Implantation Symptoms: How to Tell Bleeding from Your Period
Fertility Treatment
mbryo implantation, also known as nidation, is the very early stage of intrauterine pregnancy which occurs after sperm fertilizes an egg (fertilization). At this stage, the fertilized egg (embryo) attaches to the uterine wall and creates a connection with the mother's blood supply, which provides essential nutrients and oxygen for its growth. This can cause light bleeding from the uterine lining, known as implantation bleeding.
The embryo continues to attach to the uterine lining for about 12 weeks after fertilization. It can cause a range of symptoms that may be mistaken for the onset of menstruation. One of the most common signs of implantation is bleeding, which can be confusing for women who are trying to determine whether they are experiencing implantation bleeding or simply having a regular period. In this article, we will explore the differences between implantation bleeding and periods, including their symptoms, color, duration, and amount. By understanding these distinctions, women can better identify the signs of implantation and increase their chances of pregnancy.
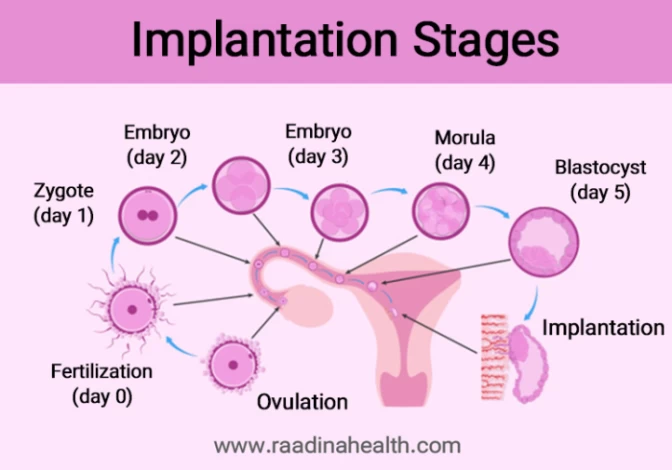
What Is implantation, and What are its Stages?
As mentioned, implantation is a crucial early step in every pregnancy, especially for women who have undergone IVF. The implantation process begins with fertilization when a sperm successfully penetrates an egg and forms a zygote. In this stage, the first Mitosis occurs, where a single cell divides into two, 2, 4, and 8 identical daughter cells. The zygote then undergoes rapid cell division to form a berry-shaped mass of cells called a morula.
As the morula continues to divide, it travels through the fallopian tube to the uterus by peristaltic movements and cilia (small, hair-like projections that line the fallopian tubes). Implantation occurs when the morula reaches the uterine lining and begins to attach. This usually happens 6 to 10 days after fertilization. Once the morula reaches the uterus, it becomes a blastocyst that consists of two tissues: the embryoblast (inner cell mass) and the trophoblast (outer layer).
What Is Implantation Bleeding, and When Does It Occur?
As the fertilized egg implants in the endometrium, small capillaries in the wall can be ruptured, causing light spotting, called implantation bleeding. It usually occurs around 10 to 14 days or in some cases 5 days, after fertilization. Implantation bleeding is a common occurrence and is usually nothing to worry about. However, if you experience heavy bleeding, severe cramping, or any other unusual symptoms, it is important to consult with your doctor to ensure there are no underlying complications.
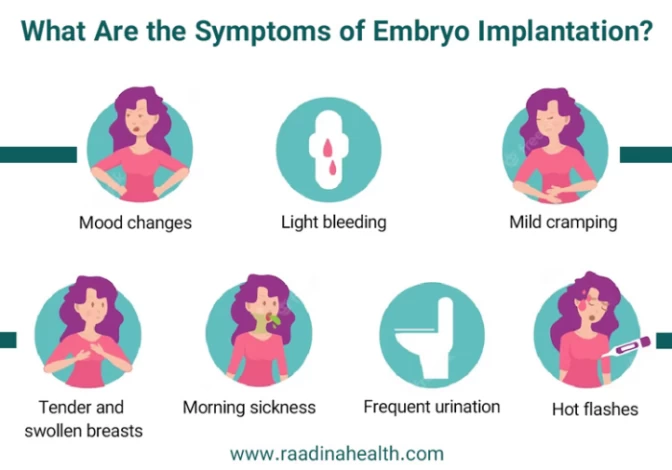
What Are the Symptoms of Embryo Implantation?
The symptoms of embryo implantation can vary from women to women and may include:
- Light bleeding;
- Tender and swollen breasts;
- Mild cramping;
- Frequent urination;
- An Increase in Basal Body Temperature
- Hot flashes;
- Food Cravings and aversions
- Lower Back Pain;
- Mood changes;
- Morning sickness like nausea.
It is important to note that not all women will experience implantation symptoms, and some may experience them without being pregnant.
Light Bleeding / Spotting
Light bleeding can be a sign of pregnancy that happens when a fertilized egg (embryo) implants into the lining of the uterus. However, it can be attributed to other factors such as such as periods and friable cervix and may not necessarily indicate pregnancy.
Tender and Swollen Breasts
When the berry-shaped mass of cells (morula) implants into the uterine lining, it begins to produce the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This hormone signals the ovaries to produce more estrogen and progesterone, which can cause breast tissue to swell and become sensitive. These hormonal changes are preparing the body for pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Mild Cramping
Mild cramping, especially in the lower abdomen, can occur during implantation due to hormonal changes in the body. These cramps are typically milder than menstrual cramps and do not last as long. It is worth mentioning that embryo implantation to the uterus lining is a simple process that does not cause pain,
Frequent Urination
Frequent urination can occur during implantation due to hormonal changes in the body. The hormone progesterone, which is produced during pregnancy, can cause the muscles in the bladder to relax, leading to an increased urge to urinate.
This condition can also be due to an increase in blood circulation in the pelvis. When blood circulation volume increases, the kidneys process its fluids and expel them as urine.
An Increase in Basal Body Temperature
Basal body temperature (BBT) is the normal body temperature at rest. During implantation, the fertilized egg burrows into the lining of the uterus and begins to release hormones such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This hormone signals the body to increase production of progesterone. Changes in progesterone levels during ovulation and menstruation can lead to changes in basal body temperature. BBT usually drops temporarily for one day during implantation (known as implantation dip), after which it begins to rise significantly.
Hot Flashes
Some women may experience hot flashes during implantation.
Food Cravings and Aversions
During implantation, the body undergoes significant hormonal changes as it prepares to support a growing fetus. These hormonal changes can affect a woman's sense of taste and smell, leading to food cravings and aversions. For example, some women may crave salty or sweet foods, while others may develop an aversion to certain smells or flavors.
Lower Back Pain
The uterus may change and begin to expand during implantation, which can cause discomfort by putting pressure on the pelvis and lower back. This pain is temporary and usually does not last more than three days.
Mood Changes
Mood changes can occur due to the hormonal fluctuations that take place in a woman's body during implantation. Like period mood swings, this can lead to feelings of irritability and emotional sensitivity.
Morning Sickness
The increase in levels of hCG and estrogen, as well as changes in progesterone levels, can contribute to the symptoms of morning sickness during implantation. These hormonal fluctuations can affect the gastrointestinal system, leading to nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to smell.
What is the difference between Implantation vs menstrual bleeding?
Many implantation symptoms are similar to period symptoms. So how to tell the difference?
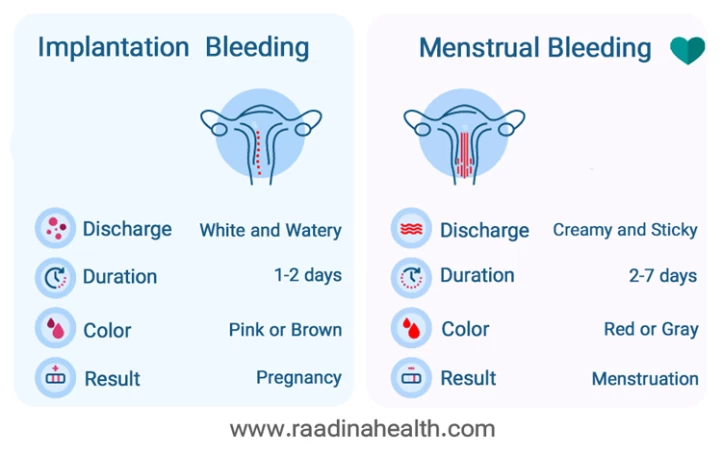
Implantation vs Period Symptoms
These symptoms may include:
- Color;
- Vaginal Discharge;
- Duration;
- Amount;
- Clotting;
- Cramping.
Implantation vs. Periods Blood Color
The color of blood during implantation is usually pink or brown. Brown blood is usually a sign of old blood or blood that takes longer to exit the uterus. The color of period blood, on the other hand, can indicate different health conditions in a woman. For example, red color can mean that the blood is fresh and has not been long in the uterus. The gray color period may also indicate an infection.
Vaginal Discharge
Cervical mucus can change depending on the stage of the menstrual cycle. It may become white and watery during ovulation time and look creamy and sticky after menstruation. After implantation, mucus gets to be very gummy.
Implantation Bleeding vs Periods: Duration
Implantation bleeding typically lasts no more than a day or two. Contrarily, menstrual bleeding lasts for a few days, usually two to seven.
Amount of Blood Loss in Implantation vs Menstruation
Women may experience light spotting or a small amount of bleeding during implantation, with no need for a feminine pad. However, menstrual bleeding is typically heavier, about 10 to 30 ml per period. This amount may reach 500 ml in some women.
Implantation vs. Period Clotting
During the menstrual cycle, small clots are frequent. They never happen, though, when there is implantation bleeding.
Implantation vs. Period Cramps
Implantation cramps are typically milder and shorter in duration compared to period cramps. They may feel like light pressure or twinges in the lower abdomen. Some women may not even notice them at all.
Period cramps, on the other hand, are typically more severe and may cause lower back pain. For some women, they can be incapacitating and frequently persist for several days.
What Are the Do's and Don'ts to Increase the Chance of Implantation?
The necessary precautions during the implantation process that can increase the chances of pregnancy are as follows:
- Avoid stress;
- Eat fiber-rich foods such as green leafy vegetables, as they can help support healthy progesterone levels;
- Avoid eating foods made with growth hormones as well as non-organic products containing xenoestrogens;
- Consume foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish (e.g., salmon and mackerel), as they can prevent persistent uterine contractions and improve implantation chances;
- Consume multivitamins such as folic acid, vitamin D, and sources of omega-3 under a doctor's supervision;
- Eat fresh fruit, vegetables, and nuts;
- Stay hydrated by drinking enough water;
- Eat fermented foods that contain probiotics, such as sauerkraut, yogurt, kefir, and kimchi.
How Long May Implantation Camps Last?
As mentioned, implantation pain is mild and temporary and typically lasts one to three days. However, you should see a doctor if you experience severe implantation cramps or pain that lasts longer than usual.
What Are the Other Causes of Bleeding in Early Pregnancy?
First-trimester bleeding can have several reasons. However, the amount of implantation bleeding is usually less than other causes of bleeding.
Some of the common causes of bleeding in early pregnancy can include:
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Miscarriage;
- Infection;
- Cervical changes.
When to Take a Home Pregnancy Test?
Home pregnancy tests typically measure the level of the hormone hCG. hCG is produced only during pregnancy and appears in the blood and urine of pregnant women around 10 days after conception. hCG levels increase rapidly, usually doubling every 24 hours, and peak within 8 to 10 weeks.
Therefore, the best time to take a home pregnancy test is 12 to 15 days after ovulation, i.e., 1 to 2 weeks after implantation.
What Are the Warning Signs of a Failed Implantation?
The following measures should be taken during the implantation process to improve the likelihood of becoming pregnant:
- Incontinence or the inability to hold urine in the bladder;
- Dizziness;
- Fever;
- Passing blood clots;
- Rectal pressure;
- Bright red vaginal bleeding.
FAQs About Liposuction Aftercare
Is the color of implantation bleeding different from period blood?
Implantation bleeding is typically lighter in color (pink, light brown, or rust-colored), compared to a regular period which is bright or dark red.
How long does implantation bleeding last?
Implantation bleeding usually lasts from a few hours up to 2 days, while periods typically last 3 to 7 days.
Does implantation bleeding contain clots?
No, implantation bleeding does not include clots, while menstrual bleeding usually does.
Are cramps common with implantation bleeding?
Cramping may occur as the uterus adjusts to the fertilized egg. However, it is usually mild and short-lived, unlike the strong menstrual cramps.
Does every woman experience implantation bleeding?
Not every woman experiences implantation bleeding; some may not notice it at all.
What are positive signs of implantation?
Light spotting, mild cramping, and breast tenderness are common early signs. Some women also notice fatigue or heightened sense of smell. These signals usually appear 6–12 days after ovulation
Can implantation happen without bleeding?
Yes, many women implant without any bleeding. Mild cramping, subtle bloating, or mood changes can indicate successful implantation even if spotting doesn’t occur.
What does implantation feel like?
Implantation can feel like a mild twinge or pressure in the lower abdomen. Some report a dull ache similar to pre-period cramps, but typically lighter and shorter in duration.
What are signs of implantation failure?
Sharp or severe cramps, heavy bleeding, or no pregnancy symptoms after expected implantation may suggest failure. However, a missed implantation doesn’t always indicate a problem with fertility.
Can implantation cause nausea?
Mild nausea can occur for some women, often accompanied by fatigue or breast tenderness. This usually appears a few days after implantation and may fade or develop into early pregnancy symptoms.












No reviews
Your comment