In rhinoplasty, the nose's structure is manipulated, so breathing problems are not surprising. Once the nasal swelling is down and the stitches are removed, you can breathe normally and easily through your nose. This process takes about 8 to 12 weeks, depending on your healing rate and the complexity of your procedure.
Having a healthy and nutritious post-IUI diet increases the chance of pregnancy and live birth. Foods containing protein, fiber, vitamins, and Omega-3 should be added to your table after IUI. Have more leafy vegetables, legumes, fresh fruit, chicken breast, egg, and seeds, and avoid refined carbs, artificial sweeteners, and junk food during this period.
During rhinoplasty surgery, some vessels and tissues of the nose may get hurt and cause bruising. Fortunately, bruising after a nose job will be resolved within a month on its own, but you can use a cold compress, drink more water, avoid blood-thinning medications, and have a healthy diet to get rid of it faster.
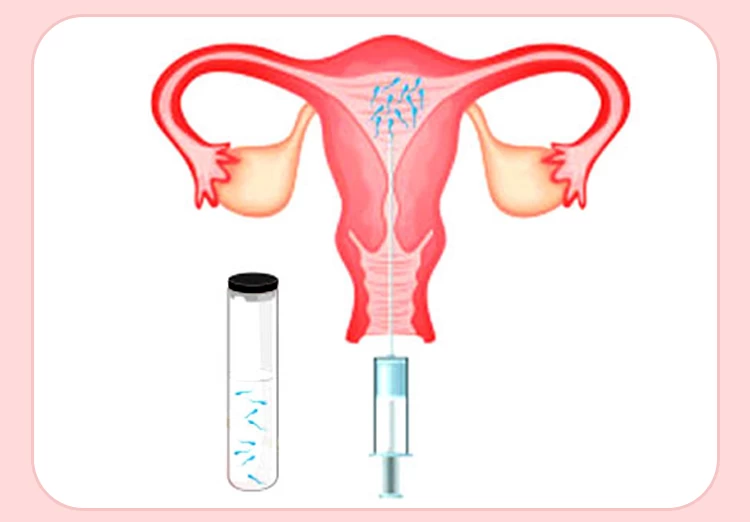
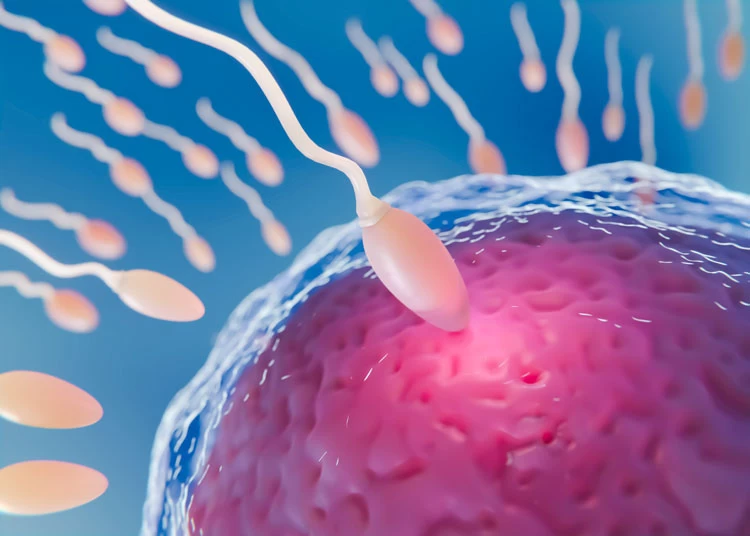
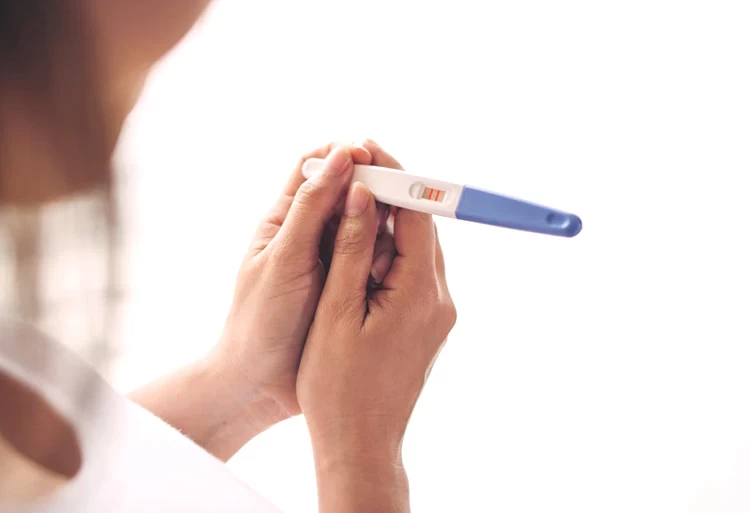
IUI is used for couples who have uterine issues or poor sperm parameters. Before this treatment, you need to perform several examinations, inject drugs, avoid unhealthy habits, and eat nutrients to increase your pregnancy chance. The IUI procedure involves four steps and takes almost two weeks. The result of this fertility treatment is determined 15 days after sperm insemination through a blood test.
An IVF cycle may fail because of high maternal age, low quality of sex cells and embryo, low receptivity of the uterus, endometriosis, and chromosomal abnormalities of the embryo. Also, if the mother has uncontrolled elevated blood pressure, unbalanced TSH level, or blood clotting disorders, the IVF may fail.
Whether ovulation is done naturally or with medication, it has some common symptoms like mood swings, mucus changes, spotting, bloating, breast tenderness, changes in sex drive, and mild pelvic pain. Ovulation may take 12 to 48 hours, but you can try conceiving for up to 10 days after it happens.
The first symptoms of implantation are nausea, light spotting, mild cramping, and food craving. Remember that implantation spotting differs from period to period in terms of color, amount, duration, and other factors. Implantation bleeding usually takes a couple of days, and its color is pink or brown. Also, its amount is so small that you don’t need a maxi pad.
IVF is the most popular type of assisted reproductive technology, which involves seven steps in total, from taking hormone medications to preparing the womb for carrying the baby to the embryo transfer procedure.
In a testicular biopsy, the doctor gets a sample from the testicle and retrieves sperm from it. The sperms are then examined in a laboratory, and the healthy ones are used in IVF. Four types of testicular biopsy are done for men with fertility problems: PESA, TESE, TESA, MESA.
IVF with donor egg helps women with poor egg quality, diminished ovarian reserve, endometriosis, and fallopian tube issues have children. Despite being extremely helpful, this treatment is costly, and many people cannot afford it. Iran, Turkey, and India are the cheapest IVF countries with donor eggs, respectively.