Warning Signs & Symptoms You Might Have PCOS
Fertility Treatment
Polycystic ovary syndrome or PCOS is a common hormonal disorder in women of reproductive age, which may cause male hormone (androgen) growth, irregular or long period cycles, anovulation, and difficulty in pregnancy. According to OWH (Office of Women's Health), PCOS affects 5–10 percent of women between 15 to 44 years old.
Suppose polycystic ovary syndrome, considered the most common endocrine disorder in women, is not treated early and well. In that case, it can lead to cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, endometrial hyperplasia, and fertility problems. However, despite PCOS's effect on women's ability and chances of fertility, most patients of this type have children with perfect physical health.
Read on to learn more about the role of PCOS in reproductive health, signs of PCOS, treatment methods, and more.

What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)?
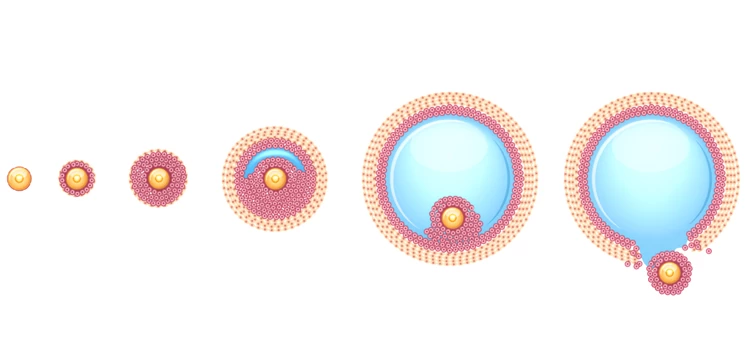
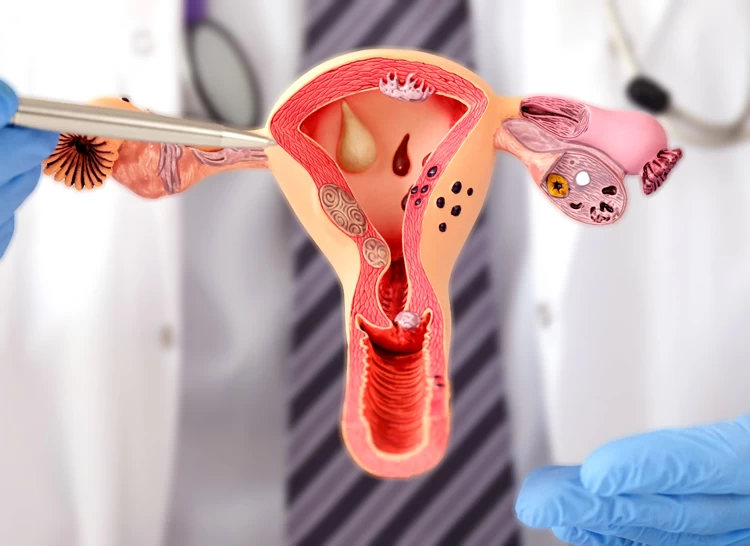
The ovary contains many small fluid-filled sacs or follicles under its surface. The eggs grow in these follicles. In polycystic ovary syndrome, the said follicles do not mature and release the eggs well.
In a normal situation, one follicle grows larger out of 5 to 6 follicles produced totally by the ovary monthly. The other follicles remain small or will be destroyed. Therefore, about three to four large half-grown follicles are observed on the surface of the ovaries every month.
However, in people with PCOS, multiple small follicles (small cysts 4 to 9 mm in diameter) accumulate in the ovary. In other words, ovulation does not occur in the polycystic ovaries due to the raised LH/FSH ratio and factors such as the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis. So, does PCOS cause infertility? Not necessarily, but it can make it harder and longer to get pregnant.
Signs & Symptoms of PCOS
According to the research, PCOS symptoms mainly start from the first-period cycle and increase during puberty. However, we should note that these symptoms are different in each individual depending on the ovary activity.
If you wonder what are the first signs of PCOS, read the following.
High Androgen Level
Androgen is a general name for natural and synthetic compounds that cause the development of male characteristics. One of the most known Androgen hormones is testosterone.
An increase in androgen levels or male hormones in women can cause severe acne, facial and body hair growth, and male-pattern baldness. In case these symptoms occur, one should do a PCOS diagnosis test.
Irregular Menstruation
Heavy bleeding, long period cycles, and severe pelvic and abdominal pain during menstruation are the most common symptoms of PCOS. If your period cycle exceeds 35 days or has less than nine menstrual cycles during the year, you may have PCOS.
Heavy and long menstrual bleeding
If the lining of the uterus (called the endometrium) becomes thicker, it can result in heavy and/or prolonged bleeding.
Obesity
Obesity is a sign of PCOS and one of the main reasons for aggravating other PCOS symptoms like insulin resistance.
Excessive hair growth
Most women with PCOS experience thick, dark hair on their face (chin area) and body (around the breasts, navel, and below the navel).
Hair loss
Women with PCOS sometimes experience male-pattern hair loss due to increased male hormones (in the temples and middle of the head).
Oily skin and acne
Male hormones make the skin oily and cause acne on the face, chest, and back.

How to Reduce PCOS Symptoms?
Some signs of PCOS, such as facial hair, acne, and dark spots on the face, can impact girls’ self-esteem, but if they know how to cope with them, they can have an easier life. Hormonal medications, depilatory creams, tweezing, waxing, and laser therapy help you get rid of PCOS facial hair. Moreover, if you have a skin rash and acne, it is recommended to take birth control pills or antiandrogens.
What Is the Cause of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
Some factors that cause PCOS include:
- Obesity. Almost 40 to 80% of women with PCOS are overweight or have a BMI over 30;
- Stress and anxiety. When you have anxiety, your body secretes a hormone (cortisol) that impacts and increases androgens and causes ovarian laziness;
- Genetic factors. PCOS has a hereditary pattern and runs in families;
- Thyroid diseases. Hypothyroidism can cause PCOS or worsen its symptoms;
- Insulin resistance. Most women with PCOS have insulin resistance. It means their body does not use insulin properly, which triggers the pancreas to produce more insulin. When the amount of insulin in the blood increases, the ovaries produce more male hormones, and that leads to PCOS;
- Pelvic and uterus inflammatory and microbial diseases;
- Adrenal gland disorders. High stress or being overweight can increase the androgen produced in the adrenal glands and cause PCOS.
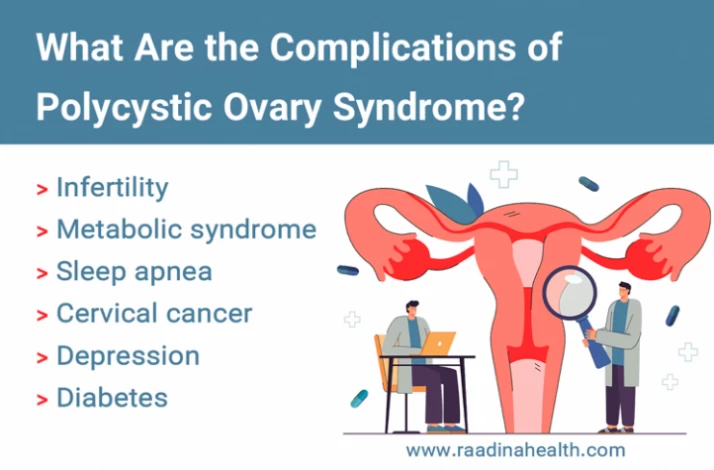
What Are the Complications of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
Women with PCOS are more likely to develop certain serious health problems. These Complications include:
- Infertility;
- Metabolic syndrome;
- Sleep apnea;
- Cervical cancer;
- Depression;
- Diabetes or pregnancy-induced high blood pressure.
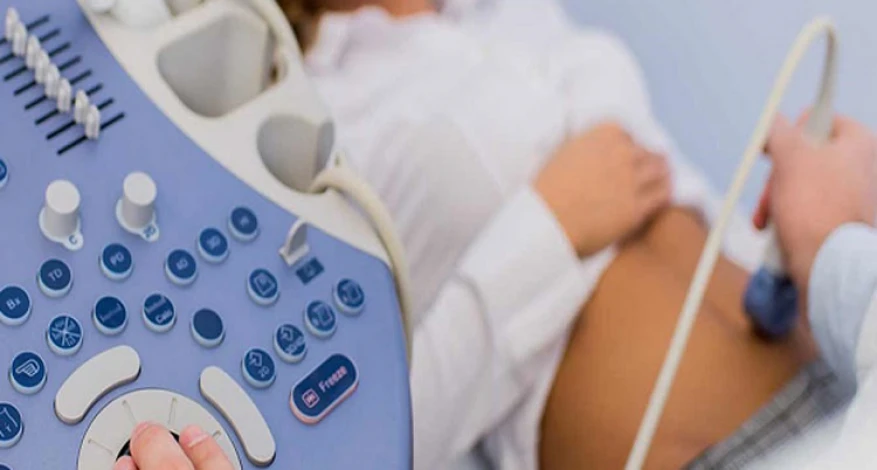
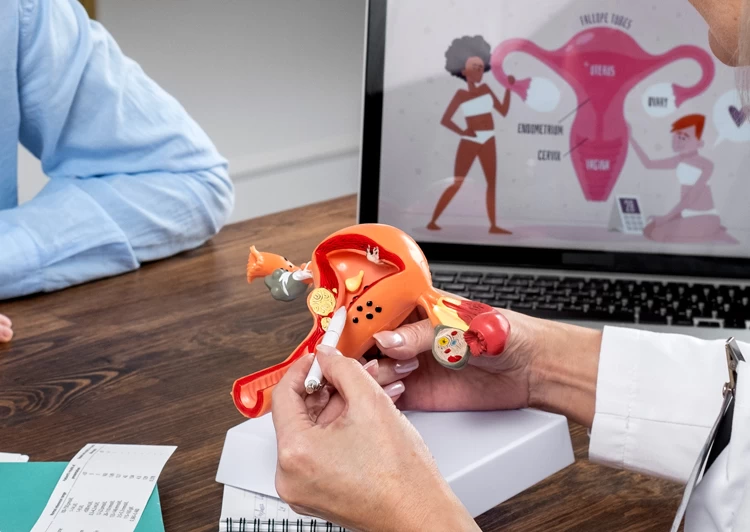
Polycystic ovary syndrome Diagnosis
The best way to check the ovaries is to use vaginal ultrasound. However, blood hormone tests are also used to diagnose PCOS. A blood test examines LH, FSH, and the amount of estrogen.
PCOS Physical Examination
Physical examination measures BMI index, blood pressure, height, weight, etc., to identify early signs of PCOS.
Sonography
One of the best ways to check the condition of the ovaries is to use an ultrasound, especially a vaginal one. Ultrasound imaging plays an important role in observing the ovaries' appearance and the uterus's thickness, discovering a large number of small follicles, and thus diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome.
If one of the ovaries is bigger, it can signify that many large follicles surround the eggs inside the ovary. This condition prevents the eggs from being released and causes the ovaries to work irregularly, leading to menstrual cycle disorders and infertility.
Blood Test
Blood tests, one the most important ways of PCOS diagnosis, consist of various tests to measure multiple factors such as blood sugar (glucose) and insulin. Blood tests are performed before and after drinking sugar water to measure fasting triglyceride and cholesterol levels, along with a glucose tolerance test.
Hormone Blood Tests
Hormone tests can identify ovaries and uterus disorders with high accuracy. Hormone blood tests can check the level of below hormones in PCOS:
- Luteinizing hormone or LH (decrease);
- Follicle-stimulating Hormone (FSH);
- Testosterone (increase);
- Estrogen (constant or increase);
- Androstenedione (increase);
- Sex Hormone Binding Globulin or SBGH (decrease);
- Anti-Müllerian or AMH (increase).
Differential Tests
Some other tests help to find other causes of PCOS and lead to a quicker diagnosis. These tests include:
- TSH (Thyroid-stimulating hormone) test to find out thyroid dysfunction;
- Prolactin (PRL) test to diagnose hyperprolactinemia;
- Cortisol level test to diagnose Cushing's Syndrome;
- 17-Hydroxyprogesterone Test to screen for congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAHI);
- IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1) test to prevent growth hormone levels from increasing.

PCOS Treatment & Medication
Unfortunately, there is no way to cure PCOS permanently. Therefore, treatment methods for infertility may differ according to the symptoms of each individual. PCOS medication generally includes hormonal drugs that improve ovulation, such as combined contraceptive pills and progestin oral contraceptives.
If you want to get pregnant in future, the following PCOS treatments can help you.
Pharmacotherapy
We should note that drugs for treating PCOS differ depending on the type of disorder that has caused this condition. The drug therapy includes:
Medication to regulate the menstrual cycle:
Contraceptive pills help to regulate the menstrual cycle through progestin therapy. Patients with PCOS should take these pills every month or every two months for 10 to 14 days. Contraceptive pills contain progesterone and estrogen and cause androgen reduction. Taking these pills minimizes the signs of PCOS, stops heavy menstrual bleeding, reduces the risk of endometrial cancer, and controls acne and excessive hair growth. Estrogen and progestin transdermal patches or vaginal rings can also be used instead of contraceptive pills.
Medications to reduce androgens:
- Spironolactone: To reduce the effect of androgens on the skin;
- Birth control pills: To reduce androgen production;
- Eflornithine cream: to slow down the growth of unwanted hair on the face;
- Electrolysis is a method that involves using a thin needle into the hair follicle to destroy the hair roots.
It is worth mentioning that you have to avoid taking any medicine arbitrarily if you are pregnant. For example, spironolactone leads to congenital disabilities in the fetus, and its use during pregnancy is not recommended.
Medications for Ovulation Induction
Some medicines that can regulate the ovulation process include:
- Letrozole: An oral medication used to stimulate ovulation;
- Clomiphene citrate (CC): An oral anti-estrogen drug that works similarly to estrogen and can be used in the first part of the menstrual cycle;
- Gonadotropin: An Injectable hormonal drug that regulates the secretions of sex hormones;
- Metformin: An effective oral drug for treating type 2 diabetes, reducing insulin resistance, fertility problems, and weight loss.
Medications that Treat Excess Hair Growth
Some of the drugs that help to reduce the growth of unwanted hair in people with PCOS include:
- Spironolactone: To reduce the effect of androgens on the skin;
- Birth control pills: To reduce androgen production;
- Eflornithine cream: to slow down the growth of unwanted hair on the face;
- Electrolysis is a method that involves using a thin needle into the hair follicle to destroy the hair roots.
It is worth mentioning that you have to avoid taking any medicine arbitrarily if you are pregnant. For example, spironolactone leads to congenital disabilities in the fetus, and its use during pregnancy is not recommended.
Surgery
If drug treatment is ineffective, surgery (laparoscopy) can be used. In this method, the surgeon makes small incisions in the ovary with laser or thin needles. This surgery can reduce male hormone production and improve the function of the ovary and the ovulation process.
Lifestyle Changes
Some lifestyle factors play a significant role in PCOS treatment. Some of them include the following:
- Exercising regularly,
- Following a proper diet,
- Avoiding high-sugar foods or drinks,
- Managing your weight.

Artificial insemination
If none of the above treatment methods are effective, reproductive technology such as IVF is the final choice for women with PCOS who want to get pregnant.
PCOS and Pregnancy
If you have polycystic ovaries and intend to get pregnant, you should first know which factors in PCOS have led to your infertility and treat them.
The main cause of infertility in patients with PCOS is anovulation, which relates to immature follicles or high testosterone levels. Even despite ovulation, the hormonal imbalance sometimes makes the endometrium (the lining of the uterus) unable to accept the embryo. In addition, the hormonal imbalance in PCOS leads to menstrual irregularities and unpredictable menstrual cycles, which will cause pregnancy disorders.
Improvement of the ovulation process and balancing the levels of hormones in the body involve some steps. Since many women with PCOS are overweight, losing weight is the first step to getting pregnant. Losing weight and having an ideal body mass index (BMI) balances body hormones, reduces blood insulin, stimulates and improves the process of ovulation, and regulates the period cycle.
Lifestyle modifications and hormonal balance can improve the chance of pregnancy in mild PCOS. However, severe PCOS cannot be treated simply by improving lifestyle and requires medical procedures. Choosing the best treatment method highly depends on the severity of PCOS and the mother's general condition.

As mentioned above, the main cause of female infertility with polycystic ovary syndrome is obesity. Excess weight causes ovulation disorders and PCOS due to disruption in hormonal balance. However, ovulation continues sometimes despite irregular menstruation. In most cases, people with a period cycle longer than 35 days have a small chance of pregnancy. Therefore, weight loss can affect the body's resistance to insulin, balance the body's hormones, and treat ovulation disorders. Even if weight loss does not improve ovulation, it can increase the chance of pregnancy.
The Best Diet for PCOS
Studies show that a proper and complete diet can be essential in treating polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), increasing the chance of getting pregnant and protecting it.
Patients with PCOS are at risk of blood sugar imbalance and insulin resistance. However, following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, getting essential nutrients, and managing stress will improve the patient's physical condition.
The recommended diet is as follows:
- Balance carbohydrate and protein intake;
- Take low glycemic index (GI) foods;
- Take high-fiber foods;
- Eat daily essential fatty acids;
- Take no caffeine;
- Eat organic foods;
- Have three meals and two snacks per day.

When to see a doctor for PCOS?
Since PCOS causes fertility problems, you must visit a specialist once you notice it. We recommend seeing a doctor in case any of the following symptoms occur.
- Your period is late, and you are not pregnant;
- You have failed to get pregnant after a year of trying;
- You have diabetes symptoms.
How to Prevent PCOS?
It is not possible to prevent PCOS. However, if it happens, you can prevent the aggravation of symptoms. For example, weight loss is an effective way to prevent symptoms from becoming more serious. Furthermore, visiting a gynecologist and taking specific medications can help prevent PCOS symptoms.
PCOS is not dangerous and does not always lead to cancer or infertility. Although, due to the high importance of the disease, it should be treated as soon as possible. Therefore, it is recommended that women and girls visit a gynecologist regularly and undergo periodical examinations from adolescence and early youth.
It also should be noted that sometimes, the hormonal fluctuations after pregnancy and breastfeeding can reduce PCOS symptoms to a great extent and make the ovaries function regularly for several years.

PCOS in Teenage Girls
Irregular menstruation, especially in the first two years of menstruation, is not always a sign of PCOS in teenage girls. However, they should see a gynecologist if this issue continues along with hairiness or hair loss and weight gain.
It is important to know adolescence is the best time to diagnose and treat PCOS or polycystic ovary syndrome. Therefore, it is necessary to visit a gynecologist regularly during this period.
The bottom Line
PCOS in many women occurs without any or very few symptoms. Therefore. PCOS diagnosis is difficult in many cases. However, if you have PCOS, you should follow some tips, such as:
- Following a healthy lifestyle;
- Performing regular and periodic checkups of menstrual cycles;
- Getting pregnant before 30;
- Following up on every symptom;
- Avoiding tension and stress.
The endometrial thickness or malignant tumors in women with irregular cycles can be detected through vaginal ultrasound or endometrial biopsy. For these cases, drug treatments can be adopted. However, due to the genetic nature of PCOS as a metabolic disorder, it is sometimes recommended that the female members of the family be examined for diabetes and glucose intolerance.
Finally, contact our team of experienced fertility specialists in Raadina Co. for more information about PCOS. We'll help you book an appointment with the best fertility treatment centers in Iran and also through the whole treatment process.

Contact us for a free initial consultation about fertility treatments
WhatsAppTelegramFacebookEmailFrequently asked questions about PCOS
1) How long does the PCOS treatment process last?
The process of treating PCOS is different depending on the severity of the disease in different people. However, it often takes one to two years under medical supervision. It is also impossible to ensure when the planned treatment is effective.
Women whose PCOS has not been diagnosed yet should attempt natural pregnancy at least one year before doing any test. If they do not get pregnant within a year of trying, the doctor will prescribe the necessary examinations.
However, for women over 35 or those with a history of abortion, there is no need for a one-year pause; they can do the necessary tests from the beginning.
2) How to Get Pregnant with PCOS?
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome or PCOS can get pregnant; however, this process may take a little longer. Therefore, you should always be hopeful. The solutions to increase pregnancy chances are to lose weight, regularize the menstrual cycle, and consume stimulation drugs.
3) How can I help the healing process?
If you are obese or overweight, you should follow a healthy diet to speed up your recovery. Even a five percent reduction in weight significantly affects the speed of polycystic ovary syndrome treatment.
4) Are women with PCOS lives different from others?
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome can live a normal life like other women. However, it is necessary to be under medical supervision to control and prevent other related diseases.
5) What Are the Chances of Getting Pregnant with PCOS?
As several individuals with polycystic ovaries have had successful pregnancies without ever knowing about their disease, there are no accurate statistics regarding the chance of getting pregnant with PCOS.
However, according to studies, about 70% of women with polycystic ovary syndrome experience difficulty in their pregnancy, either because they are not ovulating regularly or they do not have enough progesterone to support pregnancy early stages.
6) How to Maintain a Safe Pregnancy with PCOS?
Women with PCOS may face a higher risk for complications such as miscarriage, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and high fetal weight during pregnancy. Therefore, it is recommended that they be under medical supervision and constantly check their blood sugar and pressure.
7) what are the first signs of PCOS in teenagers?
The first and most important signs of PCOS in teens are irregular or missed periods. Rapid weight gain, facial hair growth, hair thinning, and severe acne are other PCOS symptoms in teenage girls.
8) what are the first three symptoms of PCOS?
Irregular or missed periods, signs of high androgen levels (acne, facial hair, hair around nipples, hair thinning, etc.), and sudden weight gain are the first signs of PCOS. Enlarged ovaries are also important signs of PCOS, which can be detected by vaginal ultrasound.
9) Is PCOS dangerous?
Polycystic syndrome is not a fatal disease, but it can lead to serious health issues such as diabetes, high blood pressure, cardiovascular diseases, endometrial problems, uterine cancer, sleep disorders, and even depression.














User
-Does polycystic ovarian syndrome ever go away?
Habib Ebrahimi
-PCOS cannot be cured permanently and it will not go away on its own, but its symptoms can be controlled and minimized by taking medication, losing weight, and having a healthy lifestyle.
User
-Is polycystic ovarian syndrome lifelong?
Habib Ebrahimi
-Usually, polycystic ovarian syndrome lasts until after the child-bearing age but some of its symptoms such as diabetes and obesity may be permanent.
User
-What's the difference between PCOS and endometriosis?
Habib Ebrahimi
-Endometriosis is a uterine disorder in which an endometrial-like tissue grows outside the uterus (usually in the fallopian tubes or pelvic) and cause infertility, heavy and painful period, painful urination or bowel movements, and spotting or bleeding between the menstrual periods. PCOS is an ovarian disorder which causes irregular menstrual periods, excess hair growth on body and face, acne, infertility, diabetes, and weight gain