Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET): Tips, Timeline & Process
Fertility Treatment
Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) is a form of assisted reproductive technology that has become increasingly popular recently. It involves the transfer of previously frozen embryos to a woman's uterus, often as part of an IVF treatment cycle. FET offers several benefits over fresh embryo transfer, including increased flexibility in timing and improved success rates.
In this article, we will explore the process of Frozen Embryo Transfer, including tips for preparing for the procedure, the frozen embryo transfer timeline, and what to expect during the transfer itself. We will also discuss the factors affecting the frozen embryo transfer success rate and provide advice for optimizing your chances of achieving a successful pregnancy. Whether you are considering FET as part of your Infertility Treatment Methods or want to learn more about this innovative technology, this article will provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your reproductive health.
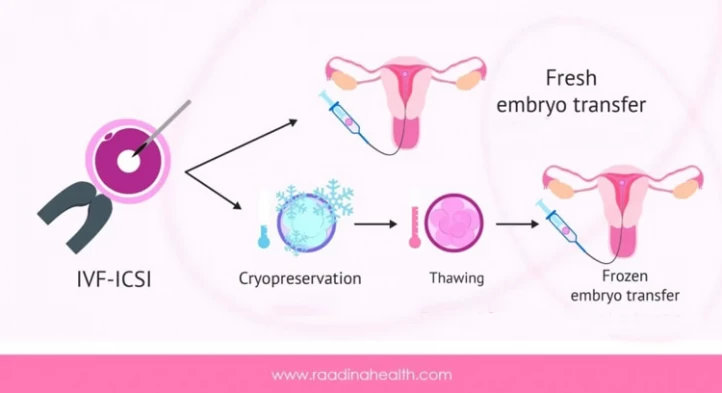
Frozen vs. Fresh Embryo Transfer
Frozen embryo transfer (FET) and fresh embryo transfer are both viable options for in vitro fertilization (IVF), with their advantages and disadvantages.
Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) enables genetic testing and significantly reduces the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). However, fresh embryo transfer may be recommended for younger patients with no chromosomal abnormalities or even older patients whose embryos are likely to have a higher implantation success rate in a fresh uterine environment.
Research shows that the likelihood of success for FET and fresh embryo transfer is nearly identical, with FET occasionally achieving slightly higher live birth rates under specific conditions, such as when genetic testing is used or OHSS risk is high. Some doctors may recommend elective FET, in which all embryos are frozen, thawed, and transferred in a subsequent cycle to optimize outcomes
Why Choose Frozen Embryo Transfer?
For several reasons, someone may choose frozen embryo transfer (FET) over fresh embryo transfer. Some of these reasons include:
·Better timing: The chances of a successful pregnancy may be raised by using FET, which allows for more precise control and coordination of the embryo transfer's timing with the woman's menstrual cycle.
·Greater success rates: Research has indicated that FET may yield greater success rates than fresh embryo transfer, especially for women who have experienced several unsuccessful IVF cycles.
·Lower chance of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), a possible side effect of IVF that can happen if a woman's ovaries are overstimulated. Because the woman does not have to have ovarian stimulation, the risk of OHSS is decreased when frozen embryos are used.
·More flexibility: Because the embryos can be stored for use at a later time if necessary, FET offers more scheduling and planning flexibility.
·Better genetic testing: FET allows embryos to undergo genetic testing prior to transfer, increasing the likelihood of a successful pregnancy and assisting in the detection of any possible genetic abnormalities.
Preparing for Frozen Embryo Transfer
Frozen embryo transfer is not a complicated procedure, but before the operation, consider the following tips:
·As directed by your doctor, take your medications, particularly the hormonal ones;
·get warm socks; warmth increases circulation and blood flow, which could help with implantation. On the day of your FET, put on cozy slippers and warm socks.
·have an ultrasound to examine the uterus and ovaries.
·Get lots of rest both before and after the transfer. Try to get between seven and eight hours every night. Sleeping enough promotes general health and fertility.
·Let your doctor know if you have a history of miscarriages or early births.
·Limit screen time for a few days prior to frozen embryo transfer (FET);
·Avoid sexual activity for three days prior to the transfer;
·Consume a diet high in omega-3 fatty acids, whole grains, legumes, healthy fats, lean proteins, and fresh produce; stay away from processed foods, cold foods, sugar, and caffeine, as these can aggravate your digestive tract;
·stay away from radiation and dangerous chemicals; and stay away from extremely hot or cold temperatures that could harm your uterus and abdomen. Stay away from hot tubs and saunas and keep your laptop away from your body.
·On the day of the embryo transfer, make sure to drink plenty of water, eat a nutritious breakfast, and arrive at the procedure with your bladder full. For the embryo placement, your doctor can see the catheter more clearly thanks to this.
What to Do the Night Before Embryo Transfer?
Embryo transfer is one of the most important steps of the IVF cycle, so you should be well-prepared for it. In order to increase the chance of IVF success, consider the following tips the night before embryo transfer:
· Take a shower;
· stay away from physically demanding activities and get lots of sleep;
· practice yoga and meditation to calm your body and mind;
· Ask your doctor if you need to take any medications, such as progesterone.
· Get someone to look after you;
·Ask your doctor if your bladder should be full for the transfer;
·Do not engage in having sex;
·and avoid wearing strong perfumes because embryos are sensitive.
Frozen Embryo Transfer Procedure Step-by-Step
FET is a two-phase process that begins with carefully preparing the uterine lining, ensuring a receptive environment for embryo implantation. This involves a Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) cycle to stimulate the growth of a thin, healthy endometrium, similar to the early stages of a natural menstrual cycle.
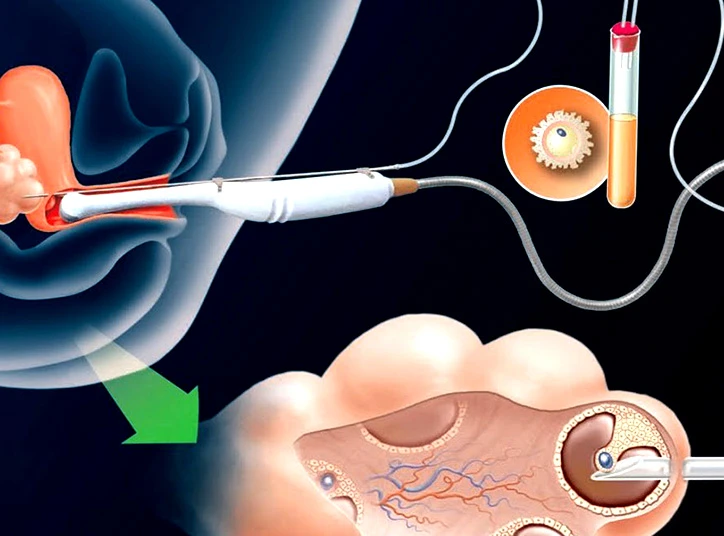
Frozen embryo transfer is a rather simple procedure that does not require anesthesia. This operation is done in a fertility clinic or hospital and takes almost 15 minutes. On the day of the transfer, the doctor will perform an ultrasound scan on your uterus to check the condition of your endometrium. If everything is good, the process of embryo transfer begins.
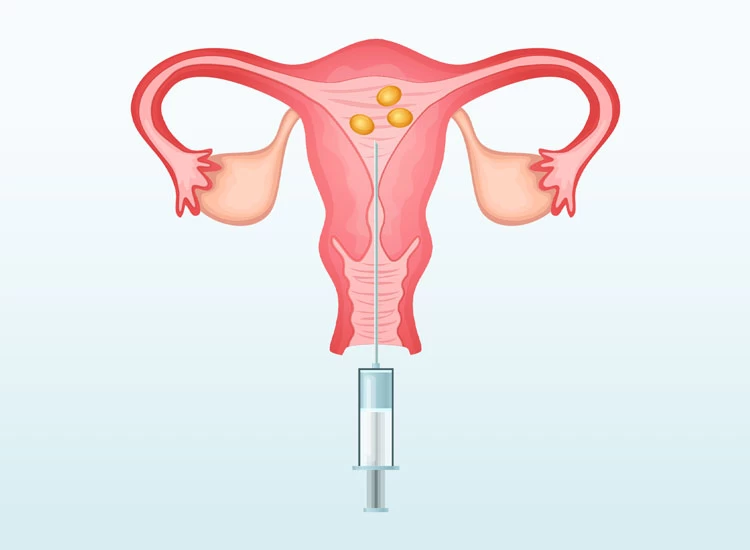
After the initial preparation and rinsing of the discharges from the vagina, the IVF specialist transfers one or more embryos to the uterine cavity by a fine tube called a catheter. After the transfer, you have to lie down for 20 minutes, and then you can go back home.
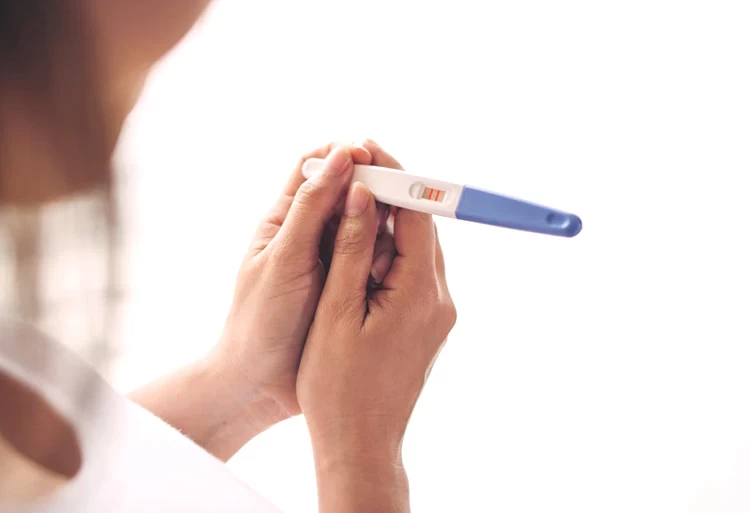
To confirm the pregnancy, you can take a blood or urine test almost two weeks after the frozen embryo transfer. Although taking a pregnancy test sooner might be tempting, specialists highly recommend waiting at least 15 days before the beta test.
What to Do after IVF with Frozen Embryo to Increase Success?
Follow these precautions after IVF using a frozen embryo:
·Continue taking all prescribed drugs as directed. Never increase or decrease the dosage of any medication at your own discretion.
·15–18 days following a frozen embryo transfer (FET), get a pregnancy test. If the test comes back negative, repeat it 48 hours later; if it comes back positive, keep taking your medication as prescribed and see your doctor right away;
·Ask someone to take care of you while you rest at home for up to three days;
·Tell your doctor if you have a history of constipation or a persistent cough;
·Engage in pregnancy exercises;
·Take brief showers following embryo transfer, but avoid spending too much time in a hot bathroom;
·You can eat anything you want after the transfer, with the exception of processed and canned foods, herbal teas, and alcoholic drinks. For a healthy diet following embryo transfer, increase the amount of fruits and vegetables to avoid constipation.
·You can sleep however you feel most comfortable, and you don't have to raise your legs;
·Keep your vagina clean;
·Call your doctor right away if you experience severe abdominal pain, bleeding, spotting, or shortness of breath.

Things to Avoid After Frozen Embryo Transfer
·Steer clear of strenuous activities and sexual activity until your pregnancy is confirmed;
·Avoid straining during bowel movements;
·Stay away from people who have the flu, chicken pox, rubella, or colds;
·Avoid wearing makeup and perfume because the embryos are chemically sensitive;
·Refrain from long road trips, hot baths, swimming, spas, and saunas for two weeks;
·Avoid stressful situations and minimize anxiety;
·Do not take over-the-counter medications without first talking to your doctor.
Frozen Embryo Transfer Timeline
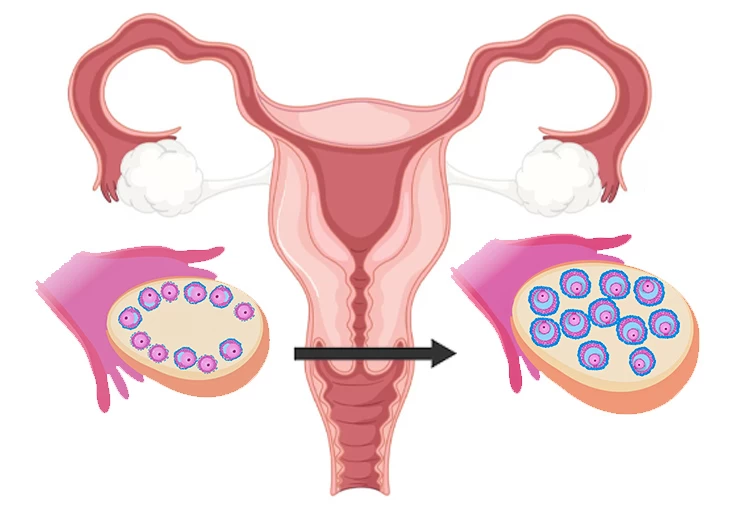
Each cycle of frozen embryo transfer will take almost three to four weeks. You must take birth control pills for about two weeks to restrain ovary activity. When the ovary is suppressed completely, it is time to check the hormone levels and endometrium. To that end, you must perform a transvaginal ultrasound scan and necessary blood work on days 2-4 of your menstrual cycle.
Based on the condition of your uterus, the doctor prescribes the estrogen injection. Usually, the patients have to inject estrogen for a week to thicken the uterus lining and prevent ovarian follicles from growing. After estrogen injections, another bloodwork and transvaginal ultrasound are needed to check the uterus lining.
If your endometrium has the expected lining, i.e., 7mm, your doctor will ask you to take daily injections or vaginal suppositories of progesterone for four to five days.
Finally, you are ready for embryo transfer almost two weeks after taking birth control pills. Your doctor will determine the exact day of the transfer. On that day, you go to a fertility clinic with a full bladder and receive the fertilized egg through a simple procedure. As doctors suggest, the embryo will be implanted within 24-48 hours after the transfer, but you must wait 15 days before taking the pregnancy test.

Why Do People Freeze Embryo?
Couples may decide to freeze and store their embryos for later use for a variety of reasons. Having cancer is one of these causes, as is having low levels of anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH), which causes the ovaries to produce fewer eggs. Before receiving chemotherapy or radiation therapy, some couples choose to freeze their embryo; others have plans to have children in the future, even during menopause; still others have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which causes hormonal imbalances in women and lowers their ovaries' reserve; while others have menstrual problems and plan to use IVF to have more children in the future; and, in a few uncommon instances, people freeze their fertilized eggs to sell to future infertile couples.
Side Effects of Frozen Embryo Transfer
In some cases, frozen embryo transfer may have temporary side effects such as:
- Pain in ovaries;
- Cramping;
- Swelling of the ovaries;
- Mild lower abdominal pain;
- Bloating and diarrhea;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen;
- Difficulty in breathing;
- Spotting or bleeding, which may last for three months;
- Pain in breasts;
- Frequent urination;
- Extreme fatigue; and
- Pelvic pain.
Success Rate of IVF with Frozen Embryo
The cause and duration of infertility, the mother's health and body mass index, uterine receptivity, the quality of the embryo (embryo grade), and—above all—the mother's age all affect the success of IVF frozen embryo transfer. The success rate of IVF using a frozen embryo decreases with the mother's age. The success rate for frozen embryo transfers is typically 60% for women under 35 and 20% for those over 40.
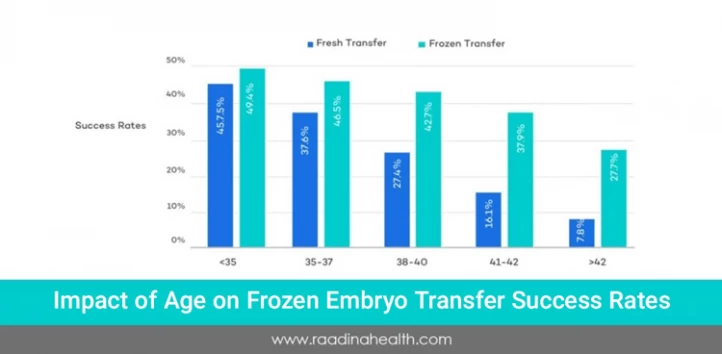
When is a Frozen Embryo Cycle Recommended?
A frozen embryo cycle is typically recommended when multiple healthy embryos are created during an IVF or ICSI cycle, but only one or two are transferred to the uterus immediately. The remaining embryos can be frozen and used in a future IVF cycle if the initial transfer does not result in a pregnancy or at a later time to create a sibling.
In some cases, a woman may be advised to freeze all her embryos and not transfer any immediately if the lining of the uterus has not developed properly or if she is at risk of developing ovarian hyper-stimulation syndrome (OHSS). It is also becoming more common for fertility specialists to recommend freezing all embryos because the more natural environment of a later cycle may increase the chances of establishing a pregnancy.
Freezing embryos can also be an option for women who wish to delay pregnancy until their late 30s or early 40s but understand that they may not have suitable eggs at that time.
Frozen Embryo Transfer Cost
The cost of IVF with frozen embryos depends on the procedure's price, embryo cryopreservation duration, hospital facilities, doctor's fees, medications, and the number of lab tests required. It would be best to ask your specialist or a fertility clinic for the exact cost of IVF with frozen embryos.
Chance of Twins with Frozen Embryo Transfer
During the IVF procedure, some specialists transfer two or more frozen embryos into the mother's womb to increase the chance of pregnancy. In some cases, more than one embryo attaches to the uterine wall and forms multiple pregnancies. The chance of twins with a frozen embryo is not very high, but if you do not intend to have twins in IVF or even triplets, discuss it with your doctor before frozen embryo transfer (FET).
Signs of Successful IVF with Frozen Embryo
- No period after embryo transfer: Menstrual bleeding no longer occurs when the embryo attaches to the uterine wall.
- Clear mucus discharge after embryo transfer: an increase in vaginal discharge can signify successful IVF with frozen embryos. Usually, women have clear mucus in the early weeks of pregnancy.
- Sore breasts after frozen embryo transfer: Most women experience swelling, tenderness, and pain in their breasts at the beginning of their pregnancy. This happens due to hormonal changes in the body.
- Feeling sleepy and tired after IVF: During the first stages of pregnancy, the amount of progesterone in the body increases, which results in extreme fatigue and muscle cramps.
- Headache and dizziness after FET (frozen embryo transfer): if the embryo transfer is successful, you may experience severe hypotension and hypoglycemia. As a result, you might feel down all day and experience headaches, dizziness, and even fainting.

Conclusion
To summarize, frozen embryo transfer is the final step of the IVF process, through which the fertilized egg(s) is directly transferred into the mother's uterus using a catheter. IVF with frozen embryos is a complex procedure and should be done in a standard hospital and under the supervision of an experienced doctor. Luckily, in Iran, thousands of knowledgeable physicians and well-equipped fertility clinics offer the best healthcare services at a reasonable price.
If you intend to do IVF with frozen embryos in Iran, contact Raadina Co. to get more information about the top fertility clinics in the country and the price of this operation in Iran. Raadina Team offers you special embryo transfer packages, which include booking doctor's appointments, applying for a medical visa, arranging transportation in the country, and booking suitable and affordable accommodations.
FAQs about Frozen Embryo Transfer
How many days after your period is the frozen embryo transfer done?
If a three-day embryo is being transferred, the FET takes place on the 18th day of your cycle, and if a five-day embryo is used in IVF, FET happens on the 20th day of your period.
Are frozen embryos better than fresh ones?
Recent studies show frozen embryos have a higher implantation chance and live birth rate than fresh embryos.
How long does a frozen embryo transfer cycle take?
Based on the general FET timeline, each cycle of IVF with a frozen embryo takes three to four weeks. In the first two weeks, the uterine lining is prepared for implantation, and the next two weeks are dedicated to preparing the womb for holding the baby and adjusting the hormones.


 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
 Telegram
Telegram
 Facebook
Facebook
 Email
Email












User
-It was an totally good content. Thank you for sharing.