Best Foods to Boost Implantation After IVF: What to Eat and Avoid
Fertility Treatment
ll couples who use assisted reproductive techniques such as IVF treatment seek different methods to increase their chance of successful pregnancy. Considering what to eat after embryo transfer is crucial to enhance the likelihood of IVF implantation. This essay introduces what foods support implantation and outlines specific recommendations to help implantation for IVF. Additionally, it provides insights into foods to avoid after embryo transfer, aiming to assist individuals in making informed dietary choices that can positively impact the success of their IVF journey.

Importance of IVF Diet after Embryo Transfer
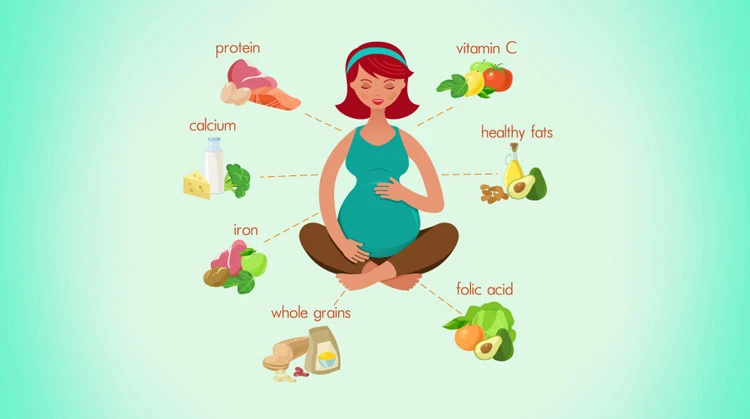
Foods have different nutritional values and can highly affect hormone production, sperm production, the number of eggs, and their quality. Therefore, a balanced diet before and after IVF is essential for this successful method. Moreover, having a nutrient-rich diet rich in vitamins and minerals will boost your immune system, and the embryo will be protected against free radicals.
What to Eat after IVF Embryo Transfer?
Read on to learn what you should eat after IVF embryo transfer:
After Embryo Transfer Diet Chart |
Foods to Eat | Foods to Avoid |
Water | Alcoholic beverages |
Nuts | Caffeine |
Egg | Sodas |
Salmon | Processed and canned foods |
Sweet Potato | Junk food |
Foods Rich in Folate | Undercooked meat |
Beetroot | Unpasteurized milk |
Lean Protein | Processed meats |
Fresh Fruits and Vegetables | Undercooked meat |
Healthy fats | Foods with artificial color & sugar |
Water
Drinking 6 to 8 glasses of water after embryo transfer has many advantages, such as:
- It makes pre-IVF medications enter the blood circulation system;
- It balances the hormones;
- It boosts the immune system;
- It removes impurities from blood (detoxification);
- It improves blood flow and
- It thickens the uterine wall and prepares the uterus for implantation.

Also, adding several drops of lemon juice to a glass of water increases the absorption of IVF medications. It eliminates the common post-IVF digestive problems such as constipation and nausea.
Nuts
Nuts, especially Brazil nuts, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, folate, antioxidants, protein, and other necessary nutrients for implantation. Moreover, nuts such as almonds and walnuts have selenium, which directs blood flow to the uterus and ovaries, thickens the uterine wall, and protects the embryo from free radical damage.
Egg
Egg yolk contains omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A, D, E, and K2, which are very useful for implantation and preventing the formation of blood clots. Also, egg white is a good source of protein and B-12 vitamin. Raw eggs contain harmful microbes like salmonellas, so they should be cooked before eating.
Salmon
Salmon is rich in protein, healthy fats, vitamin B6, and omega-3 fatty acids. So, it is a wholesome food you should add to your IVF diet, especially considering the importance of foods after embryo transfer in enhancing the chances of successful implantation.
Sweet Potato
Sweet potatoes can provide 70% of the vitamin A needed by the body after IVF. Also, since it has antioxidants, potassium, and fiber, it plays an important role in supporting digestive health, maintaining normal blood pressure levels, regulating hormones, boosting the immune system, and reducing inflammation.

Foods Rich in Folate
Folic acid is necessary to properly develop the neural tube -the embryonic brain and spinal cord. Dark green vegetables such as spinach and kale, citrus fruits, beans, peas, avocados, and broccoli are rich in folate. Moreover, nuts, beans, lentils, eggs, and peanut butter are good sources of folate.
Beetroot
Beetroot, rich in iron, glutamine, and antioxidants, thickens the uterine wall and prepares the uterus for implantation. It also contains nitric oxide, a molecule that dilates blood vessels, increases oxygen delivery speed and helps nutrients and blood cells reach the uterus and ovaries.
Lean Protein
Having lean proteins at least twice weekly makes antibodies for your immune system and regulates your hormones and enzymes. Good sources of lean protein include beans, eggs, nuts, seeds, salmon, and yogurt.
Fresh Fruits and Vegetables
Fresh fruits and vegetables, such as bananas, oranges, berries, dates, sprouts, broccoli, etc., eliminate your post-IVF digestive problem and keep you and the baby healthy. Considering the significance of fruits after embryo transfer, incorporating various nutritious options into your diet can contribute to overall well-being. Additionally, it is essential to avoid fruits after embryo transfer, making informed choices supporting the IVF process's success.

Healthy fats
Although some fats are harmful to the body, healthy fats such as olive oil, sesame oil, flaxseed oil, and chia seed oil contain vitamins A and B and benefit both the mother and the baby.
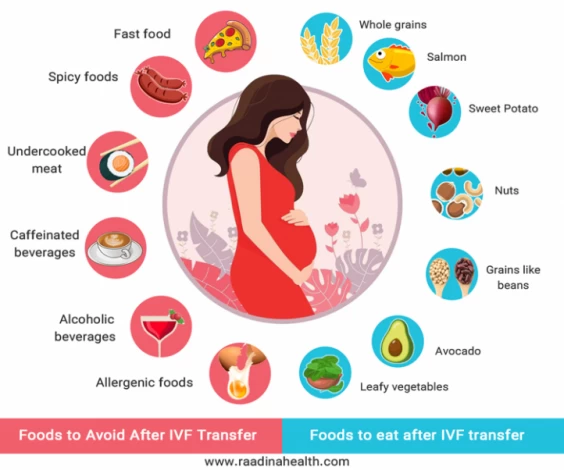
Foods to Avoid After IVF Transfer
After IVF transfer, you should avoid the following foods:
- Alcoholic beverages;
- Caffeinated beverages such as tea, coffee, and energy drinks;
- Sodas;
- Seafood high in mercury, such as tuna and mackerel;
- Processed and canned foods;
- Leftovers;
- Junk food;
- Unpasteurized milk;
- Processed meats;
- Foods that contain artificial color and sugar;
- Sheep and chicken liver;
- Undercooked meat or egg;
- Too much papaya and pineapple;
- Allergenic foods such as eggplant;
- Spicy foods; and
- Too much pickle and vinegar.

Mediterranean Diet after IVF Embryo Transfer
Studies have shown that a Mediterranean diet increases the chance of IVF success in women under 35. Also, women with a Mediterranean diet can maintain a healthy BMI throughout the pregnancy after IVF embryo transfer. If you wonder what is included in this type of diet, read the following:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables (raw, steamed, boiled);
- Whole grains such as pasta and quinoa;
- Lean proteins such as eggs, chicken, and fish;
- Nuts including almond, walnut, hazelnut;
- Legumes such as soybean, pea, chickpea, and lentil;
- Healthy fats such as olive and sesame oil and
- Low-fat dairies.
Also, you should reduce salt intake and avoid eating red meat, refined or hydrogenated oils, refined grains, artificial sweeteners, and processed foods when eating this diet.
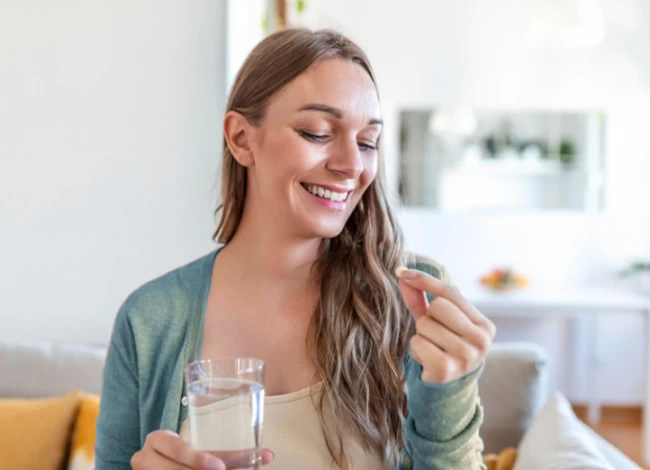
Taking Supplements after IVF Transfer
Taking vitamins and dietary supplements after IVF transfer is not an obligation, but it can significantly impact the success of the treatment. Women over 35 and those with low ovarian reserve should take coenzyme Q-10 and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) supplements for a couple of months to increase their IVF pregnancy. Also, taking vitamins D and E, folic acid, L-arginine, and omega-3 supplements positively affects fetal brain development and thickens the endometrium wall.

conclusion
In general, proper diet after embryo transfer decreases the chance of IVF failure. Notably, your diet after embryo transfer should be similar to that of a woman who has naturally attained pregnancy. If you want a successful IVF, the Raadina team provides you with the most affordable and customized fertility treatment packages in Iran.
Contact us for a free initial consultation about IVF Diet after Embryo Transfer
FAQs About Liposuction Aftercare
What are the best foods to eat after embryo transfer?
Focus on leafy greens (rich in folate), lean proteins like eggs, fish, and poultry, whole grains for steady energy, fruits and vegetables packed with antioxidants, and healthy fats such as avocado, nuts, and olive oil.
Should I avoid certain foods after embryo transfer?
You should avoid caffeine and alcohol, raw or undercooked meats and seafood, processed and junk foods, and unpasteurized dairy products, as they can negatively impact implantation and increase the risk of infection or hormonal disruption.
Can I eat dairy products after embryo transfer?
Yes, but stick to pasteurized and low-fat dairy, which provides calcium and protein. Avoid unpasteurized cheeses or milk due to the risk of listeria infection.
What drinks are recommended after embryo transfer?
Stay well-hydrated with water, warm herbal teas, and fresh vegetable or fruit juices. Avoid sugary sodas and energy drinks.
Should I take supplements after embryo transfer?
Taking prenatal vitamins, especially those with folic acid, iron, vitamin D, and omega-3s are affective in successful implantation.
Can I drink milk after embryo transfer?
Yes, milk is generally safe and provides calcium and protein that support early pregnancy. Opt for pasteurized milk and avoid unpasteurized varieties to reduce any risk of infection.
Can I eat boiled eggs after embryo transfer?
Boiled eggs are an excellent choice because they are rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals that can support embryo implantation. Make sure they are fully cooked to avoid bacterial contamination.
Are warm foods beneficial after embryo transfer?
Warm foods can improve digestion and provide comfort after IVF. Soups, stews, and warm grains are easy on the stomach and help maintain steady energy levels.
Can I eat bread after embryo transfer?
Yes, bread is safe, especially whole-grain varieties. It provides fiber and complex carbohydrates that help maintain blood sugar levels, supporting overall reproductive health.


 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
 Telegram
Telegram
 Facebook
Facebook
 Email
Email












User
-Thanks to the information about diet after embryo transfer was very helpful to follow.
User
-Thank u so much share this diet plan very helpful
User
-Thanks
User
-thank you
User
-Most comprehensive article on this subject matter I have ever seen thanks for shearing. It was worth the read and very helpful
Fatemeh Vajhi
-Thanks for your attention
User
-Which fruit is good to eat after embryo transfer? Is it okay to eat bananas, apples, or regular fruits I consume daily?
Ferdos Tahi
-Hello
yes dear.
User
-Thank u so much for this diet plan
Ferdos Tahi
-most wellcome
User
-Hi. I'm addicted to tea and coffee, but I'm not sure if I can drink it after embryo transfer. My IVF is next week, could you guide me please?
Habib Ebrahimi
-Hello dear friend,
There is some evidence to suggest that drinking tea, mainly green tea, may have a positive impact on fertility and IVF success rates. Note that you should not consume too much green tea.
However, it is essential to note that excessive caffeine intake can have a negative impact on fertility and pregnancy outcomes. Therefore, it is recommended that women undergoing IVF limit their caffeine intake to no more than 200mg per day.
User
-Hello. All my 3 tries to get pregnant with IVF failed. I'm wondering if maybe my diet is wrong. Could you tell me about the foods to eat after IVF?
Habib Ebrahimi
-Hello dear friend,
After IVF, it is important to maintain a healthy and balanced diet to support the success of the treatment. An IVF diet chart may include plenty of fruits and vegetables, protein-rich foods such as lean meats, fish, eggs, and beans, whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread, healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, and low-fat dairy products such as milk, yogurt, and cheese.
It is also recommended that women undergoing IVF avoid alcohol and limit caffeine intake.
User
-আমার ৩বার ivf ব্যর্থ, আমার egg quality bad,
کارشناس رادینا سلامت
-please contact our team on WhatsApp for free consultation and to have access to the best infertility treatment in Iran.
+989052510125
User
-Hello. Hope you're doing well! I recently had IVF and was unsure about what foods I should be including in my diet. I'm so glad to know that cucumbers are a safe and nutritious option to add to my meals. Your blog has been a great resource for me during this process. Thank you!
Habib Ebrahimi
-Hello dear friend,
You are welcome! We are glad that our website has been helpful to you during your IVF journey. As for your question, you can eat cucumbers after embryo transfer. Cucumbers are a healthy and nutritious vegetable that can improve fertility and increase the chance of IVF success.
User
-Hi. I am always looking for ways to improve my IVF diet and support my body during this process. I was wondering if you have any information on whether it is safe to eat groundnuts after embryo transfer? I've heard conflicting opinions and would appreciate any insights you may have.
Habib Ebrahimi
-Hello dear friend,
Moderate consumption of groundnuts is generally safe and beneficial for fertility and pregnancy. Groundnuts are a good source of protein, healthy fats, and important micronutrients like folate and vitamin E, which are important for reproductive health.
User
-Thanks for the information on diet for a successful IVF. I find it very impactful.
فاطمه وجهی
-My pleasure. It's our duty.
User
-Thank you
فاطمه وجهی
-It's a pleasure