Dilation & Curettage (D&C): How it Is Done, Recovery & More
Fertility Treatment
Dilation and curettage, also known as D&C, is a minor surgical procedure used to remove tissue from the uterus after a miscarriage, diagnose and treat certain gynecological conditions (such as heavy bleeding), or clean the uterus after a miscarriage. This procedure involves dilating the cervix and gently removing tissue from the uterine lining using a specialized instrument called a curette.
It's important to note that a gynecologist can perform D&C procedures in a clinical setting, such as a doctor's office. Read on to learn about the different types of D&C procedures and their pre and post-operative care instructions.

What Is a Dilation and Curettage (D&C)?
A dilation and curettage procedure (D&C surgery) is a procedure during which the cervix is dilated or expanded, and a thin instrument called a uterine curette is used to scrape the lining of the uterus gently. Thigently, the process allows for removals for diagnostic purposes, treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding, or management of incomplete miscarriages.
It is worth mentioning that the uterine curette is a crucial component of the comprehensive dilatation and curettage (D&C) set, which encompasses all the tools required to perform curettage surgery effectively.
D&C Procedure Steps
A Dilation and Curettage (D&C) procedure is typically performed in a hospital or outpatient surgical setting. Before the procedure, the patient will be asked to change into a hospital gown and lie on an examination table while her heels rest in stirrups.
The patient will be given either general anesthesia, which puts them to sleep during the procedure, or local anesthesia, which numbs the cervix and uterus. The choice of anesthesia depends on the patient's medical history and the complexity of the procedure.
The doctor then will use a speculum to hold the vaginal walls apart and access the cervix.
D&C procedure typically includes two main steps:
Step 1:
After the cervix has been sufficiently dilated, the doctor may insert a thin Laminaria tube into it or administer misoprostol medication to soften it. The laminaria expands by absorbing fluid from the surrounding tissue, gradually opening the cervix.
In situations where the cervix needs to be opened more than a typical dilation and curettage procedure, the doctor may opt to open the cervix a few hours or even a day before the procedure. This gradual opening process is commonly used in cases such as abortion or specific types of hysteroscopy.
Step 2:
The doctor will use a curette or a suction device to remove the contents of the uterus.
A Dilation and Curettage may be combined with another procedure called hysteroscopy, during which the doctor inserts a slim instrument with a light and camera on the end through the cervix and into your uterus.
The doctor then observes the uterus lining on a screen, identifying abnormal areas. This allows for the removal of polyps or fibroids present in the uterus.
What Are the Dilation and Curettage (D&C) Types and Their Applications?
There are three types of dilatation and curettage (D&C) procedures, each serving specific purposes, including:
- Therapeutic D&C
- Diagnostic D&C
- Elective D&C
Therapeutic D&C
Diagnostic D&C is performed to remove the remaining tissue after a miscarriage and prevent complications such as infection or excessive bleeding.
Diagnostic D&C
Diagnostic D&C is a procedure performed to investigate or diagnose certain gynecological conditions such as endometrial hyperplasia (abnormal thickening of the uterine lining), uterine polyps, or endometrial cancer. It involves dilating the cervix and scraping the lining of the uterus to collect tissue samples for examination (biopsy).
If abnormal Pap smear results indicate possible cervical or endometrial abnormalities, diagnostic D&C may be recommended to obtain tissue samples for further evaluation and diagnosis.
Additionally, when a woman experiences abnormal menstrual bleeding, such as heavy or irregular periods, diagnostic D&C can help determine the underlying cause by examining the uterine lining for abnormalities.
Elective D&C
Elective D&C may be performed for certain gynecological conditions or as part of a planned treatment strategy. During this procedure, a tissue sample is taken from the cervix and sent to the laboratory for detailed examination.
What Are the Main Reasons for the D&C Procedure?
Dilation and Curettage (D and C) procedure is performed to:
- Remove any remaining tissue from the uterus after a miscarriage to prevent infection and heavy bleeding;
- Remove the remaining placenta in the uterus to treat excessive bleeding after delivery;
- Remove molar pregnancy (where abnormal tissue grows in the uterus instead of a normal embryo);
- Diagnose and treat infection, abnormal uterine bleeding, heavy menstrual bleeding, postmenopausal bleeding, and hormonal imbalance;
- Examine conditions such as fibroids, polyps, uterine cancer (endometrial cancer), heart diseases, and lung diseases;
- Remove infected scar tissue caused by pelvic inflammatory disease (PID);
- Remove IUD.

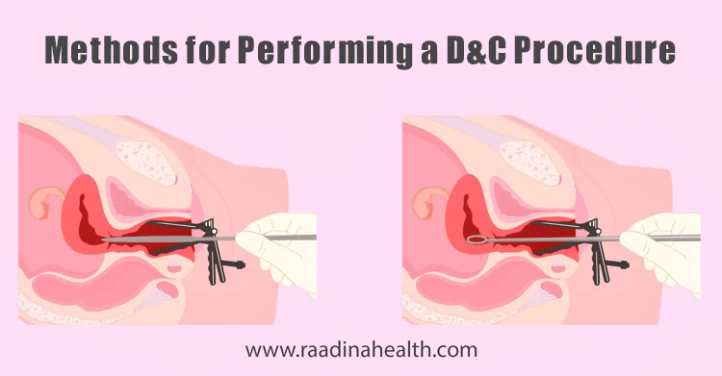
What Are the Main Methods for Performing a D&C Procedure?
Two main methods exist for performing a Dilation and Curettage (D&C) procedure. In both methods, the doctor administers a local anesthetic to numb the vagina and cervix. Then, a speculum is inserted into the vagina to dilate the cervix gently.
The D&C procedure is then carried out using one of the following methods:
D&C Traditional Scraping Method
During the traditional D&C method, the doctor inserts the curette or other D&C tools through the speculum into the uterus to scrape any abnormal tissues and perform the necessary examinations.
Suction Curettage Method
During a suction D&C, a thin tube called a cannula is inserted through the cervix into the uterus. The cannula is connected to a suction device that removes the uterine lining and any other tissue present.
The suction D&C method is less invasive than the traditional scraping method, which may result in less discomfort and a shorter recovery time for the patient.
What Are the Risks and Complications of Dilation and Curettage (D&C)?
While dilation and curettage (D&C) is generally considered a safe procedure, there are some potential risks and complications. These may include:
- Abnormal spotting or bleeding;
- blood clotting;
- Muscle cramping;
- Damage to the cervix;
- Uterine or pelvic infection;
- Persistent (lasting longer than 48 hours) fever, pain, or cramps;
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge;
- Abdominal tenderness;
- Perforation of the uterus, bladder, or blood vessels (rare);
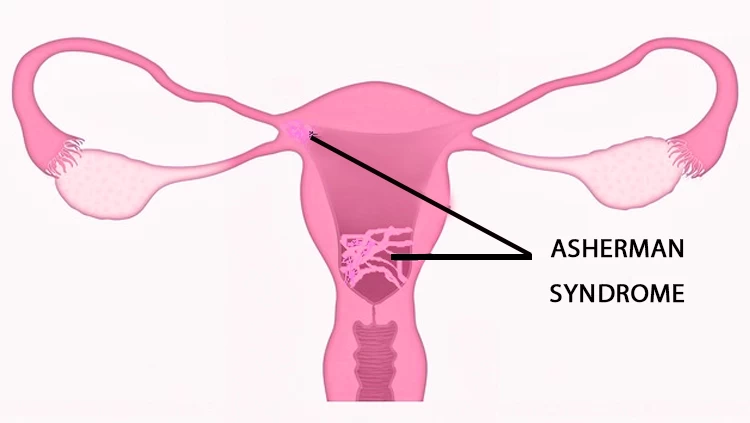
- Asherman syndrome (the formation of scar tissue in the uterus).
D&C risks future pregnancy by potentially causing the formation of scar tissue within the uterus, known as Asherman syndrome, which can affect future fertility. Additionally, the procedure risks future pregnancy by causing damage to the cervix or uterine wall, which can pose risks to future pregnancies.
Preparing for D&C Procedure
Your doctor may conduct a thorough physical examination and review your medical history. Additional diagnostic tests, such as blood work, might be necessary to assess your overall health status.
You'll receive specific instructions depending on the type of anesthesia required—general, spinal, epidural, or local. For general, spinal, or epidural anesthesia procedures, fasting typically begins eight hours before, usually after midnight. If local anesthesia is used, your doctor will provide tailored fasting guidelines.
It's essential to disclose any pertinent health information, including pregnancy or suspicions, as this can impact procedural decisions. Your healthcare provider may recommend a pregnancy test beforehand. Inform your doctor about allergies to medications, iodine, latex, tape, or anesthetic agents. Medication management is crucial. Detail all prescribed medications, over-the-counter drugs, and herbal supplements to your doctor. Mention any history of bleeding disorders or current use of anticoagulants like aspirin, which may necessitate temporary cessation before the procedure.
Due to potential lingering effects from sedation procedures, you must arrange for a responsible adult to drive you home afterward. Additionally, consider bringing a sanitary napkin for comfort post-procedure.
Finally, based on your health profile, your doctor may advise further specific preparations to optimize your safety and comfort during the procedure.
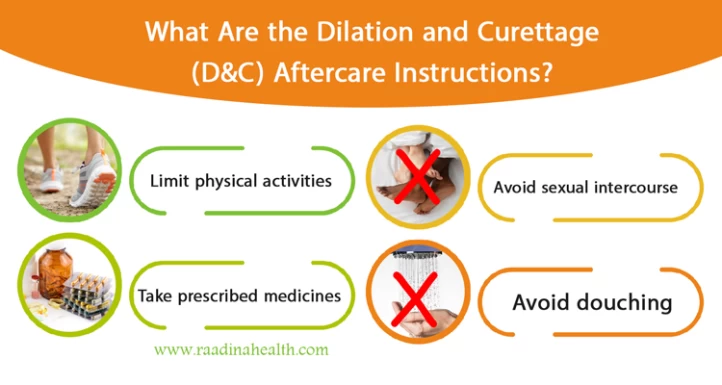
What Are the Dilation and Curettage (D&C) Aftercare Instructions?
Have you wondered what to do and what not to do after a D&C? After undergoing a dilation and curettage (D&C) procedure, following certain aftercare instructions to promote healing and reduce the risk of complications is important. Here are some common aftercare guidelines for D&C:
- Avoid sexual intercourse or use tampons for at least one to two weeks after a D&C procedure to allow the cervix to return to its original size and reduce the risk of infection;
- Prioritize rest to allow your body to recover after the D and C. If general anesthesia is administered during the procedure, you may experience symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. Therefore, it is advisable to limit physical activities and ensure sufficient rest;
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers to alleviate any cramping or discomfort following the D&C;
- Take prescribed medicines regularly to prevent infection;
- Avoid heavy exercises, douching, and swimming until complete recovery from the D&C;
- Avoid cycling as it may put excessive pressure on the uterus;
- Watch for warning symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, dizziness, prolonged cramps, foul-smelling discharge, or persistent bleeding. Promptly contact your doctor if any of these symptoms manifest.
It is important to note that following a D&C, the uterus will regenerate its lining, potentially causing your next period to occur earlier or later.
Who Are Not Good Candidates for Dilation and Curettage (D&C)?
Some factors that may make a woman unsuitable for a diagnostic D&C can include:
- Cervical stenosis: Cervical stenosis, a condition characterized by narrowing of the cervical opening, can make it challenging to perform a D&C safely and effectively;
- Difficulty seeing the opening of the cervix: If the doctor is unable to visualize or access the opening of the cervix during a D&C procedure, it can make the procedure technically challenging and potentially increase the risk of complications;
- Active pelvic infection: If a person has an active pelvic infection, undergoing a D&C can spread or lead to complications. It is crucial to treat the infection before considering a D&C;
- Pregnancy: D&C is typically avoided during pregnancy unless it is necessary for specific medical reasons, such as treating a miscarriage or performing an abortion. In other cases, D&C during pregnancy can pose risks to the developing fetus;
- Uterine perforation risk: Individuals with a high risk of uterine perforation, such as those with specific uterine abnormalities or conditions such as arthritis that make the procedure technically challenging, may not be good candidates for D&C.
Additionally, here are some signs you need a D&C:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding;
- Irregular menstrual cycles;
- Severe abdominal pain;
- Unusual vaginal discharge;
- Abnormal results from a Pap smear.
Is Curettage Necessary After a Miscarriage?
The need for a D&C procedure following an abortion depends on several factors, such as the type of abortion procedure performed, the completeness of the abortion, and the presence of any complications.
There is no need for D&C if the abortion is performed before the 10th week of pregnancy. However, if it occurs after this timeframe, there is a risk of incomplete miscarriage. In such cases, a healthcare provider might advise a D&C to remove any remaining tissue from the uterus.
It is crucial to recognize that many women who experience miscarriages may have a history of malnutrition, which can heighten the likelihood of complications during a D&C. To minimize these risks, abortions should be performed within the first trimester of pregnancy. In some cases, the curettage may be used for a faster resolution when waiting for a natural miscarriage is not feasible.
Is Dilatation and curettage (D&C) Painful?
Patients may typically experience mild discomfort or cramping during a dilation and curettage (D&C) procedure. However, it is typically not considered painful. Most patients are given anesthesia or sedation to help minimize any discomfort during the procedure. It should be noted that muscle contractions in the abdomen and uterus during the procedure can cause some discomfort; however, many women can tolerate it well and undergo it successfully.
Infertility Treatment in Iran
Iran has emerged as a sought-after destination for international patients seeking infertility treatment. Iranian doctors are highly trained and experienced in the field, and many have received their education and training in reputable medical schools and hospitals worldwide. This ensures that patients receive the best possible care and treatment for their infertility issues.
The affordability of medical treatment in Iran is another key factor driving its popularity among patients. Despite the lower costs, the quality of care remains uncompromised, with many patients expressing high satisfaction with their treatment outcomes. This cost-effectiveness makes Iran a compelling choice for those seeking high-quality infertility treatment without breaking the bank.
Iran's advancements in infertility treatment have also significantly contributed to its attraction of patients from around the globe. With cutting-edge facilities, equipment, and access to the latest treatment methods, patients can benefit from the most advanced and effective Infertility Treatment Methods available, increasing their chances of achieving successful outcomes.
Moreover, Iran's warm and welcoming culture adds to the overall positive experience for international patients seeking infertility treatment. The supportive environment created by medical staff and locals can benefit patients' mental and emotional well-being, potentially enhancing their chances of a successful pregnancy.
Infertility Treatments in Iran
Final Word
Curettage serves both a therapeutic and diagnostic purpose. Typically, diagnostic D&C is a relatively quick procedure with a short recovery time. After following the doctor's instructions and receiving post-operative care, the individual can resume normal activities soon.
It is important to note that the uterus will be at a higher risk for infection after a D&C. Therefore, failure to adhere to proper post-operative care may result in the spread of infection, potentially leading to serious health complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) How long does a D&C procedure take?
A D&C (dilation and curettage) procedure typically takes 5 to 10 minutes but may sometimes take longer. After the procedure, you should rest a few hours in the recovery room.
2) How long does it take to get your period after D&C?
The timing of menstruation after a curettage procedure can vary from person to person. However, it typically occurs between 2 to 6 weeks after the procedure. It is important to note that the uterus forms a new layer after D&C, which can lead to an early or delayed period. Additionally, menstrual bleeding may be more intense than usual for one or two cycles following the procedure.
3) How long will I bleed after diagnostic D&C?
Light vaginal bleeding can last for a few days to up to two weeks after a diagnostic dilatation and curettage (D&C) procedure. The amount and duration of bleeding can vary depending on individual factors, such as the reason for the D&C, the person's overall health, and how the body responds to the procedure.
Patients may also experience pain similar to menstrual cramps after the procedure.
4) How many days should you rest after a D&C?
The recovery time after a D&C may last 2 to 3 days. During this time, it is recommended that patients rest at home to recover faster. Once fully recovered, individuals can gradually resume their usual daily activities. It is important to note that women who have undergone a D&C due to a miscarriage are advised to rest for 48 hours before resuming normal activities.
5) Can dilatation and curettage (D&C) cause female infertility?
There is a 30% risk of developing Asherman Syndrome from dilatation and curettage (D&C). This condition can result in the formation of scar tissue within the uterine cavity, which may cause changes in menstrual flow, potentially impacting female fertility in the future.
6) At what stage of pregnancy do people get a D&C?
The decision to undergo a D&C during pregnancy depends on various factors and is best discussed with your healthcare provider. Typically, a D&C may be considered as an option for terminating a pregnancy during the first trimester, generally up to about 13 weeks of gestation.
7) Are there alternatives to a D&C?
Depending on the reason for the procedure, alternatives may include expectant management (allowing the tissue to pass naturally), medication to help the uterus contract and expel tissue, or other surgical procedures tailored to specific conditions.
8) Can a D&C be performed for diagnostic purposes?
Yes, a D&C is often used for diagnostic purposes to obtain tissue samples from the uterus. This can help diagnose conditions such as abnormal uterine bleeding and suspected uterine cancer or investigate fertility issues.
9) What happens to the tissue removed during a D&C?
Tissue removed during a D&C is usually sent to a laboratory for examination. This helps determine the cause of symptoms or confirm a diagnosis, such as identifying abnormal cells or ruling out cancer.
10) How soon after a D&C can I resume normal activities?
Recovery time varies, but many people can resume normal activities within a few days to a week after a D&C. Your healthcare provider will provide specific guidance based on your recovery progress.
11) What should I do if I experience complications after a D&C?
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience severe pain, heavy bleeding, fever, or other concerning symptoms after a D&C. Prompt medical attention can help address any potential complications.






No reviews
Your comment