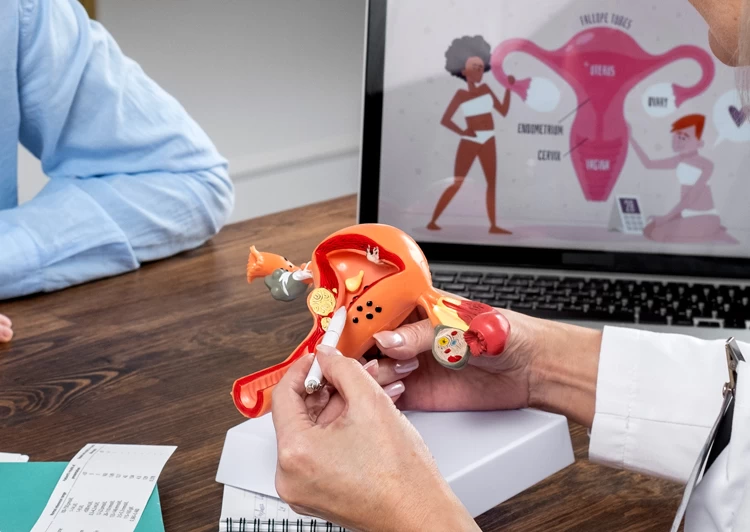
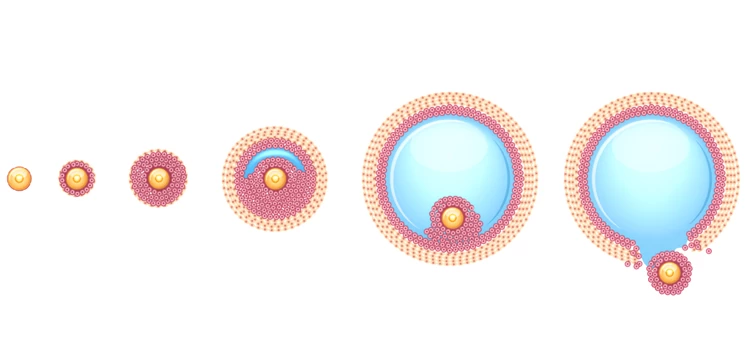
An ovarian follicle is a fluid-filled sac in the ovaries that contains one or more immature eggs. These sacs, including antral follicles, play a critical role in a woman's reproductive cycle. Several follicles, including antral follicles, start to grow at the beginning of each menstrual cycle. However, typically only one follicle reaches the point of ovulation, releasing a mature egg.
The irregular period is an issue that affects nearly all women throughout their lifetime. This situation occurs when the time interval between menstrual cycles is more or less than the normal limit. While this is considered completely normal in some cases, like the first cycles after puberty or the last cycles preceding menopause, it might be an indicator of an underlying health condition in other cases.
Small ovarian cysts rupture without any sign and resolve on their own. But when the large cysts pop, women feel severe abdominal pain, bleeding, bloating, sharp pain in the back, and lightheadedness. A ruptured ovarian cyst is detected by ultrasound, urine or blood test, endocervical culture, and CT scan.
Premature menopause doesn’t have a definite treatment yet, but some methods are being used to reduce its side effects, such as menstrual problems, vaginal dryness, and irregular ovulation. Usually, doctors prescribe hormonal medications, antidepressants, lubricants, and multivitamins to lessen the complications of premature menopause.
Women with ovarian cysts are not infertile, but they may have problems conceiving naturally. Functional adenoma and dermoid cysts do not impede pregnancy; however, endometriomas -cysts caused by endometriosis- lead to infertility as they form adhesions that prevent the sperm from reaching the egg.
Removing ovarian cysts through surgery (laparoscopy and laparotomy) increases your chance of conceiving and eliminates your pain and discomfort. After this operation, you have to avoid putting pressure on your abdomen, have a light and healthy diet, avoid smoking, and many more.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome doesn’t have an immediate treatment; therefore, you should seek help to control it months before trying to get pregnant. The treatments that are usually advised for PCOS include taking hormone medications to regulate the menstrual cycle and remove ovarian follicles, taking diabetes drugs, laparoscopy, assisted reproductive techniques, and following a healthy lifestyle.
Early menopause adversely affects women's fertility and may cause cardiovascular diseases, psychiatric diseases, osteoporosis, and other health issues in the long run. The main symptoms of early menopause include hot flashes, constant fatigue, insomnia, irregular menstruation, sudden hair loss, and increased facial wrinkles. Fortunately, this problem can be treated by hormone therapy, taking calcium supplements, changing lifestyle, etc.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) involves the formation of small cysts in ovaries, which may cause infertility and serious health issues. Controlling PCOS by having a healthy, insulin-resistant diet can reduce the mentioned risks and increase the chance of fertility.
Irregular menstruation and hormonal problems that lead to hair loss or sudden weight gain are the main symptoms of female infertility. Factors like age, premature menopause, low-quality eggs, problems in the reproductive system, endometriosis, infection, etc., are the leading causes of female infertility.