Navigating Laparoscopic Surgery: A Comprehensive Guide
Fertility Treatment
Laparoscopy is one of the new surgical methods that has been used for the treatment of many diseases over the past 20 to 30 years. Due to the minimal scarring during surgery, laparoscopy is considered a practical and safe method. This surgery is performed in women to address various issues, including uterine laparoscopy and ovarian laparoscopy. In addition to its diagnostic application, this procedure serves as a method for treating internal diseases and disorders. It is often performed in the pelvis and the abdominal regions. However, it is crucial to be aware of short-term and long-term the side effects of laparoscopic surgery, including laparoscopic surgery recovery time, and patients should consult with their healthcare providers to gain a comprehensive understanding of potential outcomes and risks associated with the procedure.
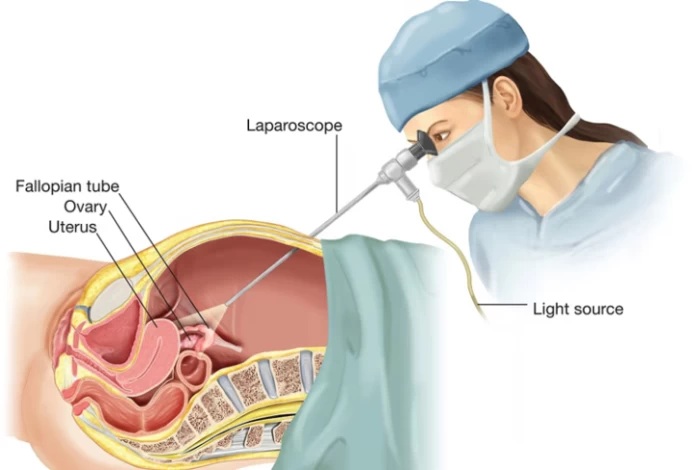
What Is Laparoscopic Surgery?
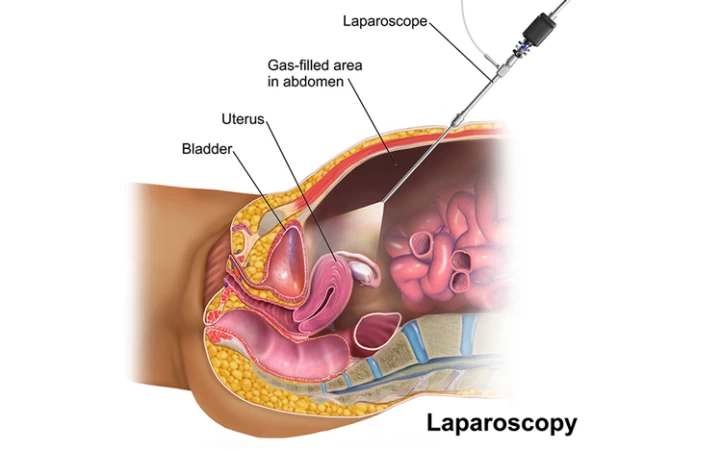
In laparoscopic surgery, also known as keyhole surgery, it is possible to treat a disease with only a small incision without the need to open the abdomen for deep surgeries. A laparoscope, which is a thin tube with a camera at the end, is inserted into the internal parts of the abdomen and pelvis after a tiny incision is made in the abdominal region. This eliminates the need for a larger incision and the related risks of open surgery, enabling the performance of surgical procedures or diagnostic tests. So, why is laparoscopic surgery done? It offers reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and less scarring compared to traditional open surgery methods.
Laparoscopy surgery is more frequently used in women's diseases than in other situations, and it is frequently used to treat uterine or ovarian issues. A tiny incision must be made beneath the navel in order to perform laparoscopic surgery on the uterus and ovaries. The device is then inserted into the body to examine the female organs. This operation is used to remove a woman's uterus (hysterectomy). The doctor's diagnosis determines which procedure is best, and laparoscopic hysterectomy typically has a shorter recovery time than abdominal hysterectomy.
Laparoscopy: In a Glance |
Aspect | Details |
Definition | A minimally invasive surgical procedure used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. |
Common Uses | Diagnosing and treating conditions like endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, ovarian cysts, and appendicitis. |
Procedure | Small incisions are made in the abdomen through which a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube with a camera) and surgical instruments are inserted. |
Advantages | Reduced postoperative pain Shorter hospital stays Faster recovery Minimal scarring |
Risks | Infection Bleeding Injury to internal organs Complications from anesthesia |
Preparation | Fasting before the procedure Stopping certain medications Preoperative tests (e.g., blood tests, imaging) |
Recovery | Typically quick recovery (a few days to a week) Possible mild pain and discomfort Follow-up visit to check healing and remove stitches if necessary |
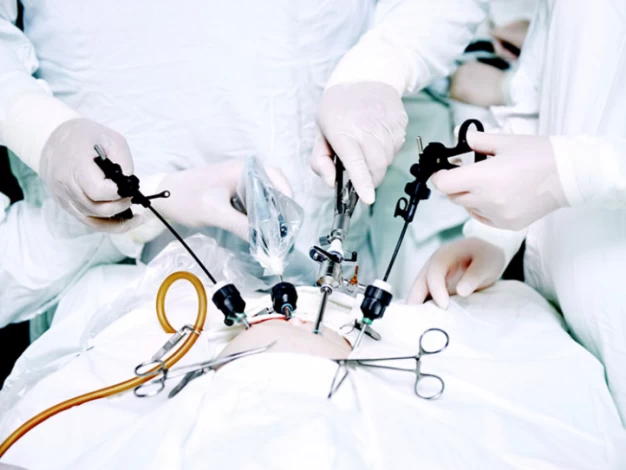
How Is Laparoscopic Surgery Performed?
A trained medical team performs laparoscopy surgery in a hospital setting despite the minimal invasion. Usually, spinal or epidural anesthesia is used in addition to general anesthesia.
Patient Positioning and Duration:
- During the procedure, the patient assumes a head-down and legs-up position. The surgery lasts approximately 2 to 3 hours.
- The patient's physical condition must be considered in assessing susceptibility to respiratory, vascular, and other internal issues.
Preparation and Initial Steps:
- Intravenous fluids or medications are administered.
- A breathing tube is placed into the patient's mouth.
Incisions and Carbon Dioxide Gas:
·One to three tiny incisions are made around the navel region.
- The abdomen is filled with carbon dioxide gas, which pushes the intestines out of the way for improved visibility.
Instrument Introduction and Procedures:
·Surgical tools are inserted into the body.
·The laparoscope looks at the organs, enabling tissue sampling (biopsy) or the treatment of illness, possibly with laser-equipped laparoscopes.
·To view information on a monitor, the doctor operates the laparoscope manually.
Closure and Recovery:
·The surgical site is sutured and bandaged following the release of carbon dioxide gas.
·Recovery happens quickly because of the small incisions.
·Laparoscopic surgery takes at least 30 to 90 minutes, and it may take longer for more complicated cases.
Post-Procedure Care and Discharge:
- The patient is transferred to the recovery unit.
- Depending on anesthesia type and individual response, hospital discharge is possible after 2 to 4 hours.
- Laparoscopy is often an outpatient procedure, with discharge on the same day.
To add a second camera for a more thorough examination, a 1.5 cm incision can sometimes be made on the right or left side. Along with examination and diagnosis, other instruments like forceps and scissors are also used for the treatment. Take into account that the first seven days after surgery are usually accompanied by mild shoulder and abdominal pain.
What Are the Differences Between Diagnostic and Operative Laparoscopy?
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique for identifying and removing the cause of abdominal pain or infertility and for the assessment of internal organs and tissue. It is useful in the diagnosis and treatment of infertility as it enables doctors to view reproductive organs to identify obstructions, endometriosis or adhesions. This procedure is employed when non-invasive tests such as ultrasonography (USG) or hysterosalpingography (HSG) cannot detect abnormalities and the cause of the diseases.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is recommended for patients experiencing recurrent miscarriages or women with unexplainable infertilities. The reason is that diagnostic laparoscopty enables a methodical assessment of the anatomy of the pelvis, fallopian tubes, ovaries, uterus, and the surrounding structures. Additionally, a significant amount of the laparoscopic procedure is dedicated to investigating fallopian tube blockages, which are the main cause of infertility problems.
A contrast material can be injected into the uterine cavity through special tools for tubal obstruction diagnosis. By following the trail of that colored fluid through the uterus, ovaries, and tubes and imaging them, areas of blockages or adhesion can be detected.
It should be noted that this approach is not comprehensive and does not encompass the diagnostic benefits of laparoscopy, which can directly visualize pelvic abnormalities. Other techniques, such as hysterosalpingography (HSG), can detect external blockages or peritubal adhesions around the fallopian tubes in approximately 18% of cases, even when HSG confirms patent tubes, though laparoscopy remains more accurate for such diagnoses.
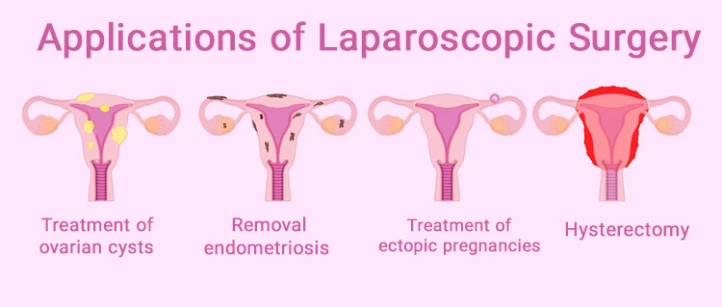
Applications of Laparoscopic Surgery
The applications of laparoscopic surgery have revolutionized the field of medicine, offering minimally invasive solutions for a diverse range of conditions. This advanced surgical technique has been widely applied in various medical specialties, transforming traditional procedures and significantly enhancing patient outcomes. Herein, we'll explore the applications as follows:
- Performing biopsy or tissue sampling from internal body tissues;
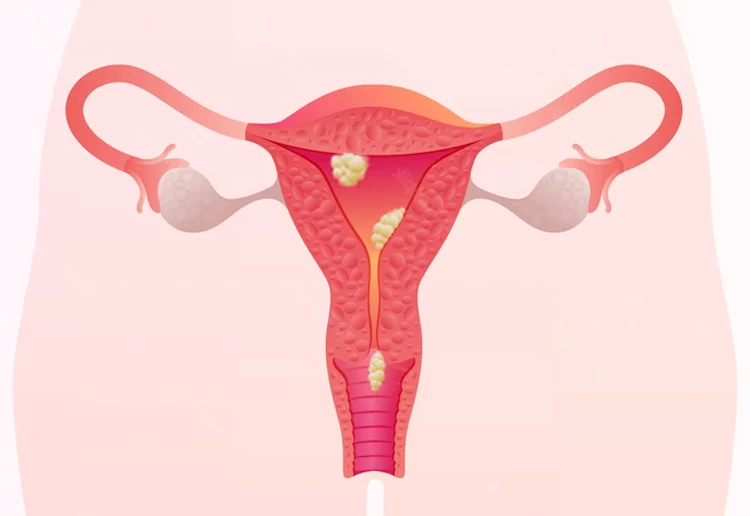
- Removal of abnormal and harmful tissues such as endometriosis (thickening of the uterine wall) or uterine fibroids (myomectomy);
- Root cause analysis of certain symptoms;
- Extraction of lymph nodes and other similar tissues;
- Removal of a portion or entire ovaries and fallopian tubes as diagnosed by a physician;
- Complete or partial removal of the uterus or damaged parts (hysterectomy);
- Aid in diagnosing other diseases;
- Treatment of ovarian cysts (cystectomy) and any abnormal masses in internal reproductive organs;
- Removal of cancerous tumors in the uterus and ovaries, as well as any harmful tumors in the pelvic and abdominal regions;
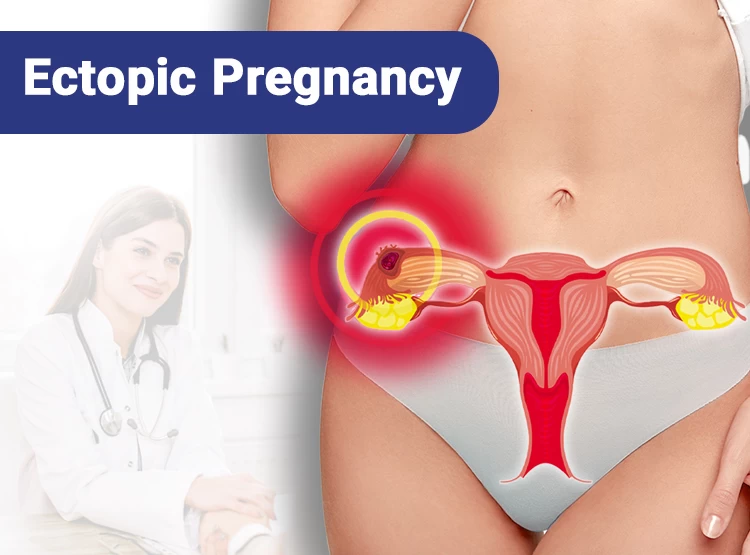
- Diagnosis and treatment of ectopic pregnancies;
- Identification and treatment of chronic and abnormal pain in the pelvic area;
- Diagnosis of certain fertility issues;
- Sampling of eggs for use in the IVF process.
Which Individuals Are Unable to Perform Ovarian and Uterine Laparoscopy?
Individuals meeting the following conditions cannot undergo laparoscopic surgery of the uterus and ovaries:
- Menopausal women;
- Individuals with severe obesity;
- Those with heart and lung diseases;
- Women with a history of abdominal surgery.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy is a relatively modern technique that offers numerous benefits and advantages compared to other open surgical procedures, including:
- Minimal and narrow incisions compared to other open surgeries;
- Effectiveness in the diagnosis and treatment of many diseases;
- Brief laparoscopic surgery recovery time and short hospital stays;
- Minimal risks and complications;
- Higher safety levels;
- Reduced postoperative pain;
- Lower likelihood of infection after surgery;
- Preservation of the natural appearance of the abdomen due to small and fewer incisions;
- Capability for more precise and better surgical procedures;
- Decreased risk of hernia;
- No adhesion.
The Use of Uterine Laparoscopy for Diagnosing Infertility
As previously stated, uterine laparoscopy is a simple, minimally invasive surgical technique that helps identify and treat ovarian cysts, fibroids, adhesions, infections, and endometriosis, among other causes of female infertility, through tiny incisions. This approach can be used when hysteroscopy or other tests are unable to identify the cause of infertility. It also helps with the removal of extraordinary and dangerous tissues.
When uterine laparoscopy is used to diagnose and treat the causes of infertility, procedures like opening the fallopian tubes, examining and treating infections and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and sampling tissues from the ovaries and uterus are commonly carried out.
How Long Can You Get Pregnant After Laparoscopy?
The possibility of pregnancy after undergoing a uterine laparoscopy procedure is very high. Usually, within a year after the surgery, there is a chance of fertility. However, couples should be informed about the complete recovery of the woman before attempting pregnancy to ensure a successful and healthy natural conception.
Preparations and Precautions Before Laparoscopy:
Before performing laparoscopic surgery, it is necessary to take precautionary measures and provide proper care, which encompasses the following:
- Obtain sufficient information and recommendations from the doctor or the nurse;
- Avoid eating and drinking for 12 hours before laparoscopy surgery;
- Arrive on time on the day of the surgery (about 1 to 2 hours before the scheduled surgery time) ;
- Remove contact lenses, glasses, and jewelry before the operation;
- Take bowel-clearing medications as instructed by the doctor a few hours or a day before laparoscopy;
- Undergo necessary tests and checks such as CT scans, ultrasound, MRI, and blood and urine tests;
- Inform the doctor about medications, supplements, over-the-counter pain relievers, and herbal remedies being taken;
- Inform the doctor in case of any substance use;
- Schedule uterine laparoscopy after the completion of the menstrual cycle;
- Stop using blood-thinning medications such as ibuprofen, aspirin, and warfarin as per the doctor's instructions;
- Avoid smoking in the days before and after the surgery;
- Take essential medications with a minimal amount of water on the night before laparoscopy;
- Bring comfortable clothing and personal hygiene items such as pads, and avoid wearing tight clothes;
- Empty the bladder 1 hour before the operation.
It is important to note that individuals should inform their doctor of conditions such as abdominal hernia, drug allergies, cancer in any abdominal organ, pregnancy or the possibility of pregnancy, history of abdominal surgery, and other relevant information before undergoing laparoscopy surgery.
What Is the Distinction Between Laparoscopy and Open Surgery?
Contrasting open surgeries, diagnosis, and treatment are performed in laparoscopic surgery without direct manual intervention and solely with precise and delicate instruments. Unlike open surgery, laparoscopic surgery does not require large abdominal incisions; creating only a few small holes is sufficient. Additionally, laparoscopy allows the visualization of internal organs through a camera and on a monitor, enabling more precise and detailed surgical procedures.
Laparoscopy Aftercare and Recovery Period
The patient recovers as quickly as possible if the recovery period following laparoscopy is completed and specific precautions and care are taken. Vital signs like blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and body temperature are tracked while the patient receives medical attention after the procedure. Recovery time following laparoscopic surgery can also be greatly impacted by comprehension and adherence to suggested post-operative measures. Following a laparoscopy, the patient should take the following postoperative actions:
- Avoid strenuous exercise for 1 week, limit heavy lifting for 3 weeks
- Take 1–2 days off work to rest;
- Prioritize gradual recovery to prevent complications.
- Take prescribed pain relievers and antibiotics to prevent potential infections;
- Wash and dry the incision areas with water, soap, and a suitable towel;
- Avoid driving within 24 hours after the surgery;
- Avoid carbonated and alcoholic beverages for 24 hours after the surgery;
- Abstain from sexual activity for one week;
- Consume light and nutritious foods.
What Are the Risks and Complications of Laparoscopy?
The individual may experience skin damage and bladder infection if laparoscopy is performed. They might also feel brief pain at the incision sites, which can be alleviated with prescribed pain relievers. However, in rare cases, the following laparoscopic surgery side effects have been reported:
- Nerve damage;
- Allergic reactions;
- Injury to adjacent organs such as the bladder, liver, and intestines;
- Blood clotting;
- Some urinary problems;
- Bleeding and damage to abdominal blood vessels;
- Bloating and abdominal discomfort for a few days due to the injection of carbon dioxide gas;
- Throat swelling caused by the insertion of a breathing tube during surgery;
- Shoulder and neck pain (treatable with pain relievers or lying on the side).
Sex After Laparoscopy
After a uterine laparoscopy, it is advisable to abstain from sexual intercourse for at least one week or preferably 3 to 5 days. If you observe post-coital bleeding, pain during intimacy, prolonged and heavy vaginal discharge, or the discharge of fluid and blood from suture sites, you should inform your doctor.
In general, uterine laparoscopy may delay menstruation, although bleeding similar to menstruation can occur in the days following the procedure, sometimes lasting up to three weeks. It is recommended to perform uterine laparoscopy between the seventh and tenth days before ovulation. Usually, if there are no specific complications, ovulation proceeds as usual, but a menstrual cycle disruption is possible.
It's worth noting that irregularities in the menstrual cycle can be attributed to post-surgery stress, concerns, or hormonal changes. Sometimes, the menstrual period may be delayed by up to 40 days, and the first menstruation after uterine laparoscopy is typically short and brief.
When to Visit a Doctor After Laparoscopy?
If the following symptoms are observed after laparoscopy, it is important to consult a doctor or report these symptoms to a gynecologist:
- Severe vaginal bleeding;
- Excessive bleeding from the incision sites;
- Fever and chills;
- Chest pain and shortness of breath;
- Redness and discharge from the surgical wounds;
- Vomiting;
- Severe or worsening abdominal pain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, laparoscopy stands as a transformative force in modern medicine, redefining the landscape of surgical interventions across diverse medical domains. Its minimally invasive approach has not only revolutionized traditional procedures but has also brought about significant benefits such as reduced recovery times, minimal scarring, and enhanced patient well-being.
From gynecological and urological surgeries to interventions in the abdominal and pelvic regions, laparoscopic techniques continue to offer precision and efficacy. Laparoscopy's versatility and wide-ranging applications underscore its pivotal role in advancing patient care and shaping the future of surgical practices. As technology and methodologies evolve, laparoscopic surgery remains at the forefront, continually pushing the boundaries of what is achievable in the realm of medical innovation.
FAQs
1. How does laparoscopy differ from traditional open surgery?
Unlike traditional open surgery, which requires large incisions, laparoscopy utilizes small incisions, resulting in reduced trauma to surrounding tissues, minimal scarring, less pain, shorter recovery times, and decreased risk of complications such as infection and blood loss.
2. What are the common procedures performed using laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy is used for a wide range of procedures across various medical specialties, including gynecology (e.g., hysterectomy, ovarian cyst removal), urology (e.g., kidney removal, prostate surgery), gastroenterology (e.g., gallbladder removal, appendectomy), and general surgery (e.g., hernia repair, bariatric surgery).
3. Who is a candidate for laparoscopic surgery?
Many patients are suitable candidates for laparoscopic surgery, but eligibility depends on factors such as the specific medical condition, overall health, and individual anatomy. Your healthcare provider will assess your suitability for laparoscopy and discuss the benefits and risks based on your circumstances.
4. What are the benefits of laparoscopic surgery?
The benefits of laparoscopy include smaller incisions, reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, improved cosmetic outcomes due to minimal scarring, and decreased risk of complications such as infections and hernias.
5. Are there any risks associated with laparoscopic surgery?
While laparoscopy is generally considered safe, like any surgical procedure, it carries certain risks, including bleeding, infection, organ injury, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. However, the overall risk of complications is typically lower compared to traditional open surgery.
6. What questions should I ask my surgeon before undergoing laparoscopic surgery?
Before undergoing laparoscopic surgery, it's essential to ask your surgeon about the specific procedure, including its purpose, risks, benefits, alternative treatment options, expected recovery time, and any postoperative care instructions. Additionally, you may inquire about the surgeon's experience and success rate with similar procedures.
7. How long does a laparoscopic procedure typically last?
The duration of a laparoscopic procedure varies depending on the type and complexity of the surgery. Some procedures may take only 30 minutes to an hour, while others may require several hours to complete. Your surgeon will provide an estimate of the expected duration based on your specific case.
8. Will I need general anesthesia for laparoscopic surgery?
In most cases, laparoscopic surgery is performed under general anesthesia to ensure that you remain unconscious and pain-free throughout the procedure. However, in certain situations, regional anesthesia or conscious sedation may be used instead. Your anesthesia provider will discuss the options with you before surgery and address any concerns you may have.
9. Are there any dietary restrictions before laparoscopic surgery?
Your healthcare provider may recommend dietary restrictions before laparoscopic surgery to reduce the risk of complications during the procedure. This may include fasting for a certain period before surgery or avoiding specific foods and beverages. It's essential to follow these instructions closely to ensure a safe and successful outcome.
10. Can laparoscopic surgery be performed on pregnant women?
Laparoscopic surgery may be performed on pregnant women in certain cases, but it carries additional risks and considerations due to the potential impact on both the mother and the fetus. Your healthcare provider will carefully evaluate the risks and benefits and discuss the best course of action for your specific situation.
11. Is laparoscopic surgery covered by insurance?
In many cases, laparoscopic surgery is covered by health insurance plans, but coverage may vary depending on factors such as the type of procedure, your insurance provider, and your individual policy. It's essential to check with your insurance company beforehand to understand your coverage and any potential out-of-pocket expenses.






No reviews
Your comment