreciate how well the risks and management strategies are explained. Those pursuing a Fellowship in reproductive medicine would also find this information useful in understanding patient care during assisted reproduction. Thanks for sharing this informative piece!
فاطمه وجهی
-Thank you for your feedback! I'm glad that the article was helpful to you and provided the necessary information about OHSS and its management. Awareness of potential complications for patients undergoing IVF is very important. Additionally, your mention of the significance of this information for professionals in training in the field of reproductive medicine is very relevant. I hope this article also helps others gain a better understanding of this topic!