Embryo Freezing: Process Timeline & Success Rate
Fertility Treatment
Embryo freezing, also known as embryo cryopreservation, is one of the valuable assisted reproductive technologies that allow couples to preserve their fertility for future use. This innovative technique not only provides a sense of security but also grants couples the freedom to plan their family at their convenience.
Embryo freezing allows couples to delay pregnancy, such as in cases where they may be focused on career advancements or undergoing medical treatments that can temporarily affect fertility. By preserving their embryos through freezing, couples can ensure that they have the option of starting a family when the time is right for them.
The embryo freezing technique is used alongside in vitro fertilization (IVF) or microinjection (ICSI) to preserve embryos for future use. The process involves retrieving multiple eggs from a woman's ovaries, fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory to create embryos, and then carefully selecting the healthiest ones for freezing. These frozen embryos are typically stored in specialized containers, often in liquid nitrogen, ensuring their viability for an extended period, spanning several years.
Embryo freezing success rate is above %95; so, it can increase the chance of a successful pregnancy by eliminating the need for repeated egg retrievals and fertilization procedures.
However, it is important to note that not all embryos will be viable after the freezing and thawing process. Some may not survive or develop as expected, thus decreasing the likelihood of achieving a successful pregnancy. For this reason, it is of utmost importance to freeze an adequate number of top-quality embryos to maximize the chances of success.
What Is Embryo Freezing?
Embryo freezing is an innovative reproductive technology that enables the freezing and preservation of embryos for future use. Performing embryo freezing during in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI treatment) ensures the possibility of pregnancy at a later time.
Through this advanced procedure, embryos are carefully preserved at extremely low temperatures (-196 degrees Celsius), maintaining their viability for future utilization. The process involves the retrieval of multiple eggs from a woman's ovaries, their fertilization with sperm in a laboratory to create embryos, and the meticulous selection of the most viable ones for freezing. These frozen embryos are then stored in specialized containers, typically filled with liquid nitrogen, where they can remain viable for extended periods.
When the time is right for a couple to utilize their frozen embryos, they undergo a procedure known as embryo transfer. During this process, the frozen embryos undergo thawing and are subsequently transferred into the woman's uterus. This transfer can occur naturally during the woman's menstrual cycle or in combination with hormone therapy to prime the uterus for implantation.
Embryo Freezing Timeline
The embryo freezing timeline varies from one person to another, but it usually takes 2 to 3 weeks. The main stages of embryo freezing include:
- Ovarian Stimulation;
- Egg Retrieval;
- In-vitro Fertilization;
- Embryo freezing;
- Thawing and embryo transfer.
Ovarian Stimulation
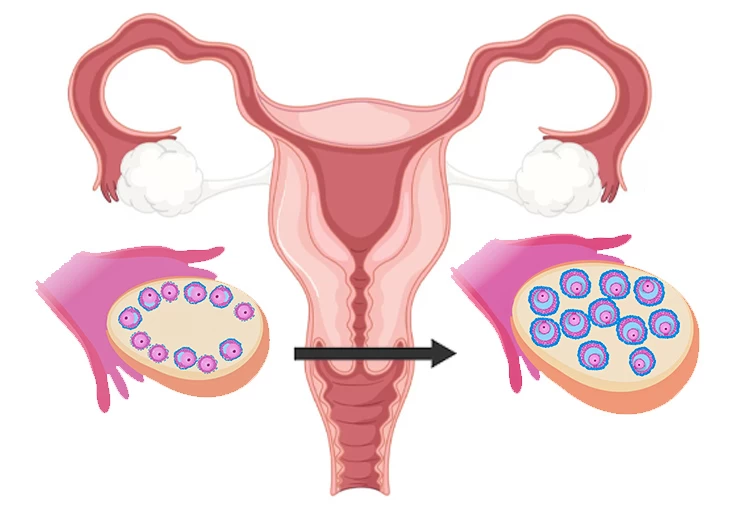
Ovarian stimulation involves administering an injection of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and/or luteinizing hormone (LH) approximately 8-10 days after the end of the last period. Ovarian stimulation can also involve taking medication orally instead. The purpose is to assist the ovaries in producing multiple mature eggs for release.
HCG injection is administered when the ovary has developed mature follicles. The injection helps to trigger the release of the eggs from the follicles, a process known as ovulation.
Egg retrieval
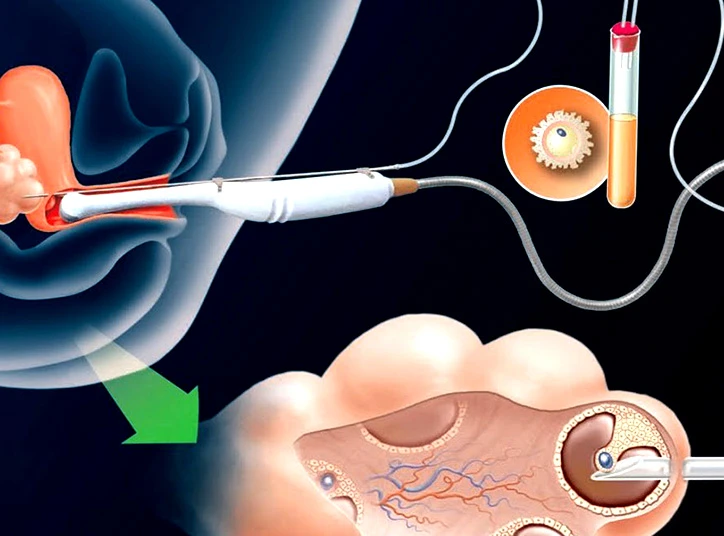
Egg retrieval is a medical procedure that is part of the in vitro fertilization (IVF) process. It involves removing mature eggs from a woman's ovaries to be fertilized with sperm in a laboratory. The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia.
During egg retrieval, a doctor uses a transvaginal ultrasound-guided needle to aspirate the follicles in the ovaries. The follicles contain the mature eggs. The doctor punctures the follicles and extracts the eggs using suction. The fluid from the follicles is collected and examined by an embryologist who identifies the eggs. The eggs are then prepared for fertilization either by conventional IVF or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) depending on the specific circumstances of the couple.
Collecting a Semen Sample
The collection of a semen sample for IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) typically occurs on the day of the egg retrieval procedure. The male partner needs to abstain from ejaculation for 2-5 days before the scheduled collection to ensure a sufficient quantity and quality of sperm for the IVF process. The semen sample is collected through masturbation into a sterile container provided by the fertility clinic. It is then immediately processed and used for fertilizing the retrieved eggs in the IVF procedure.
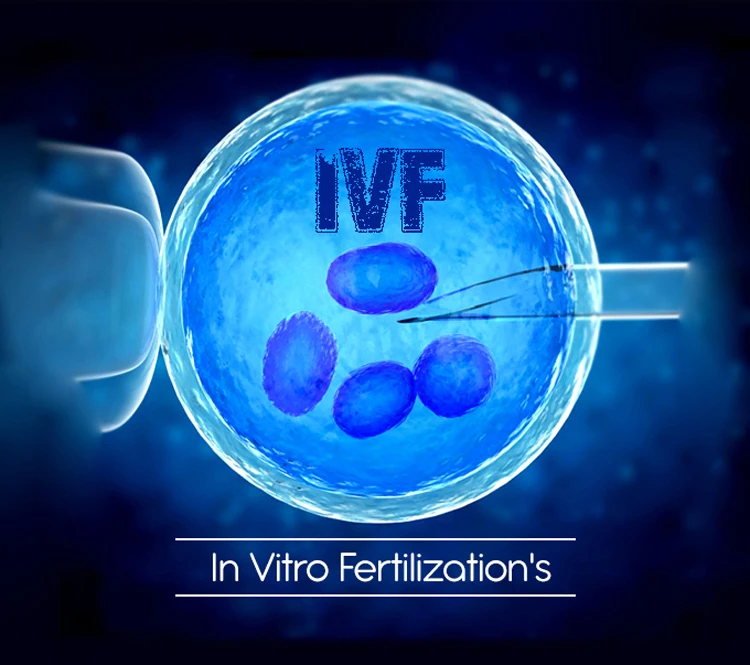
In-vitro Fertilization
The eggs and sperm are placed together in a culture dish under controlled laboratory conditions for 16-20 hours. The fertilized eggs, now called embryos, are then kept in an incubator for 2-6 days. During this time, they are carefully monitored for growth and development. At least 50% of embryos (for women over 35) reach the blastocyst stage after fertilization. Embryos that demonstrate good development and quality are selected for freezing.
Embryo Freezing
Embryos consist mostly of water, which may crystalize as it freezes. Crystallization destroys cells. To prevent ice crystal formation during the embryo freezing process, a cryoprotectant agent (CPA) is used to gradually replace the water present in the embryos.
There are two methods for freezing embryos, slow freezing and vitrification.
During slow embryo freezing, the CPAS is injected into the embryo within 10-20 minutes and then the embryos are then gradually cooled down within 2 hours until they reach the freezing temperature of -196 degree Celsius. The slow freezing technique prevents the embryo's cells from aging and lowers the risk of damage. However, it is time-consuming and expensive.
The vitrification process uses a much stronger CPA, resulting in a rapid freezing process. The embryos are then transferred to liquid nitrogen.
Thawing and Embryo Transfer
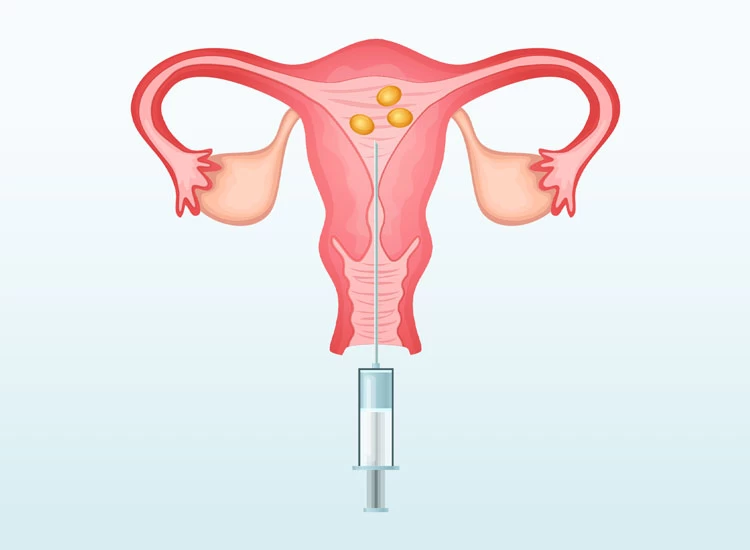
The thawing process is initiated when the couple is ready to use the frozen embryos. The embryos are carefully warmed and rehydrated, and the best-quality embryos are selected for transfer into the woman's uterus. Embryo transfer is the procedure of placing the thawed embryos into the uterus of a woman who is undergoing IVF treatment. This is done using a thin catheter that is inserted through the cervix. A successful embryo transfer can result in implantation and pregnancy.
In case of failed IVF and negative pregnancy, frozen embryos can be thawed and transferred in a subsequent cycle, without the need for additional egg retrieval or fertilization. This can reduce the cost of infertility treatment.
This technique can also help prevent genetic disorders.
What is the Success Rate of Embryo Freezing?
The success rate of embryo freezing is high, with a live birth rate of around 35% per transfer. This is comparable to the success rate of fresh embryo transfer, which is around 40% per transfer.
Factors that can affect the embryo freezing success rate include:
- Embryo quality: The quality of the embryos frozen is the most important factor that affects the success rate of embryo transfer. Embryos graded as high quality are more likely to survive the freezing and thawing process and implant in the uterus.
- Maternal age: Women who are younger than 35 years old typically have higher success rates with embryo freezing than older women. This is because older women's eggs are more likely to have chromosomal abnormalities, which can prevent them from developing into healthy embryos.
- Number of embryos transferred: The success rate of embryo transfer also increases with the number of transferred embryos. However, it is important to note that transferring too many embryos can increase the risk of multiple births.
- The overall health of the parents: if both parents are completely healthy, the embryo freezing success rate increases. But if the mother, for example, has endometriosis or uterine polyps, the success rate of this treatment decreases significantly.
Contact us for a free initial consultation about embryo freezing.
WhatsAppTelegramFacebookEmail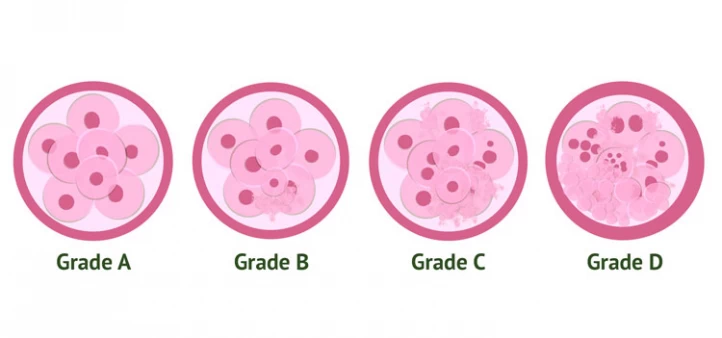
Who Needs to Freeze Embryo?
People with the following conditions are good candidates for embryo freezing.
- Have a serious health issue and want to have children after their treatment (like chemotherapy or endometriosis surgery);
- Are near the age of 35 and their ovaries are diminishing, but don’t want to have children now;
- Have an ovarian or uterine issue that prevents them from getting IVF with a fresh embryo;
- Already have children and want to use their embryos in future IVF;
- Are prone to azoospermia or varicocele;
- Want to get a vasectomy soon;
- Have a history of recurrent miscarriage due to endometrial problems;
- Their body has reacted to ovulation induction drugs and cannot receive the embryo now;
- Have not decided what the gender of their baby should be (couples can use PGD for gender selection).

What Are the Top 10 Reasons for Embryo Freezing?
There are a variety of reasons why couples choose to freeze embryos. Here are the top 10 common reasons:
- Diminished ovarian reserves or low AMH hormone levels in females;
- Fertility preservation for later use;
- Past failed IVF attempts;
- Fertility preservation after cancer treatment that may affect fertility such as certain medications, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy;
- Egg donation;
- Excessive embryos resulting from an IVF cycle and reluctance to repeat the treatment in the future;
- Poor endometrial receptivity
- Prevention of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (which can occur during IVF treatment);
- Fertility Preservation before undergoing endometriosis surgery
- Surrogacy due to uterine conditions such as Asherman syndrome (intrauterine adhesions or intrauterine synechiae) and Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH) Syndrome (underdeveloped or absent vagina and uterus).
What Is IVF Embryo Grading?
Embryo grading is a process used to assess the quality of embryos created through in vitro fertilization (IVF) and the optimal timing for their transfer. The goal of embryo grading is to determine whether the number of days the embryos are developed in vitro (the number of days between egg retrieval and embryo transfer) has any effect on IVF success.
Embryo transfer is done either 3 days or 5 days after the egg retrieval. As embryos are developmentally different on these days.

Embryo Freezing vs. Egg Freezing: Which One is Better?
Both embryo freezing and egg freezing have their advantages and disadvantages. The choice between the two options largely depends on the individual's specific circumstances and goals.
Embryo freezing involves the fertilization of eggs with sperm in a laboratory setting, followed by the freezing of resulting embryos for future use. This option is typically used by couples who are undergoing Types of Infertility Treatment Methods and have excess embryos that they do not want to discard. Embryo freezing can also be used by couples who want to preserve their fertility before undergoing treatments that may affect their reproductive system, such as chemotherapy.
Egg freezing, on the other hand, involves the extraction and freezing of unfertilized eggs for future use. This option is typically used by women who want to preserve their fertility for later use, as well as those who are undergoing treatments that may affect their fertility.
What Are the Advantages of Embryo Freezing?
Embryo cryopreservation has several benefits, including:
- Increased chances of future successful pregnancy, even with repeated IVF and ICSI failures or unsuitable candidates for ovarian stimulation;
- Reduced Cost, as it removes the need to undergo the entire IVF process repeatedly, which can be expensive. Instead, couples can opt to use the frozen embryos for subsequent transfers, reducing the overall cost of treatment as well as decreasing the complications of ovulation induction medications;
- Reduced mental and physical stress on the mother, as it removes the initial stages of IVF treatment;
- Increased ease in embryo transfer, as it doesn't require surgery or complicated treatments;
- Reduced risk of genetic disorders;
- The possibility of gender selection before embryo transfer using PGD (Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis) and PGS (Preimplantation Genetic Screening) testing;
- Reduced risk of miscarriage by selecting best-quality embryos;
- Reduced risk of high estrogen levels in the mother due to the time gap between egg retrieval and embryo transfer.
- Flexibility in timing, as couples can choose to delay embryo transfer for various reasons, such as personal circumstances, health reasons, or simply to time the pregnancy more conveniently. This flexibility allows couples more control over their reproductive choices.
- Opportunity to donate embryos.
What Are the side effects of embryo freezing?
While the process of embryo freezing is generally safe, there are some potential side effects and risks associated with the procedure. These may include:
- Bleeding the embryo transfer;
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) in which the ovaries become swollen and painful;
- Higher risk of multiple pregnancies;
- Cramping or bloating;
- Infections;
- Unexplained early satiety.
What Is the Cost of Embryo Freezing in Iran?
The cost of embryo freezing in Iran can vary depending on the clinic and the specific services included in the package. On average, the cost of each egg-freezing cycle typically ranges from $1,500 to $3,500 in Iran, two major costs of which are hormone therapy and frozen embryo storage. There will be also an extra charge for the annual storage fee.
Why Iran for Infertility Treatment?
Infertility treatment in Iran is popular for several reasons. Firstly, Iran has made significant advancements in medical technology and is home to highly skilled and experienced fertility specialists. These specialists are often trained in reputable international institutions and are well-qualified to provide quality infertility treatments.
Secondly, the cost of infertility treatment in Iran is relatively affordable compared to other countries, making it an attractive option for couples seeking treatment. This is particularly beneficial for individuals who may not have access to affordable or comprehensive healthcare coverage in their home country.
Thirdly, the laws and regulations surrounding infertility treatment are relatively flexible in Iran. This means that a wider range of treatments and options are available to patients, including assisted reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Additionally, Iran's cultural and social attitudes towards infertility are generally more accepting compared to some other countries. The society is understanding and supportive of couples facing fertility challenges, reducing the stigma often associated with infertility.
Final Word
Embryo freezing has become a prevalent technique in infertility treatment and prevention. It offers several benefits, including the ability to preserve embryos for future use, increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy, and reducing the need for multiple rounds of IVF treatments.
With the advancements in technology and medical expertise, more couples are now turning to embryo freezing as a viable option for overcoming infertility-related problems. However, it is crucial to seek the services of experienced and reliable doctors who have the expertise to perform the procedure successfully.
FAQ About Embryo Freezing
1) How long can the frozen embryos be stored?
In general, most clinics store frozen embryos for about 10 years, although some may allow storage for longer periods. It's important to note that the longer embryos are stored, the more their quality may deteriorate, which can affect their viability and chances of success if they are eventually used for a pregnancy.
2) Which is more successful, fresh or frozen embryo transfer?
The success of fresh or frozen embryo transfer can vary depending on factors such as the woman's age, underlying fertility issues, and the quality of embryos.
However, several studies have suggested that frozen embryo transfer (FET) may have slightly higher success rates compared to fresh embryo transfer.
Some potential reasons for the higher success rate of FET include:
- Improved Endometrial Receptivity: FET allows for better synchronization between the embryo and the endometrium, as it allows the uterus to recover from any hormonal stimulation used during ovarian stimulation for fresh embryo transfer.
- Embryo Selection: With FET, embryos go through a process of cryopreservation and thawing, which allows for the selection of high-quality embryos that have survived the freezing process.
- Reducing Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) Risk: OHSS is a potential complication of ovarian stimulation during fresh embryo transfer. FET eliminates the risk of OHSS as it allows for controlled ovarian stimulation and postpones the transfer to a later cycle.
3) What is the Importance of Maternal Age When Deciding Between Fresh or Frozen Embryo Transfer?
As women age, the quality of their eggs decreases, which can affect the success rates of both fresh and frozen embryo transfer.
Studies have shown that for women over the age of 35, frozen embryo transfer may result in higher pregnancy rates and lower rates of miscarriage compared to fresh transfer. This is because frozen embryos can be transferred during a cycle that has been optimized for implantation, rather than relying on the woman's natural cycle.













No reviews
Your comment